This Impressive Storm Captured By Geoff Green Over West Australia In August 2018, Gives You An Idea Of
This impressive storm captured by Geoff Green over West Australia in August 2018, gives you an idea of the huge frequency at which lightning happen in an extreme weather event
Instagram: wonders_of_the_cosmos
More Posts from Sergioballester-blog and Others

Update your phones with our #CountdownToMars wallpapers, like this one, today: https://www.nasa.gov/feature/perseverance-mars-rover-wallpaper-images/
It's LANDING DAY for our Perseverance Mars Rover and her mission to search for ancient signs of life on the Red Planet!
Watch LIVE coverage today starting at 2:15pm ET (18:15 UTC):
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System 10 Things: Looking Back at Pluto
In July 2015, we saw Pluto up close for the first time and—after three years of intense study—the surprises keep coming. “It’s clear,” says Jeffery Moore, New Horizons’ geology team lead, “Pluto is one of the most amazing and complex objects in our solar system.”
1. An Improving View

These are combined observations of Pluto over the course of several decades. The first frame is a digital zoom-in on Pluto as it appeared upon its discovery by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930. More frames show of Pluto as seen by the Hubble Space Telescope. The final sequence zooms in to a close-up frame of Pluto taken by our New Horizons spacecraft on July 14, 2015.
2. The Heart

Pluto’s surface sports a remarkable range of subtle colors are enhanced in this view to a rainbow of pale blues, yellows, oranges, and deep reds. Many landforms have their own distinct colors, telling a complex geological and climatological story that scientists have only just begun to decode. The image resolves details and colors on scales as small as 0.8 miles (1.3 kilometers). Zoom in on the full resolution image on a larger screen to fully appreciate the complexity of Pluto’s surface features.
3. The Smiles

July 14, 2015: New Horizons team members Cristina Dalle Ore, Alissa Earle and Rick Binzel react to seeing the spacecraft’s last and sharpest image of Pluto before closest approach.
4. Majestic Mountains

Just 15 minutes after its closest approach to Pluto, the New Horizons spacecraft captured this near-sunset view of the rugged, icy mountains and flat ice plains extending to Pluto’s horizon. The backlighting highlights more than a dozen layers of haze in Pluto’s tenuous atmosphere. The image was taken from a distance of 11,000 miles (18,000 kilometers) to Pluto; the scene is 780 miles (1,250 kilometers) wide.
5. Icy Dunes

Found near the mountains that encircle Pluto’s Sputnik Planitia plain, newly discovered ridges appear to have formed out of particles of methane ice as small as grains of sand, arranged into dunes by wind from the nearby mountains.
6. Glacial Plains

The vast nitrogen ice plains of Pluto’s Sputnik Planitia – the western half of Pluto’s “heart”—continue to give up secrets. Scientists processed images of Sputnik Planitia to bring out intricate, never-before-seen patterns in the surface textures of these glacial plains.
7. Colorful and Violent Charon

High resolution images of Pluto’s largest moon, Charon, show a surprisingly complex and violent history. Scientists expected Charon to be a monotonous, crater-battered world; instead, they found a landscape covered with mountains, canyons, landslides, surface-color variations and more.
8. Ice Volcanoes

One of two potential cryovolcanoes spotted on the surface of Pluto by the New Horizons spacecraft. This feature, known as Wright Mons, was informally named by the New Horizons team in honor of the Wright brothers. At about 90 miles (150 kilometers) across and 2.5 miles (4 kilometers) high, this feature is enormous. If it is in fact an ice volcano, as suspected, it would be the largest such feature discovered in the outer solar system.
9. Blue Rays

Pluto’s receding crescent as seen by New Horizons at a distance of 120,000 miles (200,000 kilometers). Scientists believe the spectacular blue haze is a photochemical smog resulting from the action of sunlight on methane and other molecules in Pluto’s atmosphere. These hydrocarbons accumulate into small haze particles, which scatter blue sunlight—the same process that can make haze appear bluish on Earth.
10. Encore

On Jan. 1, 2019, New Horizons will fly past a small Kuiper Belt Object named MU69 (nicknamed Ultima Thule)—a billion miles (1.5 billion kilometers) beyond Pluto and more than four billion miles (6.5 billion kilometers) from Earth. It will be the most distant encounter of an object in history—so far—and the second time New Horizons has revealed never-before-seen landscapes.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

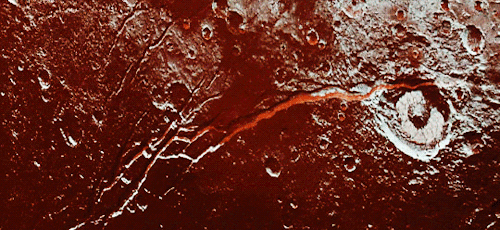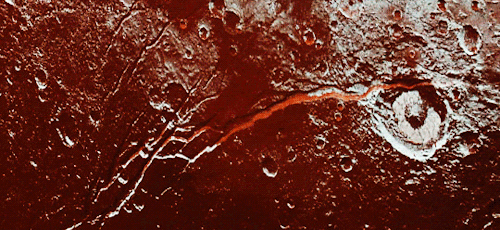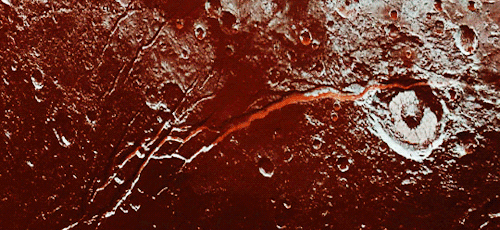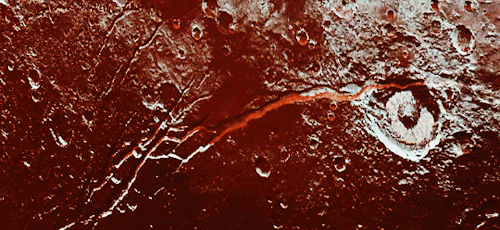

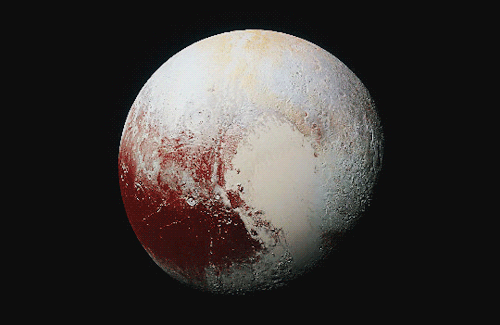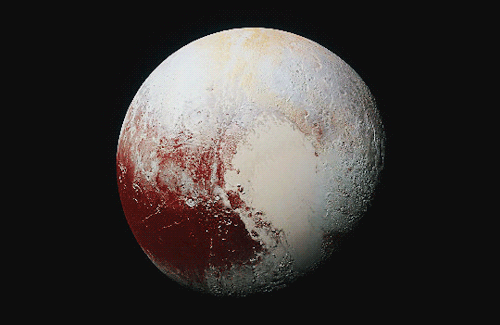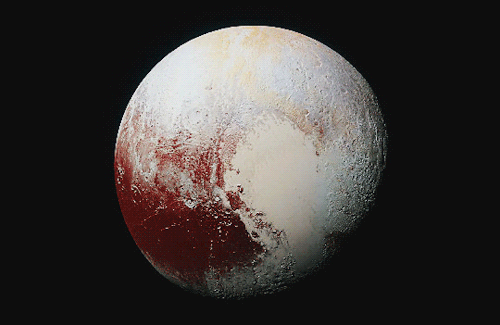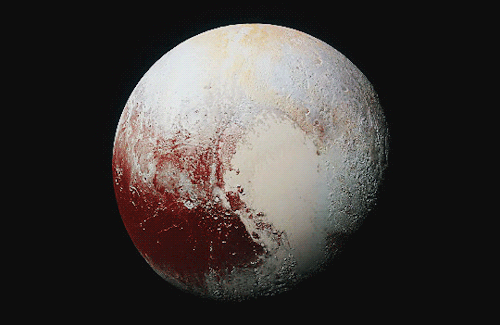


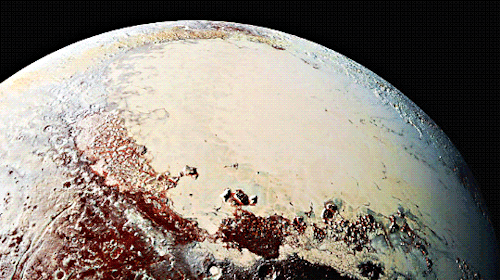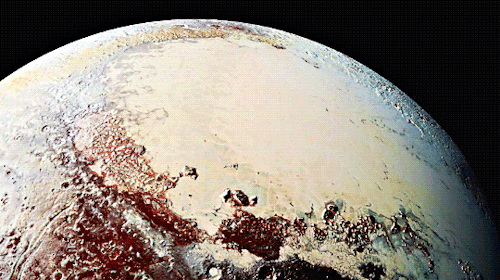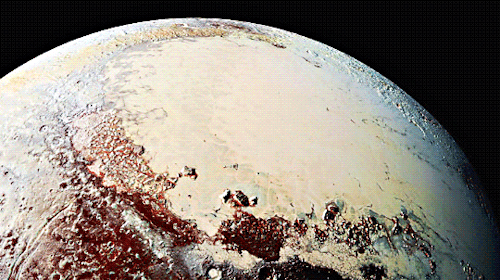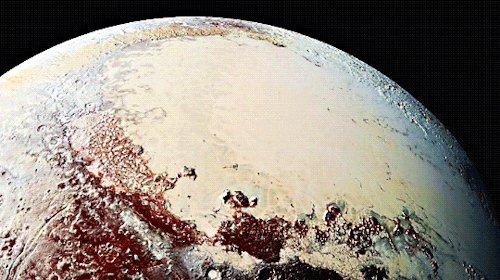



Pluto as seen from NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft ; Its heart-shaped sea is filled with poisonous ice.

It was time for their close-up. Two days ago Jupiter and Saturn passed a tenth of a degree from each other in what is known a Great Conjunction. Although the two planets pass each other on the sky every 20 years, this was the closest pass in nearly four centuries. Taken early in day of the Great Conjunction, the featured multiple-exposure combination captures not only both giant planets in a single frame, but also Jupiter's four largest moons (left to right) Callisto, Ganymede, Io, and Europa -- and Saturn's largest moon Titan.
Image Credit: Damian Peach
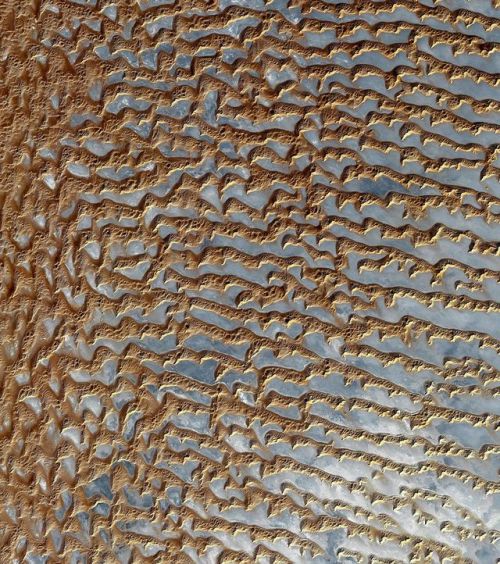
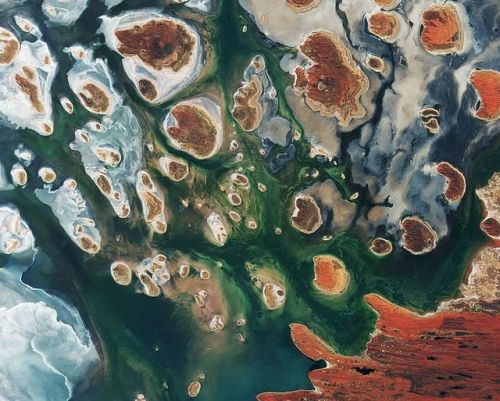
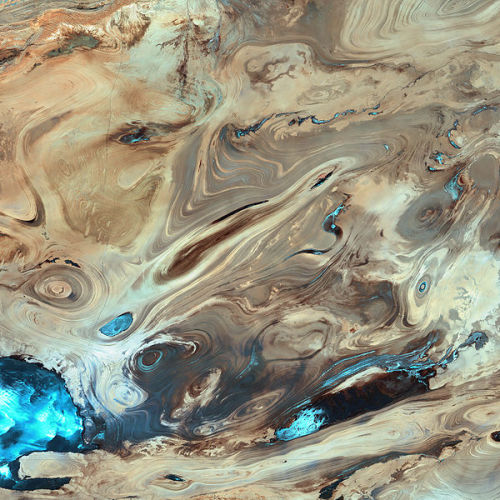
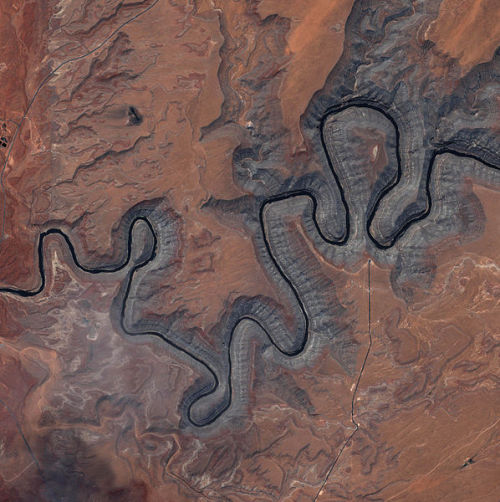
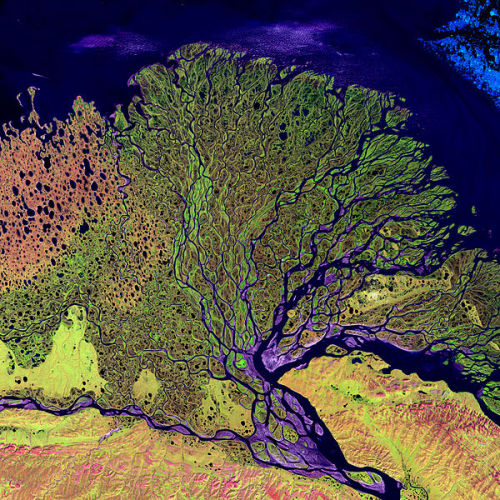
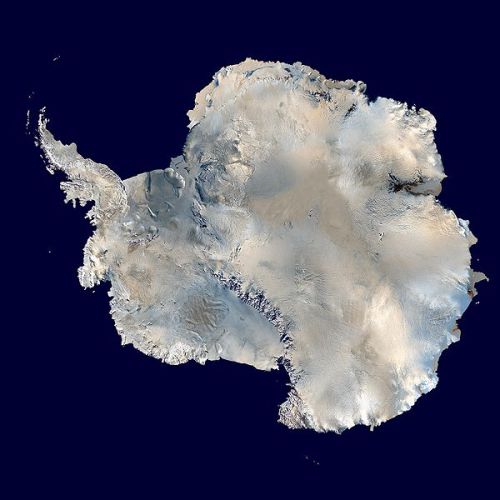











Earth images photographed by satellites and the International Space Station
images
Mars Helicopter: 6 Things to Know About Ingenuity

When our Perseverance Mars rover lands on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021, it will bring along the Ingenuity helicopter.
This small-but-mighty craft is a technology demonstration that will attempt the first powered, controlled flight on another planet. Its fuselage is about the size of a tissue box, and it weighs about 4 pounds (1.8 kg) on Earth. It started out six years ago as an implausible prospect and has now passed its Earthbound tests.
Here are six things to know about Ingenuity as it nears Mars:
1. Ingenuity is an experimental flight test.

This Mars helicopter is known as a technology demonstration, which is a project that aims to test a new capability for the first time with a limited scope. Previous technology demonstrations include Sojourner, the first Mars rover, and the Mars Cube One (MarCO) CubeStats that flew by Mars.
Ingenuity does not carry any science instruments and is not part of Perseverance’s science mission. The only objective for this helicopter is an engineering one – to demonstrate rotorcraft flight in the thin and challenging Martian atmosphere.
2. Mars won’t make it easy for Ingenuity.

Mars’ atmosphere is around 1% the density of Earth’s. Because of that lack of density, Ingenuity has rotor blades that are much larger and spin faster than a helicopter of Ingenuity’s mass here on our planet. It also must be extremely light to travel to Mars.
The Red Planet also has incredibly cold temperatures, with nights reaching minus 130 degrees Fahrenheit (-90 degrees Celsius) in Jezero Crater, where our rover and helicopter will land. Tests on Earth at the predicted temperatures indicate Ingenuity’s parts should work as designed, but the real test will be on Mars.
3. Ingenuity relies on Perseverance for safe passage to Mars and operations on the Martian surface.

Ingenuity is nestled sideways under Perseverance’s belly with a cover to protect the helicopter from debris during landing. The power system on the Mars 2020 spacecraft periodically charges Ingenuity’s batteries during the journey to the Red Planet.
In the first few months after landing, Perseverance will find a safe place for Ingenuity. Our rover will shed the landing cover, rotate the helicopter so its legs face the ground and gently drop it on the Martian surface.
4. Ingenuity is smart for a small robot.

NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory will not be able to control the helicopter with a joystick due to delays communicating with spacecraft across interplanetary distances. That means Ingenuity will make some of its own decisions based on parameters set by its engineering team on Earth.
During flight, Ingenuity will analyze sensor data and images of the terrain to ensure it stays on a flight path designed by project engineers.
5. The Ingenuity team counts success one step at a time.

Ingenuity’s team has a long list of milestones the helicopter must pass before it can take off and land in the Martian atmosphere.
Surviving the journey to and landing on Mars
Safely deploying onto the Martian surface from Perseverance’s belly
Autonomously keeping warm through those intensely cold Martian nights
Autonomously charging itself with its solar panel
Successfully communicating to and from the helicopter via the Mars Helicopter Base Station on Perseverance
6. If Ingenuity succeeds, future Mars exploration could include an ambitious aerial dimension.

The Mars helicopter intends to demonstrate technologies and first-of-its-kind operations needed for flying on Mars. If successful, these technologies and flight experience on another planet could pave the way for other advanced robotic flying vehicles.
Possible uses of a future helicopter on Mars include:
A unique viewpoint not provided by current orbiters, rovers or landers
High-definition images and reconnaissance for robots or humans
Access to terrain that is difficult for rovers to reach
Could even carry light but vital payloads from one site to another
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Landing Day for InSight by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center

Cassini’s farewell mosaic of Saturn by europeanspaceagency

Curiosity: Sol 3048 via NASA https://ift.tt/3vSSsDz
-
 greenstrong liked this · 2 months ago
greenstrong liked this · 2 months ago -
 uraeuseraph reblogged this · 5 months ago
uraeuseraph reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 uraeuseraph liked this · 5 months ago
uraeuseraph liked this · 5 months ago -
 cernunnos1990 reblogged this · 5 months ago
cernunnos1990 reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 cernunnos1990 liked this · 5 months ago
cernunnos1990 liked this · 5 months ago -
 firstsciencepoemcop reblogged this · 5 months ago
firstsciencepoemcop reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 firstsciencepoemcop liked this · 5 months ago
firstsciencepoemcop liked this · 5 months ago -
 pundelmurra2 reblogged this · 6 months ago
pundelmurra2 reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 pundelmurra2 liked this · 6 months ago
pundelmurra2 liked this · 6 months ago -
 briery liked this · 6 months ago
briery liked this · 6 months ago -
 asherha111 liked this · 8 months ago
asherha111 liked this · 8 months ago -
 glenmir reblogged this · 8 months ago
glenmir reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 my-jnhill liked this · 9 months ago
my-jnhill liked this · 9 months ago -
 rank-sentimentalist reblogged this · 1 year ago
rank-sentimentalist reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 rank-sentimentalist liked this · 1 year ago
rank-sentimentalist liked this · 1 year ago -
 72eli liked this · 1 year ago
72eli liked this · 1 year ago -
 gillianleeeza reblogged this · 1 year ago
gillianleeeza reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 krampn reblogged this · 1 year ago
krampn reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 artzandfashion reblogged this · 1 year ago
artzandfashion reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 cataradical liked this · 1 year ago
cataradical liked this · 1 year ago -
 introspectivesolely liked this · 1 year ago
introspectivesolely liked this · 1 year ago -
 chrisbel liked this · 1 year ago
chrisbel liked this · 1 year ago -
 darth-puma-vader reblogged this · 1 year ago
darth-puma-vader reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 darth-puma-vader liked this · 1 year ago
darth-puma-vader liked this · 1 year ago -
 messier47 reblogged this · 1 year ago
messier47 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 usmcbuss liked this · 1 year ago
usmcbuss liked this · 1 year ago -
 1st-day reblogged this · 1 year ago
1st-day reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 blacknerdinspiration liked this · 1 year ago
blacknerdinspiration liked this · 1 year ago -
 blacknerdinspiration reblogged this · 1 year ago
blacknerdinspiration reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 celticwarriorcj liked this · 1 year ago
celticwarriorcj liked this · 1 year ago -
 boddigarwinsmas liked this · 1 year ago
boddigarwinsmas liked this · 1 year ago -
 brumeximkalju liked this · 1 year ago
brumeximkalju liked this · 1 year ago -
 sleepersclub reblogged this · 1 year ago
sleepersclub reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 sleepersclub liked this · 1 year ago
sleepersclub liked this · 1 year ago -
 silentvoiceoftheheart liked this · 1 year ago
silentvoiceoftheheart liked this · 1 year ago -
 browneyes1414 reblogged this · 1 year ago
browneyes1414 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 bytesizeambs reblogged this · 1 year ago
bytesizeambs reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 bytesizeambs liked this · 1 year ago
bytesizeambs liked this · 1 year ago -
 thisk57 liked this · 1 year ago
thisk57 liked this · 1 year ago