Some Notes From Last Exam


some notes from last exam
Ig: cllalagram
More Posts from Marathon-notasprint and Others
How to Take Notes: from a Textbook
(Be sure to change the post type from link to text post when you reblog, if that’s what you want to do)
This method is best suited for textbook or article notes, and is a version of revised notes. It is also well suited for books you plan on returning to the bookstore or books you have rented, as it does not involve writing directly in the book itself.
First, you’ll need to find a notebook, and the pens you like the best. My favorite notebooks to work with for note-taking, especially for my “revised” notes, are the Moleskine, hard or soft cover, in size extra large. For this specific class (Intro to Gender and Women’s Studies), I decided that lined pages would suit my needs better. For my math, engineering, and science classes, I usually opt for squared paper, as I draw in lots of diagrams and graphs.
My favorite pens ever are Staedtler Triplus Fineliners, so even though they show through the pages a little bit, I still choose to use them. I just love the way they write. I usually write out my notes themselves with a Pilot G2 05 with black ink, as it writes with a finer line and doesn’t bleed through quite as much.
I usually try to set up my notebooks about a week or so before class starts, that way it’s ready to go on my first day of class.

You’ll want to start off by setting up your notebook. On my first page, I put my course code for my university, as well as the course title.

Next, and this is perfectly optional (I just like the way it makes the book look, especially at the end of the semester), I include some sort of related quote to the course. For my engineering courses (which are related to my major), I put a different quote at the beginning of each section. But as this is a two-month long course during the summer, I opted for one quote by Mohadesa Najumi at the beginning of my book.

Next I set up my table of contents and include a page with basic course information. As this course is all online, my course information just included the start and end dates of the course, what time content is posted and on what day, and the name of my professor. For my usual courses, I will include the days of the week the class meets on and where, TA names and contact info, as well as posted office hours for my professors and TAs and tutoring hours either in the library or in the College of Engineering.

Next is one of the things I’m most proud of.
While I religiously use my Erin Condren planner to map out my days, weeks, and months, I have found throughout my college experience that including monthly views for the months my class ranges has been helpful. This way, there’s no sifting through the multiple colors I have in my planner, and everything related to that class is in the same notebook.
On this calendar I include start dates of the class, the end date, the dates of exams or quizzes, assignment deadlines, office hours, etc.
For this course, as I just started a few days ago, I don’t have a lot of dates or information, so my calendars are still very empty.


Next up I go to my weekly overview. At the beginning of each week, I set up a weekly layout, and I include a list of assignments, tests, quizzes, tasks, projects, etc that need my attention throughout the week, and I place the days I plan on doing them or the days they need turned in onto the weekly layout.

Now you’re finally ready to get into taking the notes.
Gather your book, some sticky notes, and your favorite pen or pencil.
I color code my stickies so that the “revision” process later goes a bit smoother. In this case, I’m using blue to denote something interesting, intriguing, or thought provoking, greenish-yellow to represent the facts or important concepts, and pink for important vocabulary words and their definitions.

Read the selection once.
As you read along the second time, write notes on your stickies, and place them in a place of relevance directly on the page in the book. Just make sure you don’t cover up anything you need to keep reading.



Now, once you’ve read all the material in questions (you can choose to break it up however you want, but since Chapter 1 was assigned for the week, I’ve elected to break it into chapters), carefully remove your stickies one by one and lay them out on a flat surface. This is when having a separate color for vocab can be helpful, as I sometimes put all of my vocab at the beginning or end of a section, especially if the section of reading was particularly large.
Organize your stickies in an order that makes sense to you, and use this order as your basis for transferring those notes into your notebook. The order you choose can just be lumping them under similar headings. Some classes even lend themselves to a nice chronological order. Whatever you choose, just make sure it’s something that will make sense to you when you come back to it in the end.

Okay so up there I wasn’t following my own advice, I just thought I would include the picture because my handwriting looks nice…

Now organize the stickies!

Now you just start writing everything from the stickies into your notebook. I like to take each category or subgroup and put them in the book on the facing page, then put them back in my textbook as I finish with each post it.

Moving on to the next category.


Before you know it, you’ve written all of your stickies into your notebooks.

Now you’re revved up and ready to go. You can either keep going and make a note summary page (which I’ll show you next week), or you can leave it. These will also be helpful when reviewing for tests and quizzes. You can highlight or underline, or use even more stickies (which is what I usually do) as you review.
Well, that’s all I have for you right now. Happy studying!
(To view this post on wordpress, click here)
My Study Method
by futurecomposer
Notes and processing info:
i write my notes with Google Drive / Docs (android / itunes)
before the lecture: First of all I write the textbook notes and maybe articles about the subject, that way, when I go to the lecture, I already understand the topic. If there’s available slides, print them, so you can annotate on them later.
during the lecture: Take as many notes as you can, but also write about the most important stuff. For this I use paper. I feel like It’s easier to link stuff, draw diagrams, etc. … It doesn’t matter if your notes are messy, you’ll rewrite them later. Remember: if it’s in the blackboard, it’s because it’s important.
after the lecture: After the lecture I write my lecture notes in the previous document. Now it’s time to get fancy: use bold, italic,, both of them to indicate keywords and/or important phrases. But be careful: don’t overuse them, or they will become useless.
At this point you should have all the information you need for the exam perfectly summarised in a doc.
Summarising and flashcards
bullet points: It’s time to make another doc. This time we’ll resume the information in bullet points. The goal is to have clear, concise, brief facts.
summary cards: Here comes the most important part. Summarise one topic in one flashcard. The point is to really condense the information and see what’s most important. Fill the flashcard with info, don’t get cut back by aesthetics. The previous doc is your guide.
This system’s point is to manage and work the information, get familiar with it, then find the most important concepts. This way, you have actively worked with it, and have more tendency to remember it.
Got an Essay to Write?
Here’s how to use up space when you are just absolutely done with life
-make all periods a font size or two up from the one you’ve been directed to use
-put two spaces after every period
-WATCH YO COMMAS you’re prob missing fifty of them
-2.15 space it
-MLA format the header
-use “such as” instead of “like”
-use “therefore” or “as a result of” instead of “so”
-add a space after every indent
-make the margins on your paper a TINY bit bigger
-get rid of all contractions
-see that word that’s so close to being on the next line? put it on the next line
*keep in mind that one or two of these may conflict with the essay’s instructions
*don’t forget to take a break and breathe some non-recycled air and close your eyes and love yoself <3
this has gotten me through several papers so i hope this helps. reblog this please, save a grade and some sanity
Maybe it’s just me, but I think a significant part of career planning and goal setting in medicine is developing the ability to acknowledge that you can have an interest in many things (which is a good thing, it keeps you keen and motivated) but you become conscious of the fact that that doesn’t necessarily mean you want to/can/should aim for a career in that area, if you know what I mean? And that realisation that you now have an idea of where you want your career to go is what ends up motivating you once you get past that initial ‘everything in medicine is exciting’ phase. At the beginning of med school/clinics, you think to yourself “woah, I’m interested in so many things - neuro, cardio, infectious diseases, general surgery, anaesthetics - I wish there was a path that would combine everything!” and yeah there are generalists and all that but (at least personally) sometimes you think about it all and you realise that there are aspects of medicine that you are happy to keep as just a ‘personal interest’, and others which you just can’t let go of. For example, I am fairly committed to paeds (I mean, I haven’t graduated yet but I’m 99% certain I want to work in paeds) but I also have special interests in psychiatry and anaesthetics/intensive care medicine - but over the years I’ve come to realise that just because I’m particularly interested in it does not mean I’m now ‘destined’ to be a psychiatrist or an anaesthetist, nor do I think an academic interest in neurological research would make me a good neurologist. When it comes down to it, even the basic divisions like medicine/surgery/GP can feel confusing when you’re 95% set on medical but have a lingering interest in ENT or neurosurgery - and I’ve talked to a couple different people who have interpreted this lingering interest as a sign that they need to somehow combine all their interests into one impossible career. When you’re younger and in school it feels like you have so many routes and can keep up with every single little thing you’re interested in, and everything seems so pressured, when in reality I think the path is a little clearer than some people would have us believe? As intelligent, curious people, it’s only natural to feel keen on learning about so many different things, but I think we all have to recognise that not everything is a 'sign’ - sometimes you are just interested in interesting things.
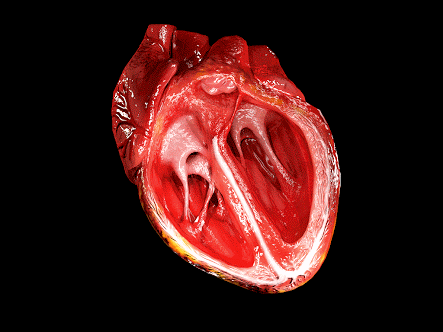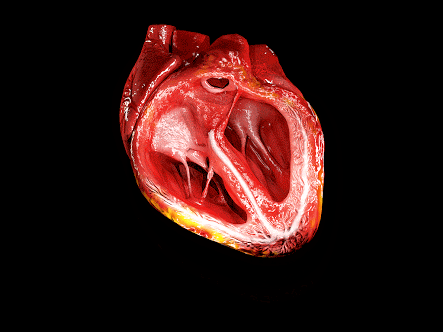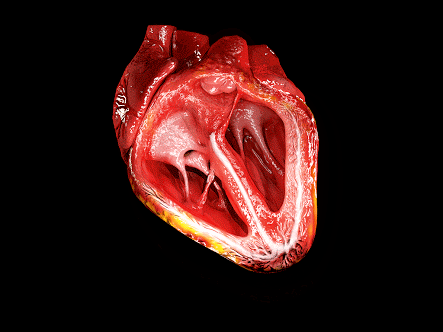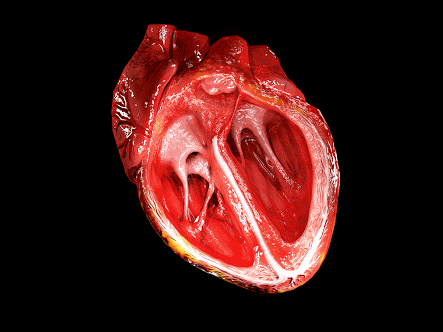
This is how heart works <3 <3 <3
this school year will go successfully, and we will figure things out
this school year will go successfully, and we will figure things out
this school year will go successfully, and we will figure things out
this school year will go successfully, and we will figure things out
this school year will go successfully, and we will figure things out
this school year will go successfully, and we will figure things out
this school year will go successfully, and we will figure things out
this school year will go successfully, and we will figure things out
this school year will go successfully, and we will figure things out
this school year will go successfully, and we will figure things out
Superb Study Guides and Mini Moleskines
(A more concise version of this will be published in my college’s newspaper on Thursday. I will likely add or link diagrams and examples to this post, so you can check the original here.)
As a tutor, many students ask me for tips on making study guides. Generally, my response is that, “it depends”.
But hold on. Before we continue we should discuss what the purpose of a study guide really is.
Study guides fall into two main categories: study guides that prompt you to find/think about information and study guides that directly organize the information you need to know. Some professors provide you with study guides of the former kind (i.e., you’re not given the answers), and it’s essentially your job to create your own study guide of the latter type. Both categories serve the purpose of organizing information you already have in order to synthesize a study tool that best facilitates your comprehension and memorization of the information at hand, just at a different stage in the process.
Before you even start, it is helpful to be aware of the level at which you are required to know the information for your test. The most basic of these is recalling definitions, which can accomplished by use of flashcards. Other information you’ll have to know will require you to compare ideas or apply them. Think of your learning process as literal → interpretive → applicative, meaning you will need study guides that help you visualize, draw relationships, and understand material so you may memorize less in a way that helps you answer more, and better than straight memorization ever could.
–
Concept Map:
These can be anything from a basic branching diagram to a complex mind map. This type of study guide allows you to compare information in a more spatial manner than strictly linear. Let’s be honest; sometimes linear learning is unrealistic, because our world is not truly linear. This format allows you to start from the basic, bare bones of the topic you’re studying and expand into very specific details and examples. This way you can get a really solid overview of the information and delve deeper as necessary. At least for mind maps in specific, Mindly is a beautiful and highly functional mind mapping app for iOS. It’s worth the small price, I can tell you that.
Comparison Chart:
Another visually-oriented type of study guide, comparison charts are the easiest way to map out similarities and differences for various topics. The biggest advantage of this method is that you can easily find the important similarities and differences of the subjects in question without having to reread a chapter or search through your piles of notes. It won’t help you visually connect topics like a mind map would, but this very simple tool is important and useful in its own rite.
Index Cards:
Before you skip over this because you think you know what I’m talking about, this is not the same as a flashcard. Flashcards have the very basic purpose of helping you memorize information, and little else. Index cards, however, are like flashcards on steroids because they contain much more information and are used primarily to summarize key information in a portable way that allows you to easily locate more details if necessary. Allow me to break down how you might want to use this method.
Front:
Middle: Main idea [e.g. alveoli]
Upper Right: Organizational term [e.g. respiratory system]
Bottom Middle: Source of information [e.g. Chapter 17, pg. 479 or Notes from 11/26/2013]
Back:
In your own words, what’s most important to know about the concept.
Include examples, summaries, diagrams, definitions, etc.
Be detailed! Remember, this is not about strictly memorizing.
Make sure the content corresponds to level of understanding your professor excepts
Diagram:
This one is pretty self-explanatory, but is extremely dependent on the topic at hand. This could be anything from a chemical reaction scheme, a cycle, Venn diagram, etc. You may even consider making a timeline, which is great for chronological organization of ideas. This is not limited to history, though! You can also organize information from classes such as anthropology, psychology, biology, anatomy, physiology, ecology, etc. If it has a specific, linear order, it can be made into a timeline.
Question Prompts:
This method I find works very well if you use the Cornell note-taking method. If you’re using Cornell notes, you would write your prompts in the left hand column next to where the answers are located, then just cover up the answers when studying. For example, for something as simple as a definition you could write, “What is _____?” For something more complicated such as a comparison chart, you could write, “What are the key differences between _____ and _____?” If you want, you can even ask questions that aren’t directly answered in the adjacent text such as, “Why is [idea] important to [concept]?”
–
Now that you know what formats you might use for your study guides (remember you don’t have to stick with just one), you may wonder where you can put this information. The basic answer to that question: anywhere. Many people like to draw these things on computer paper. You may want to type some of these things. If you’re using Mindly then you would be inputting the information into an app. I would like to offer up the suggestion of little mini notebooks for each class. I personally make these study guide materials on paper or a computer first, then when I’m satisfied with the result, I copy it down into my pocket-sized Moleskine notebooks. I personally prefer the squared, dotted, or blank notebooks, but whatever suits your fancy. The benefit to these little notebooks is that you have all of the information you need to study for in a small, convenient little book that you can easily keep in your backpack all the time because of its size. (Ladies, it will even fit in a clutch!) Study on the bus, waiting for class to start, when eating at the cafeteria, while waiting for your laundry to finish, etc. Not to mention, this will help you avoid losing papers because they’re all in one place.
Just try not to lose the notebook.
-
 vanessainstem liked this · 5 years ago
vanessainstem liked this · 5 years ago -
 nadia-isabel liked this · 5 years ago
nadia-isabel liked this · 5 years ago -
 estudiaretudier reblogged this · 5 years ago
estudiaretudier reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 layl1999-blog liked this · 5 years ago
layl1999-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 itsunicorngirlposts-blog liked this · 5 years ago
itsunicorngirlposts-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 marathon-notasprint reblogged this · 5 years ago
marathon-notasprint reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 mal-evolent101 liked this · 5 years ago
mal-evolent101 liked this · 5 years ago -
 ayatochan606-blog liked this · 5 years ago
ayatochan606-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 lausramajor-blog liked this · 5 years ago
lausramajor-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 antormworld liked this · 5 years ago
antormworld liked this · 5 years ago -
 zille-elliz liked this · 5 years ago
zille-elliz liked this · 5 years ago -
 nicolinscastiel-blog liked this · 5 years ago
nicolinscastiel-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 ashling12 liked this · 5 years ago
ashling12 liked this · 5 years ago -
 xxmedstudy reblogged this · 5 years ago
xxmedstudy reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ann-stay liked this · 5 years ago
ann-stay liked this · 5 years ago -
 ssokkas-instinctss liked this · 5 years ago
ssokkas-instinctss liked this · 5 years ago -
 krystal-aldaine-yay liked this · 5 years ago
krystal-aldaine-yay liked this · 5 years ago -
 tryingmybestrn liked this · 5 years ago
tryingmybestrn liked this · 5 years ago -
 acxilles liked this · 5 years ago
acxilles liked this · 5 years ago -
 plannersbyjoana-blog liked this · 5 years ago
plannersbyjoana-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 sippingtea-and-studying reblogged this · 5 years ago
sippingtea-and-studying reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 roseinstem liked this · 5 years ago
roseinstem liked this · 5 years ago -
 myhoneststudyblr reblogged this · 5 years ago
myhoneststudyblr reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 katastrophenerfinder liked this · 5 years ago
katastrophenerfinder liked this · 5 years ago -
 wicked-wick-fromsgold liked this · 6 years ago
wicked-wick-fromsgold liked this · 6 years ago -
 the-third-me liked this · 6 years ago
the-third-me liked this · 6 years ago -
 supersizedtwix liked this · 6 years ago
supersizedtwix liked this · 6 years ago -
 snakestudiesss reblogged this · 6 years ago
snakestudiesss reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 snakestudiesss liked this · 6 years ago
snakestudiesss liked this · 6 years ago -
 the-life-of-a-band-geek liked this · 6 years ago
the-life-of-a-band-geek liked this · 6 years ago -
 silence986-blog liked this · 6 years ago
silence986-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 thiag0511 liked this · 6 years ago
thiag0511 liked this · 6 years ago -
 lottiesfilms reblogged this · 6 years ago
lottiesfilms reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 ineedtaehyung liked this · 6 years ago
ineedtaehyung liked this · 6 years ago -
 iliwy-s liked this · 6 years ago
iliwy-s liked this · 6 years ago -
 paraelyn liked this · 6 years ago
paraelyn liked this · 6 years ago











