NASA’s MAVEN Discovers How Mars Lost Its Atmosphere





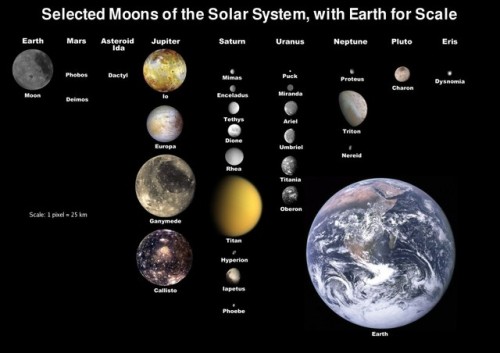
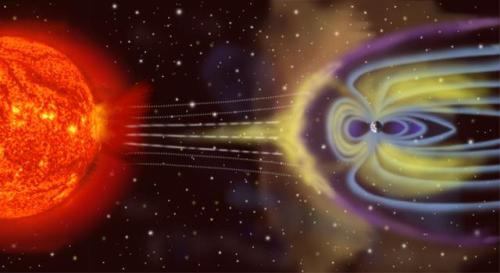
NASA’s MAVEN Discovers How Mars Lost Its Atmosphere
“The good news for us, mind you, is that the magnetic field here on Earth shows no sign of ceasing anytime soon. The dynamo in the core may do things like flip and reverse, swapping north-and-south magnetic poles, but we should continue to stay protected from the solar wind far into the foreseeable future: for billions of years (at least) to be sure. We could, conceivably, one day suffer the same fate as Mars, but our mass, our rotation and our active, dynamic core should keep the Earth’s magnetic field in business for at least as long as the Sun shines!”
If you had taken a trip to our Solar System four billion years ago, you would have found two worlds with liquid water oceans, temperate atmospheres and all the conditions we believe are needed for life. Earth would have been one of them, but Mars would have met all those criteria, too. It was long suspected that something happened to Mars around a billion years into the Solar System’s history that caused it to lose its atmosphere, something that should still be going on today. Thanks to NASA’s Maven mission, we’ve measured this atmospheric stripping by the Sun for the first time, and we’ve reached a few incredible conclusions, including that in about two billion years, Mars will be completely airless, and that if we were to terraform Mars today, it would hang onto this new atmosphere for millions of years.
Come get the full story of how Mars lost its atmosphere, and learn what NASA’s Maven mission has taught us so far!
More Posts from Astrotidbits-blog and Others
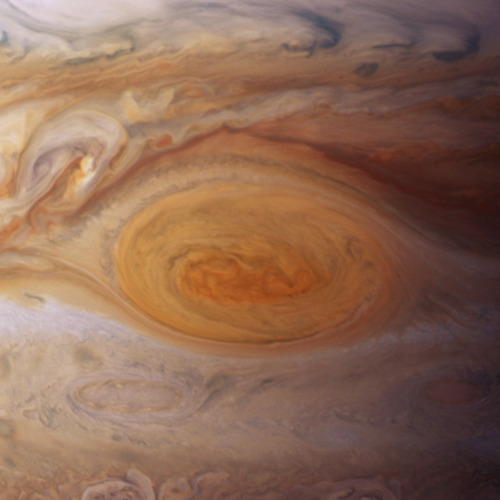


Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is such a crazy, turbulent storm (the largest known storm in the universe) that it creates sound waves that travel hundreds of miles up and actually heat the planet’s upper atmosphere.
I repeat: sound waves are heating Jupiter’s atmosphere. The area above the Spot is a thousand degrees Fahrenheit hotter than the surrounding atmosphere.
Here’s the journal paper. Here’s our story.
Image credit: Space Telescope Science Institute/NASA
planets










Cassini prepares for final orbital “Grand Finale” at Saturn.
Erik Wernquist, the same filmmaker who created 2014’s “Wanderers” and a stunning New Horizons promotional film in 2015, has created a new video highlighting NASA’s Cassini mission’s final days at Saturn. The Cassini spacecraft will begin its final series of orbits to cap a 13-year groundbreaking science mission known as the Grand Finale. For the first time ever in Cassini’s time at Saturn, the spacecraft will fly in between the planet’s rings and atmosphere. No spacecraft has ever before flown in this region of any of the solar system’s ringed planets. After 23 orbits, Cassini will dive into Saturn’s upper atmosphere September 15 where it will be destroyed. In 2008, mission managers explored a range of End of Mission scenarios that would protect Saturn’s moon’s from Earthly contaminants before ultimately deciding on atmospheric reentry. Cassini began her End of Mission manoeuvres on November 26, 2016, when it began the first of 20 ring-grazing orbits. A close flyby of Titan April 22 will alter the spacecraft’s trajectory to begin the first of 23 orbits in the Grand Finale, which will begin April 26.

Cassini launched from Earth on October 15, 1997, and entered Saturn orbit June 30, 2004. Six months later, on January 14, 2005, the European-built Huygens probe attached to the spacecraft landed on Titan, becoming the first probe to land in the outer solar system.
Originally scheduled for a four-year mission ending in 2008, Cassini received two mission extensions in 2008 and 2010, with the latter ending in 2017. With the spacecraft’s fuel reserves low, the Cassini team decided to end the mission. P/C: JPL/Erik Wernquist
tfw your inactive blog gets a whole bunch of notes out of nowhere and you wonder if you could ever bring it back to life


This full functional CW Keyer was built by a spanish jeweler with watches parts. He gave it to me, as a gift, ten years ago.





Discover Bird Photo Booth, the world’s first wireless bird feeder and birdcam. Get more information here


Nasa astronomers discover new solar system of seven planets called TRAPPIST-1 where life may have evolved on three of them
Life may have evolved on at least three planets in a newly discovered solar system just 39 light years from Earth, Nasa has announced.
Astronomers have detected no less than seven Earth-sized worlds orbiting a cool dwarf star known as TRAPPIST-1.
TRAPPIST-1 is an ultracool dwarf star that is approximately 8 per cent the mass of and 11 per cent the radius of our Sun.
It has a temperature of 2550K and is at least 500 million years old. In comparison, the Sun is about 4.6 billion years old and has a temperature of 5778K.
The six inner planets lie in a temperate zone where surface temperatures range from zero to 100C.
Of these, at least three are thought to be capable of having oceans, increasing the likelihood of life.
No other star system known contains such a large number of Earth-sized and probably rocky planets.
x

Goodbye to M42 for this year. But I’ll see you again in November. Meanwhile I can look at this picture I took in January of this year.
www.astrotidbits.com


The Handle 2 camera, another doomed Kodak instant, 1979.

-
 martynkaaaak-blog liked this · 4 years ago
martynkaaaak-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 idontreallyknowwhat-imdoing liked this · 4 years ago
idontreallyknowwhat-imdoing liked this · 4 years ago -
 sintas--vel reblogged this · 4 years ago
sintas--vel reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 nulled-silently reblogged this · 4 years ago
nulled-silently reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 earthart1 reblogged this · 5 years ago
earthart1 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 agulhamagnetica liked this · 5 years ago
agulhamagnetica liked this · 5 years ago -
 lemizerableu liked this · 5 years ago
lemizerableu liked this · 5 years ago -
 osejosprout liked this · 6 years ago
osejosprout liked this · 6 years ago -
 foulkittensandwitches liked this · 6 years ago
foulkittensandwitches liked this · 6 years ago -
 roguemedicine liked this · 6 years ago
roguemedicine liked this · 6 years ago -
 cherry-asu liked this · 6 years ago
cherry-asu liked this · 6 years ago -
 elas91 liked this · 6 years ago
elas91 liked this · 6 years ago -
 nookstoaster liked this · 6 years ago
nookstoaster liked this · 6 years ago -
 lookthetart liked this · 6 years ago
lookthetart liked this · 6 years ago -
 cosmoscenti liked this · 7 years ago
cosmoscenti liked this · 7 years ago -
 astroechos liked this · 7 years ago
astroechos liked this · 7 years ago -
 rain-in-the-slums liked this · 7 years ago
rain-in-the-slums liked this · 7 years ago -
 drfrasiercraneislistening reblogged this · 7 years ago
drfrasiercraneislistening reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 knave-of-diamonds liked this · 7 years ago
knave-of-diamonds liked this · 7 years ago -
 hasona34 liked this · 7 years ago
hasona34 liked this · 7 years ago -
 isleofnajera liked this · 7 years ago
isleofnajera liked this · 7 years ago -
 tuba-david liked this · 7 years ago
tuba-david liked this · 7 years ago -
 misfit6610 liked this · 7 years ago
misfit6610 liked this · 7 years ago -
 fanboying-ace reblogged this · 7 years ago
fanboying-ace reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 fanboying-ace liked this · 7 years ago
fanboying-ace liked this · 7 years ago -
 longmire2017-blog liked this · 7 years ago
longmire2017-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 commentariolus reblogged this · 7 years ago
commentariolus reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 sixthrangerknight reblogged this · 7 years ago
sixthrangerknight reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 lordblackjesus reblogged this · 7 years ago
lordblackjesus reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 yur-rei-blog liked this · 7 years ago
yur-rei-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 xadowolfx reblogged this · 7 years ago
xadowolfx reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 toocranky-blog liked this · 7 years ago
toocranky-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 faerietalelover-blog liked this · 7 years ago
faerietalelover-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 claireblood-blog liked this · 7 years ago
claireblood-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 iskandaralkandi liked this · 7 years ago
iskandaralkandi liked this · 7 years ago -
 skyofbluediamonds liked this · 7 years ago
skyofbluediamonds liked this · 7 years ago -
 sleepysheepysub liked this · 7 years ago
sleepysheepysub liked this · 7 years ago -
 delaware-small-wonder liked this · 7 years ago
delaware-small-wonder liked this · 7 years ago