Image Of Saturn Taken By Cassini Spacecraft In October 28, 2016.

Image of Saturn taken by Cassini spacecraft in October 28, 2016.
Credit: NASA/JPL
More Posts from Sergioballester-blog and Others

NASA’s Perseverance takes first photo.




Perseverance: Some early Navcam (navigation camera) images taken over the (Earth) weekend on sol 2. Originals are here: [1] [2] [3] [4]. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
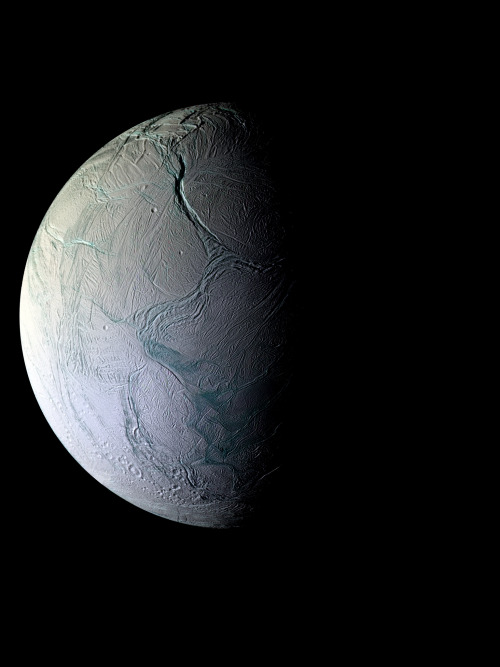
Image of the moon of Saturn, Enceladus, taken by the Cassini spacecraft
Image credit: NASA / JPL

Shuttle Endeavour’s flight deck. 🚀
This impressive storm captured by Geoff Green over West Australia in August 2018, gives you an idea of the huge frequency at which lightning happen in an extreme weather event
Instagram: wonders_of_the_cosmos










Pluto’s Surface Changes Faster Than Earth’s, And A Subsurface Ocean Is Driving It
“These mountains aren’t static and stable, but rather are temporary water-ice mountains atop a volatile, nitrogen sea. The evidence for this comes from multiple independent observations. The mountains only appear between the hilly highlands, after the edge of a basin rim, and young plains with flowing canals. These young plains occur in Pluto’s heart-shaped lobe, which itself was caused by an enormous impact crater. Only a subsurface, liquid water ocean beneath the crust could cause the uplift we then see, leaving the nitrogen to fill it in.”
In July of 2015, NASA’s New Horizons Mission arrived at Pluto, photographing the world at the highest resolution ever, with some places getting as up-close as just 80 meters (260 feet) per pixel. Not bad for a world more than 3 billion miles (5 billion kilometers) from home! What we’ve learned is breathtaking. Rather than a static, frozen world, we found one with tons of evidence for active, interior geology, as well as with a changing surface that renews itself and undergoes cycles, quite unexpectedly to many. There’s also not an enormous heart, but rather a massive, volatile-filled crater that caused Pluto to tip over at least once in its past, and may yet cause it to tip over again in the near future.
If you ever wanted to know how these distant, icy worlds come alive, there’s never been a better way to find out than in the aftermath of what New Horizons taught us!

Landing Day for InSight by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center

Update your phones with our #CountdownToMars wallpapers, like this one, today: https://www.nasa.gov/feature/perseverance-mars-rover-wallpaper-images/
It's LANDING DAY for our Perseverance Mars Rover and her mission to search for ancient signs of life on the Red Planet!
Watch LIVE coverage today starting at 2:15pm ET (18:15 UTC):
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
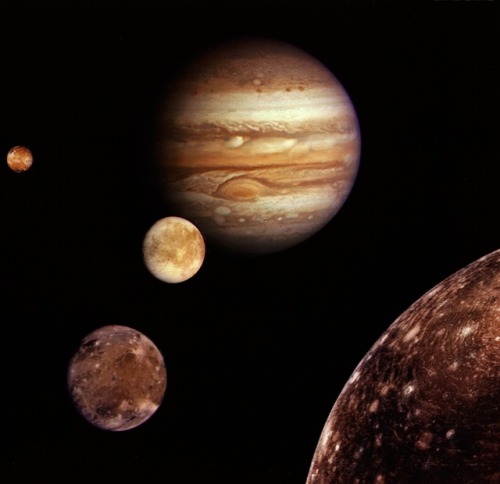
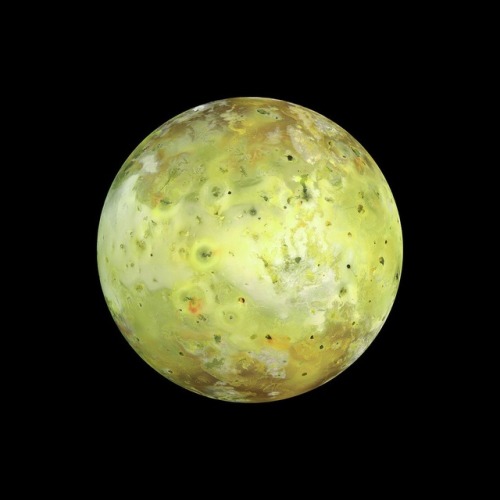
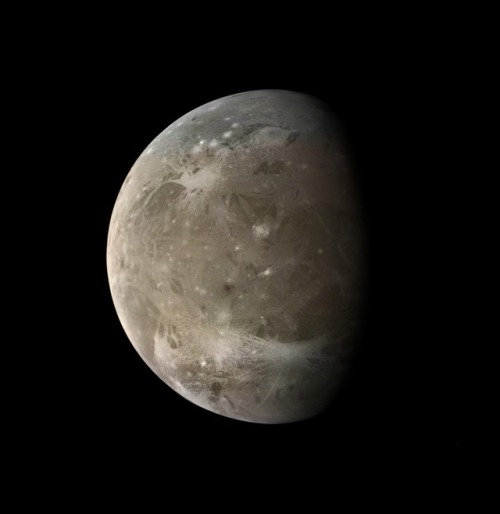
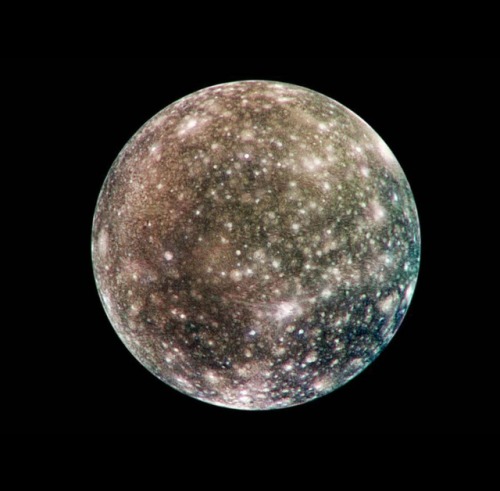


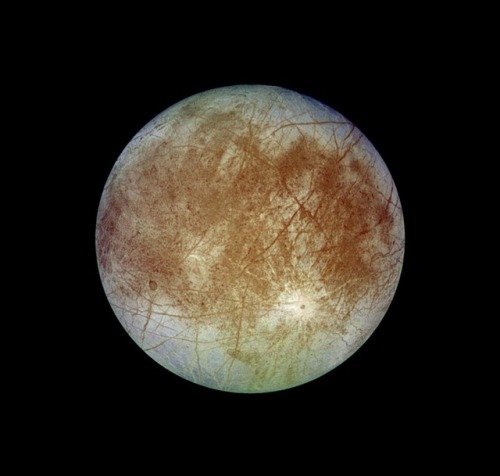


Galilean moons
The Galilean moons are the four largest moons of Jupiter — Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. They were first seen by Galileo Galilei in January 1610, and recognized by him as satellites of Jupiter in March 1610. They are the first objects found to orbit another planet. Their names derive from the lovers of Zeus. They are the first objects found to orbit another planet. Their names derive from the lovers of Zeus. They are among the largest objects in the Solar System with the exception of the Sun and the eight planets, with a radius larger than any of the dwarf planets.
Io is the fourth largest moon in the Solar System. With over 400 active volcanos, Io is the most geologically active object in the Solar System. Its surface is dotted with more than 100 mountains, some of which are taller than Earth’s Mount Everest. Unlike most satellites in the outer Solar System (which have a thick coating of ice), Io is primarily composed of silicate rock surrounding a molten iron or iron sulfide core. Although not proven, recent data from the Galileo orbiter indicate that Io might have its own magnetic field.
Europa the second of the four Galilean moons, is the second closest to Jupiter and the smallest at 3121.6 kilometers in diameter, which is slightly smaller than the Moon. The name comes from a mythical Phoenician noblewoman, Europa, who was courted by Zeus and became the queen of Crete, though the name did not become widely used until the mid-20th century. It has a smooth and bright surface, with a layer of water surrounding the mantle of the planet, thought to be 100 kilometers thick. The smooth surface includes a layer of ice, while the bottom of the ice is theorized to be liquid water. The apparent youth and smoothness of the surface have led to the hypothesis that a water ocean exists beneath it, which could conceivably serve as an abode for extraterrestrial life.
Ganymede is the largest moon in the Solar System, and is even bigger than the planet Mercury. It is the only satellite in the Solar System known to possess a magnetosphere, likely created through convection within the liquid iron core.
Callisto is the fourth and last Galilean moon, and is the second largest of the four, and at 4820.6 kilometers in diameter, it is the third largest moon in the Solar System, and barely smaller than Mercury, though only a third of the latter’s mass. It is named after the Greek mythological nymph Callisto, a lover of Zeus who was a daughter of the Arkadian King Lykaon and a hunting companion of the goddess Artemis. It is one of the most heavily cratered satellites in the Solar System, and one major feature is a basin around 3000 km wide called Valhalla.
source
image credit: NASA/JPL









Solar System
•please like or reblog if you use
-
 worldofpixels reblogged this · 1 month ago
worldofpixels reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 zunijehan reblogged this · 1 month ago
zunijehan reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 frederic-fournel liked this · 2 months ago
frederic-fournel liked this · 2 months ago -
 oralinfatuation liked this · 2 months ago
oralinfatuation liked this · 2 months ago -
 ultrasublimenegation reblogged this · 2 months ago
ultrasublimenegation reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 calmdownzuza liked this · 2 months ago
calmdownzuza liked this · 2 months ago -
 ultrasublimenegation liked this · 2 months ago
ultrasublimenegation liked this · 2 months ago -
 compvss reblogged this · 2 months ago
compvss reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 qveen-ivy reblogged this · 2 months ago
qveen-ivy reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 qveen-ivy liked this · 2 months ago
qveen-ivy liked this · 2 months ago -
 ovsilenceandblack reblogged this · 2 months ago
ovsilenceandblack reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 thegodfatherofgraffitti liked this · 2 months ago
thegodfatherofgraffitti liked this · 2 months ago -
 wbworkout liked this · 2 months ago
wbworkout liked this · 2 months ago -
 luminishenca liked this · 2 months ago
luminishenca liked this · 2 months ago -
 kolshiwalaroxanne reblogged this · 2 months ago
kolshiwalaroxanne reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 banicalite liked this · 2 months ago
banicalite liked this · 2 months ago -
 megmelodia liked this · 2 months ago
megmelodia liked this · 2 months ago -
 fe-doshin reblogged this · 2 months ago
fe-doshin reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 fe-doshin liked this · 2 months ago
fe-doshin liked this · 2 months ago -
 j-de-molai liked this · 2 months ago
j-de-molai liked this · 2 months ago -
 headlong-flight liked this · 2 months ago
headlong-flight liked this · 2 months ago -
 roamsome reblogged this · 2 months ago
roamsome reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 thesashplanet liked this · 2 months ago
thesashplanet liked this · 2 months ago -
 buttcheesetaco liked this · 2 months ago
buttcheesetaco liked this · 2 months ago -
 cxrpe-noctem reblogged this · 2 months ago
cxrpe-noctem reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 cxrpe-noctem liked this · 2 months ago
cxrpe-noctem liked this · 2 months ago -
 bloodstainedvibrator reblogged this · 2 months ago
bloodstainedvibrator reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 ashstag1 liked this · 2 months ago
ashstag1 liked this · 2 months ago -
 otherthings-pics liked this · 2 months ago
otherthings-pics liked this · 2 months ago -
 rancidtofu reblogged this · 2 months ago
rancidtofu reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 soul-paralyzed liked this · 2 months ago
soul-paralyzed liked this · 2 months ago -
 saifesque liked this · 2 months ago
saifesque liked this · 2 months ago -
 lonewolfpsycho reblogged this · 2 months ago
lonewolfpsycho reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 lonewolfpsycho liked this · 2 months ago
lonewolfpsycho liked this · 2 months ago -
 intrepidhamiltonian liked this · 2 months ago
intrepidhamiltonian liked this · 2 months ago -
 ethereal-4 reblogged this · 2 months ago
ethereal-4 reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 karlachx liked this · 2 months ago
karlachx liked this · 2 months ago -
 artemiese reblogged this · 2 months ago
artemiese reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 hamadaaa000 liked this · 2 months ago
hamadaaa000 liked this · 2 months ago -
 prjulioca reblogged this · 2 months ago
prjulioca reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 smp0729 liked this · 2 months ago
smp0729 liked this · 2 months ago -
 eyestalkbetterthanwords liked this · 2 months ago
eyestalkbetterthanwords liked this · 2 months ago -
 ladytuarach reblogged this · 2 months ago
ladytuarach reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 crissyultra reblogged this · 2 months ago
crissyultra reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 pablomilans liked this · 2 months ago
pablomilans liked this · 2 months ago