Cameras, Cameras, And More Cameras. Cameras!


Cameras, cameras, and more cameras. Cameras!
More Posts from Astrotidbits-blog and Others
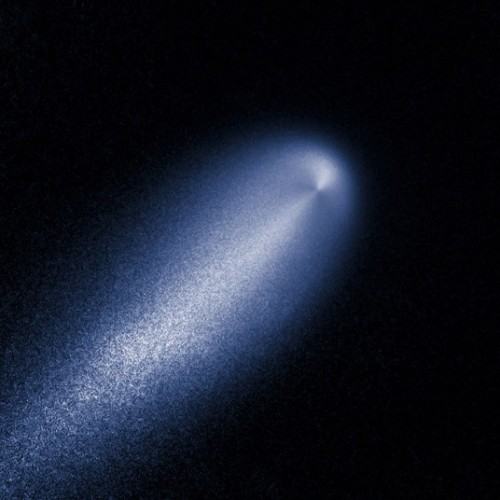

FLAIR FLIGHT A contrast-enhanced image produced from the Hubble images of comet ISON taken April 23, 2013 reveals the subtle structure in the inner coma of the comet; the coma decreases in brightness proportionally to the distance from the nucleus. Comet ISON, thought to have travelled from the Oort Cloud surrounding our solar system beginning a million years ago, will make its closest approach to the Sun on Thursday. (Photo: NASA via AP / The Telegraph)
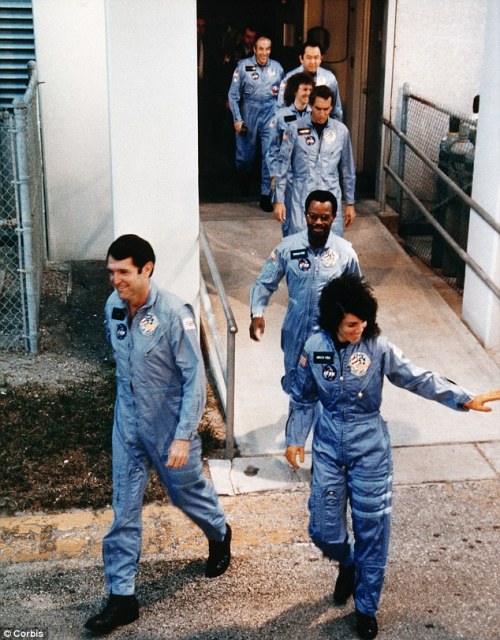
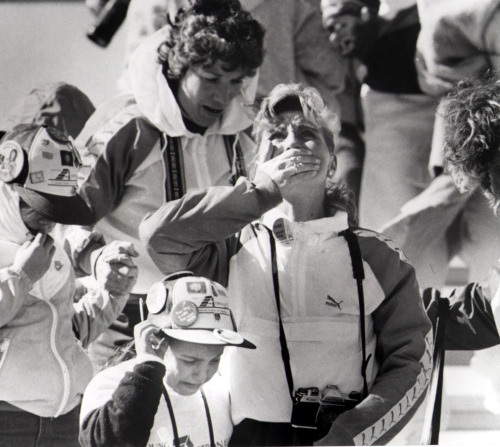



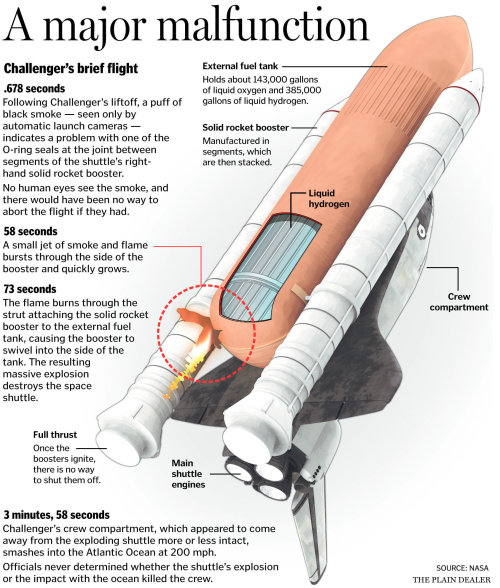







Thirty years ago today, at 11:38 a.m. EST, January 28, 1986, the space shuttle Challenger lifts off from Cape Canaveral, Florida. Christa McAuliffe, teacher from New Hampshire, was to be the first ordinary U.S. civilian to travel into space. Challenger‘s launch countdown was repeatedly delayed because of weather and technical problems. Finally, on January 28, the shuttle lifted off.
73 seconds later, hundreds on the ground, including Christa’s family, stared in disbelief as the shuttle exploded in a forking plume of smoke and fire, killing all seven crew members. Millions more watched the heart-wrenching tragedy unfold on live television.
“The future doesn’t belong to the faint-hearted. It belongs to the brave.” President Reagan said. “The Challenger crew was pulling us into the future, and we’ll continue to follow. Nothing ends here; our hopes and our journeys continue.”
Need more astro-stuff? Go to www.astrotidbits.com and see what is there.




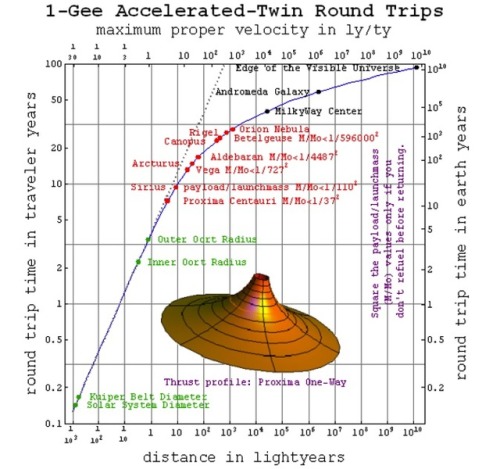
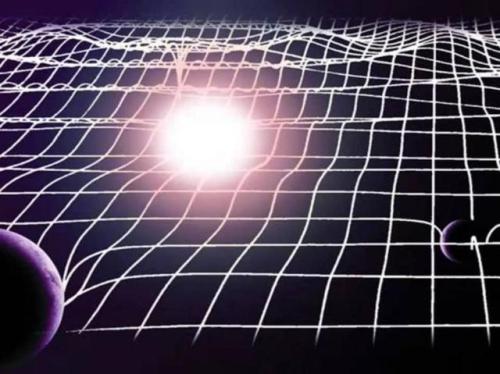
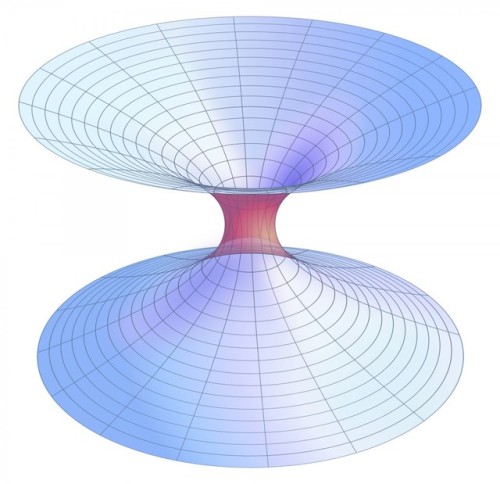

Is Time Travel Possible, According To Science?
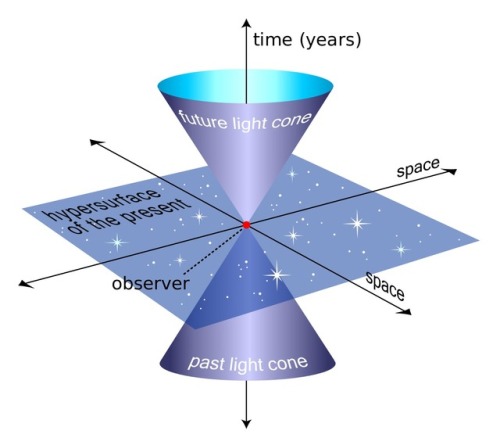
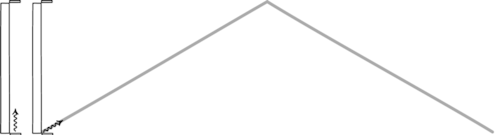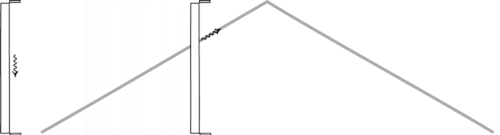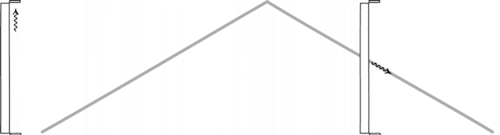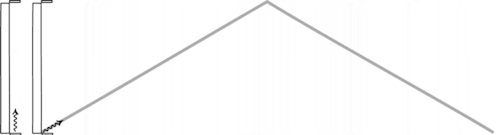
“You can witness the evolution and destruction of humanity; the end of the Earth and Sun; the dissociation of our galaxy; the heat death of the Universe itself. So long as you have enough power in your space ship, you can travel as far into the future as you like.”
Have you ever wondered about time travel? Perhaps you have your destination in the far future, and want to see how it all turns out? Maybe you want to return to the past, and alter the future or present by your actions there? Or maybe you want to freeze time altogether? If you want to know whether it’s possible, the physics of relativity holds the answer. Special relativity allows us to control our motion through time by manipulating our motion through space. The more we move through space, the less we move through time, allowing us to travel as far as we want into the future, limited only by our energy available for space travel. But going to the past requires some specific solutions to general relativity, which may (or may not) describe our physical Universe.
What’s the status of traveling through time? Come get the scientific story (with a brand new podcast) today!
*Those razor-like shadows, they’re so black they look photoshopped
Know Your “Space” Rocks:
An asteroid is a large chunk of rock left over from collisions or the early solar system. Most are located between Mars and Jupiter in the Main Belt.
A comet is a rock covered in ice, methane and other compounds. Their orbits take them much further out of the solar system.
A meteor is what we call a flash of light in the atmosphere when debris burns up.
This debris itself is known as a meteoroid. Most are so small they are vapourised in the atmosphere.
If any of this meteoroid makes it to Earth, it is called a meteorite.
Meteors, meteoroids and meteorites normally originate from asteroids and comets.
For example, if Earth passes through the tail of a comet, much of the debris burns up in the atmosphere, forming a meteor shower.

|


The Drake Equation (sometimes known as: Green Bank equation or the Green Bank Formula)
The Drake Equation is a formula that may calculate the possibility of contactable extra-terrestrial alien species.
Proposed by Frank Drake in 1961, the Drake Equation is a probability argument that would estimate how many contactable, active and communicable alien species there are in our Milky Way.
The Drake Equation is, as follows;
N = R* • fp • ne • fl • fi • fc • L.
In this equation, N = the number of civilizations in our galaxy with which communication might be possible.
R* = the average rate of star formation in our galaxy.
fp = the fraction of those stars that have planets
ne = the average number of planets that can potentially support life per star that has planets
fl = the fraction of planets that could support life that actually develop life at some point
fi = the fraction of planets with life that actually go on to develop intelligent life (civilizations)
fc = the fraction of civilizations that develop a technology that releases detectable signs of their existence into space
L = the length of time for which such civilizations release detectable signals into space
The Drake Equation acts as a summary of which we can expect to communicate (if at all) with those who are extra-terrestrial. The last four parameters: fl, fi, fc and L, are not known and are very hard to estimate, with values ranging over many orders of magnitude.
Therefore it is not a direct measurement of when we will communicate but a roadmap towards creating and estimating the means necessary to communicate with our space buddies.
Titan Touchdown
On Jan. 14, 2005, ESA’s Huygens probe made its descent to the surface of Saturn’s hazy moon, Titan. Carried to Saturn by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, Huygens made the most distant landing ever on another world, and the only landing on a body in the outer solar system. This video uses actual images taken by the probe during its two-and-a-half hour fall under its parachutes.
-
 timetravelphotobooth reblogged this · 7 years ago
timetravelphotobooth reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 cervezaparalacabeza reblogged this · 7 years ago
cervezaparalacabeza reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 moongoddesa-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
moongoddesa-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog liked this · 7 years ago
astrotidbits-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 pettyndproud-blog liked this · 7 years ago
pettyndproud-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 pattsdaya liked this · 7 years ago
pattsdaya liked this · 7 years ago -
 joeyshoots-blog1 liked this · 7 years ago
joeyshoots-blog1 liked this · 7 years ago -
 melybeyby-blog liked this · 7 years ago
melybeyby-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 montserratq-blog liked this · 7 years ago
montserratq-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 mahalinho-blog liked this · 7 years ago
mahalinho-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 loubna16djekkam-blog liked this · 7 years ago
loubna16djekkam-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 servet2001 liked this · 7 years ago
servet2001 liked this · 7 years ago -
 halfcathalffish-blog liked this · 7 years ago
halfcathalffish-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 lohanguedes-blog liked this · 7 years ago
lohanguedes-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 mickey1234567891-blog liked this · 7 years ago
mickey1234567891-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 muthafuckinmongra-blog liked this · 7 years ago
muthafuckinmongra-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 adrian12314-blog liked this · 7 years ago
adrian12314-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 amrkorany-blog liked this · 7 years ago
amrkorany-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 saraunipara-blog liked this · 7 years ago
saraunipara-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 r-shootphoto-blog liked this · 7 years ago
r-shootphoto-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 cascarita14-blog liked this · 7 years ago
cascarita14-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 4fpsecond liked this · 7 years ago
4fpsecond liked this · 7 years ago -
 insecure-toaster-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
insecure-toaster-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 insecure-toaster-blog liked this · 7 years ago
insecure-toaster-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 beunalive-blog liked this · 7 years ago
beunalive-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 dwaneloki reblogged this · 7 years ago
dwaneloki reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 dwaneloki liked this · 7 years ago
dwaneloki liked this · 7 years ago -
 noxusappreciationblog-blog liked this · 7 years ago
noxusappreciationblog-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 lucaolv-blog liked this · 7 years ago
lucaolv-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 iliana0409-blog liked this · 7 years ago
iliana0409-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 livvy1313-blog liked this · 7 years ago
livvy1313-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 monicamacall09-blog liked this · 7 years ago
monicamacall09-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 luna-ye liked this · 7 years ago
luna-ye liked this · 7 years ago -
 robertnate-blog liked this · 7 years ago
robertnate-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 pinklemondade liked this · 7 years ago
pinklemondade liked this · 7 years ago -
 alsotheyoungwild liked this · 7 years ago
alsotheyoungwild liked this · 7 years ago -
 raisa2006-blog liked this · 7 years ago
raisa2006-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 fourorfivemovements reblogged this · 7 years ago
fourorfivemovements reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 anu5031-blog liked this · 7 years ago
anu5031-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 titidb99-blog liked this · 7 years ago
titidb99-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 frenkyonlineshop liked this · 7 years ago
frenkyonlineshop liked this · 7 years ago -
 jennivision liked this · 7 years ago
jennivision liked this · 7 years ago