NGC 7023, Ghost Nebula

NGC 7023, Ghost Nebula
More Posts from Astrotidbits-blog and Others
Jupiter and beyond the Infinite…
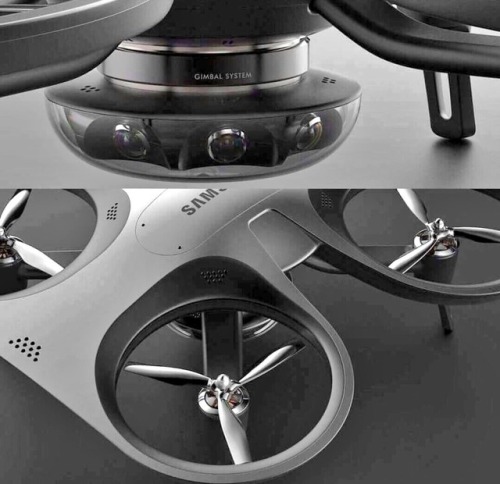

Possible 360° camera drone by Samsung?


Cameras, cameras, and more cameras. Cameras!

Goodbye to M42 for this year. But I’ll see you again in November. Meanwhile I can look at this picture I took in January of this year.
www.astrotidbits.com

ASTRONOMERS CAPTURE BEST VIEW EVER OF DISINTEGRATING COMET
Astronomers have captured the sharpest, most detailed observations of a comet breaking apart 67 million miles from Earth, using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. The discovery is published online today in Astrophysical Journal Letters [http://apjl.aas.org].
In a series of images taken over three days in January 2016, Hubble showed 25 fragments consisting of a mixture of ice and dust that are drifting away from the comet at a pace equivalent to the walking speed of an adult, said David Jewitt, a professor in the UCLA departments of Earth, Planetary and Space Sciences; and Physics and Astronomy, who led the research team.
The images suggest that the roughly 4.5-billion-year-old comet, named 332P/Ikeya-Murakami, or Comet 332P, may be spinning so fast that material is ejected from its surface. The resulting debris is now scattered along a 3,000-mile-long trail, larger than the width of the continental United States.
These observations provide insight into the volatile behavior of comets as they approach the Sun and begin to vaporize, unleashing powerful forces.
“We know that comets sometimes disintegrate, but we don’t know much about why or how,” Jewitt said. “The trouble is that it happens quickly and without warning, so we don’t have much chance to get useful data. With Hubble’s fantastic resolution, not only do we see really tiny, faint bits of the comet, but we can watch them change from day to day. That has allowed us to make the best measurements ever obtained on such an object.”
The three-day observations show that the comet shards brighten and dim as icy patches on their surfaces rotate into and out of sunlight. Their shapes change, too, as they break apart. The icy relics comprise about four percent of the parent comet and range in size from roughly 65 feet wide to 200 feet wide. They are separating at only a few miles per hour as they orbit the Sun at more than 50,000 miles per hour.
The Hubble images show that the parent comet changes brightness frequently, completing a rotation every two to four hours. A visitor to the comet would see the Sun rise and set in as little as an hour, Jewitt said.
The comet is much smaller than astronomers thought, measuring only 1,600 feet across, about the length of five football fields.
Comet 332P was discovered in November 2010, after it surged in brightness and was spotted by two Japanese amateur astronomers.
Based on the Hubble data, the research team suggests that sunlight heated the surface of the comet, causing it to expel jets of dust and gas. Because the nucleus is so small, these jets act like rocket engines, spinning up the comet’s rotation, Jewitt said. The faster spin rate loosened chunks of material, which are drifting off into space. The research team calculated that the comet probably shed material over a period of months, between October and December 2015.
Jewitt suggests that some of the ejected pieces have themselves fallen to bits in a kind of cascading fragmentation. “We think these little guys have a short lifetime,” he said.
Hubble’s sharp vision also spied a chunk of material close to the comet, which may be the first salvo of another outburst. The remnant from still another flare-up, which may have occurred in 2012, is also visible. The fragment may be as large as Comet 332P, suggesting the comet split in two. But the remnant wasn’t spotted until Dec. 31, 2015, by a telescope in Hawaii.
That discovery prompted Jewitt and colleagues to request Hubble Space Telescope time to study the comet in detail.
“In the past, astronomers thought that comets die when they are warmed by sunlight, causing their ices to simply vaporize away,” Jewitt said. “But it’s starting to look like fragmentation may be more important. In comet 332P we may be seeing a comet fragmenting itself into oblivion.”
The researchers estimate that comet 332P contains enough mass for 25 more outbursts. “If the comet has an episode every six years, the equivalent of one orbit around the Sun, then it will be gone in 150 years,” Jewitt said. “It’s just the blink of an eye, astronomically speaking. The trip to the inner solar system has doomed it.”
The icy visitor hails from the Kuiper belt, a vast swarm of objects at the outskirts of our solar system. As the comet traveled across the system, it was deflected by the planets, like a ball bouncing around in a pinball machine, until Jupiter’s gravity set its current orbit, Jewitt said.
What is the next step for hacktivists, radical or not. What’s 4Chan, what’s Anonymous and what’s the next thing? What’s the real deal - Ray Johansen gives his views.
Revolutionaries are always controversial. Some get proven right, some as a doing bad, some seen as doing equal amounts of both.The truth is complex. So we let Ray give us his views.
As part of our transparent process, we’re making some of our research interviews available for all. Check out both our Transparently Unedited interviews on our YouTube channel where you’ll and also find other awesome clips from a diverse set of characters.
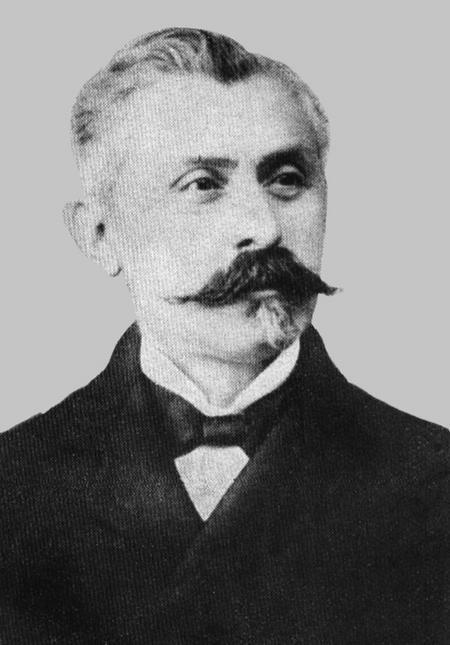

Սպիրու Կոստաքեի Հարեթ Spiru C. Haret
Romanian Armenian mathematician, astronomer and politician. He made a fundamental contribution to the n-body problem in celestial mechanics by proving that using a third degree approximation for the disturbing forces implies instability of the major axes of the orbits, and by introducing the concept of secular perturbations in relation to this. (Proved that planetary motion is not absolutely stable) As a politician, during his three terms as Minister of Education, Haret ran deep reforms, building the modern Romanian education system. He was made a full member of the Romanian Academy in 1892. He also founded the Astronomical observatory in Bucharest, The crater Haret on the Moon is named after him. The Spiru Haret University, a private university in Bucharest, Romania, bears the name of a scientist and reformer of the Romanian education.
Born 15 February 1851 in Iaşi, Moldavia to an Armenian family, He showed talent for mathematics at a very young age, publishing two textbooks, one in algebra and one in trigonometry when he was still in high school. Whilst in his second year studying physics and mathematics the in the University of Bucharest, he became a teacher of mathematics in Nifon Seminary.
After graduation, Haret won a scholarship competition organized by Titu Maiorescu and went to Paris in order to study mathematics at the Sorbonne. There he earned a mathematics diploma in 1875 and a physics diploma in 1876. Two years later he earned his Ph.D. by defending his thesis, Sur l’invariabilité des grandes axes des orbites planétaires (On the invariability of the major axis of planetary orbits), in front of examiners led by Victor Puiseux. In this work he proved a result fundamental for the n-body problem in astronomy, the thesis being published in Vol. XVIII of the Annales de l'Observatoire de Paris. Haret was the first Romanian to obtain a Ph.D. degree in Paris, (though he was of full Armenian descent)
After his return to Romania in 1878, Haret abandoned scientific research and dedicated the rest of his life to improving Romanian education, which was heavily underdeveloped at the time, both as professor and as politician. He only published an article on the secular acceleration of the Moon in 1880 and one on Jupiter’s Great Red Spot (1912). And in In 1910 he published Social mechanics, which used mathematics to explain social behaviour (somehow anticipating the fictional “psychohistory” branch of mathematics developed by Hari Seldon, the fictional character of Isaac Asimov‘s Foundation, published 40 years later).
He was appointed professor of rational mechanics at the Science Faculty in Bucharest. The next year Haret became a correspondent member of the Romanian Academy. He kept the professorship at the Science Faculty until his retirement in 1910. As Minister of Education he ran a complete reform, basically building the modern Romanian education system

⚠️️ BREAKTHROUGH ⚠️️
Nasa is currently livestreaming a conference about the discovery of a new solar system !
“Astronomers have detected no less than seven Earth-sized worlds orbiting a cool dwarf star known as TRAPPIST-1.The six inner planets lie in a temperate zone where surface temperatures range from zero to 100C.
Of these, at least three are thought to be capable of having oceans, increasing the likelihood of life.
No other star system known contains such a large number of Earth-sized and probably rocky planets.”
I AM SO EXCITED

This full functional CW Keyer was built by a spanish jeweler with watches parts. He gave it to me, as a gift, ten years ago.





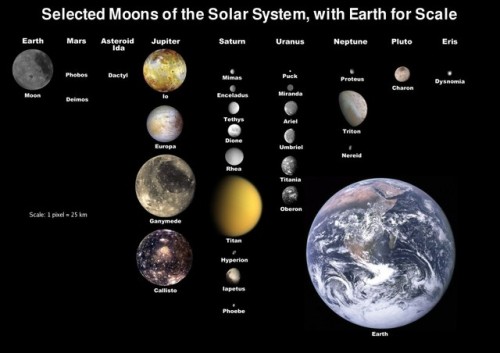
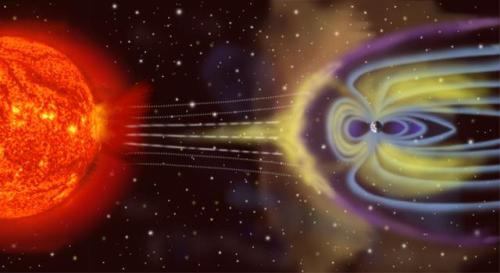
NASA’s MAVEN Discovers How Mars Lost Its Atmosphere
“The good news for us, mind you, is that the magnetic field here on Earth shows no sign of ceasing anytime soon. The dynamo in the core may do things like flip and reverse, swapping north-and-south magnetic poles, but we should continue to stay protected from the solar wind far into the foreseeable future: for billions of years (at least) to be sure. We could, conceivably, one day suffer the same fate as Mars, but our mass, our rotation and our active, dynamic core should keep the Earth’s magnetic field in business for at least as long as the Sun shines!”
If you had taken a trip to our Solar System four billion years ago, you would have found two worlds with liquid water oceans, temperate atmospheres and all the conditions we believe are needed for life. Earth would have been one of them, but Mars would have met all those criteria, too. It was long suspected that something happened to Mars around a billion years into the Solar System’s history that caused it to lose its atmosphere, something that should still be going on today. Thanks to NASA’s Maven mission, we’ve measured this atmospheric stripping by the Sun for the first time, and we’ve reached a few incredible conclusions, including that in about two billion years, Mars will be completely airless, and that if we were to terraform Mars today, it would hang onto this new atmosphere for millions of years.
Come get the full story of how Mars lost its atmosphere, and learn what NASA’s Maven mission has taught us so far!
-
 keididikay liked this · 3 years ago
keididikay liked this · 3 years ago -
 laneluthorblog liked this · 4 years ago
laneluthorblog liked this · 4 years ago -
 librarygirl liked this · 4 years ago
librarygirl liked this · 4 years ago -
 justskipper reblogged this · 4 years ago
justskipper reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 modeltpines liked this · 4 years ago
modeltpines liked this · 4 years ago -
 ritikathedestroyer liked this · 5 years ago
ritikathedestroyer liked this · 5 years ago -
 meditationrelaxationmusic reblogged this · 5 years ago
meditationrelaxationmusic reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 sleepnweep reblogged this · 5 years ago
sleepnweep reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 treewanderer liked this · 5 years ago
treewanderer liked this · 5 years ago -
 polar-night-scout liked this · 5 years ago
polar-night-scout liked this · 5 years ago -
 harpsicalbiobug reblogged this · 5 years ago
harpsicalbiobug reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 harpsicalbiobug liked this · 5 years ago
harpsicalbiobug liked this · 5 years ago -
 the-vxyn reblogged this · 5 years ago
the-vxyn reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 spaxey reblogged this · 5 years ago
spaxey reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 spaxey reblogged this · 5 years ago
spaxey reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 dreaming-marchling reblogged this · 5 years ago
dreaming-marchling reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 xevitisopx liked this · 6 years ago
xevitisopx liked this · 6 years ago -
 izayakamy liked this · 6 years ago
izayakamy liked this · 6 years ago -
 tell-megatron-lets-tango-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
tell-megatron-lets-tango-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 honeybittersweet reblogged this · 6 years ago
honeybittersweet reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 nekoshogun4 liked this · 6 years ago
nekoshogun4 liked this · 6 years ago -
 starboy-95 reblogged this · 6 years ago
starboy-95 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 starboy-95 liked this · 6 years ago
starboy-95 liked this · 6 years ago -
 xiclr liked this · 6 years ago
xiclr liked this · 6 years ago -
 annoyingpersonhorseshoe liked this · 6 years ago
annoyingpersonhorseshoe liked this · 6 years ago -
 tebabuizafet liked this · 6 years ago
tebabuizafet liked this · 6 years ago -
 medusas-eyesxx liked this · 6 years ago
medusas-eyesxx liked this · 6 years ago -
 melissaalvblog reblogged this · 6 years ago
melissaalvblog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 mkhardyphotography liked this · 6 years ago
mkhardyphotography liked this · 6 years ago -
 bugzy-123 liked this · 6 years ago
bugzy-123 liked this · 6 years ago -
 kisssmewithadventure reblogged this · 6 years ago
kisssmewithadventure reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 beepppp reblogged this · 6 years ago
beepppp reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 beepppp liked this · 6 years ago
beepppp liked this · 6 years ago -
 huntleysaysso liked this · 6 years ago
huntleysaysso liked this · 6 years ago -
 the-midnight-kid reblogged this · 6 years ago
the-midnight-kid reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 callmeleomercury liked this · 6 years ago
callmeleomercury liked this · 6 years ago -
 coloraworldwithoutgravity reblogged this · 6 years ago
coloraworldwithoutgravity reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 yahveh-el-olam liked this · 6 years ago
yahveh-el-olam liked this · 6 years ago -
 gaiagalatea reblogged this · 6 years ago
gaiagalatea reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 gaiagalatea liked this · 6 years ago
gaiagalatea liked this · 6 years ago -
 tsundoku78 reblogged this · 6 years ago
tsundoku78 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 tsundoku78 liked this · 6 years ago
tsundoku78 liked this · 6 years ago