Comet 67P/C-G Is Framed By One Of Rosetta’s Solar Wings, Which Is 46 Feet Long. A Stream Of Gas And
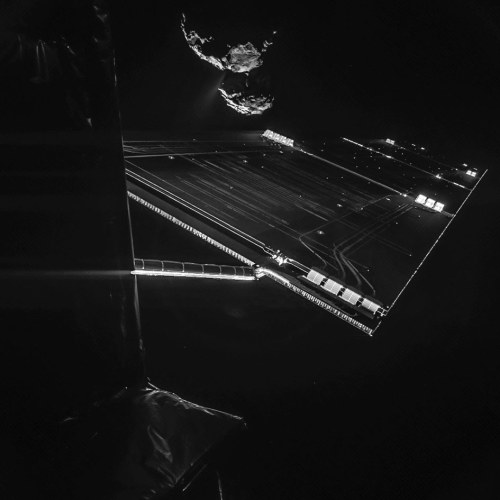

Comet 67P/C-G is framed by one of Rosetta’s solar wings, which is 46 feet long. A stream of gas and dust extends from an active area of the comet’s neck, about 10 miles away. (via NY Times)
More Posts from Astrotidbits-blog and Others
General Ham: Digital Mode Introduction
This is probably a bit more repetition, but well worth the time! So digital modes are where data are encoded as bits instead of in waves, and some are created commercially, while others are created by amateurs!
Digital modes consist of two things: a protocol and a method of modulation. A protocol is the set of rules that control the encoding, packaging, exchanging and decoding of digital data. For example, packet radio uses the AX.25 protocol standard. This standard says how each packet is constructed, how packets are exchanged, what characters are allowed, and so forth. The protocol standard doesn’t say what kind of transmitter to use or what the signal will sound like on the air.
Digital mode signals are restricted to the CW/data segments of each band and most digital mode operation is close to the top of the CW segment. Calling frequencies for the popular digital modes are incorporated into band plans and are usually the lowest frequency of operation with operators moving up in frequency as activity increases.
For example on 20m, most PSK31 signals are found near 14.070 MHz. RTTY and other digital mode signals are found above that. The modems used for digital signals often do not recognize signals from CW or other digital modes.
Here’s the Digital Signal Band Plan:

@atdiy/@tymkrs

NGC 7023, Ghost Nebula
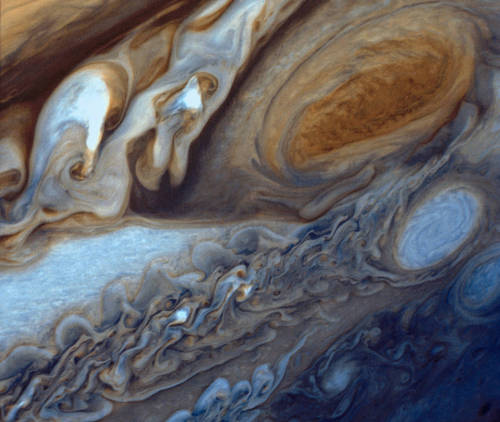

Jupiter’s Great Red Spot Viewed by Voyager 1
At about 89,000 miles in diameter, Jupiter could swallow 1,000 Earths. It is the largest planet in the solar system and perhaps the most majestic. Vibrant bands of clouds carried by winds that can exceed 400 mph continuously circle the planet’s atmosphere. Such winds sustain spinning anticyclones like the Great Red Spot – a raging storm three and a half times the size of Earth at the time of this photo, located in Jupiter’s southern hemisphere. In January and February 1979, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft zoomed toward Jupiter, capturing hundreds of images during its approach, including this close-up of swirling clouds around Jupiter’s Great Red Spot.
Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Did you see what is on www.astrotidbits.com? Loads of astronomy related stuff, including lots of pictures.

1705 Halley Documents Comet British astronomer Edmund Halley predicted the return of the comet that we now call Halley’s comet. He documented historic comet sightings and found patterns that led him to theorize that comets, which until then were considered baffling and even potentially dangerous because of their irregularity, actually had calculated orbits around the sun and would return periodically. He believed that the comets witnessed in 1531, 1607, and 1682 were actually the same comet and predicted it would return in 1758. Even though Halley died in 1742 the comet arrived on schedule and later became known as Halley’s Comet.

Orion nebula & The running man nebula, by TimMorrill
Orion nebula & The running man nebula.
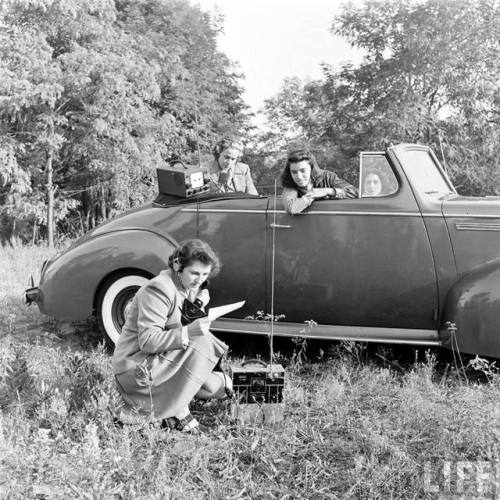

Ham radio operators for Vogue
(Nina Leen. 1941?)
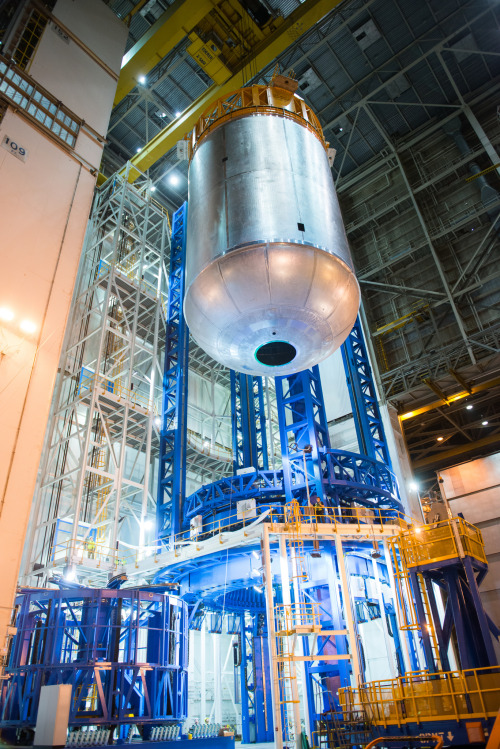
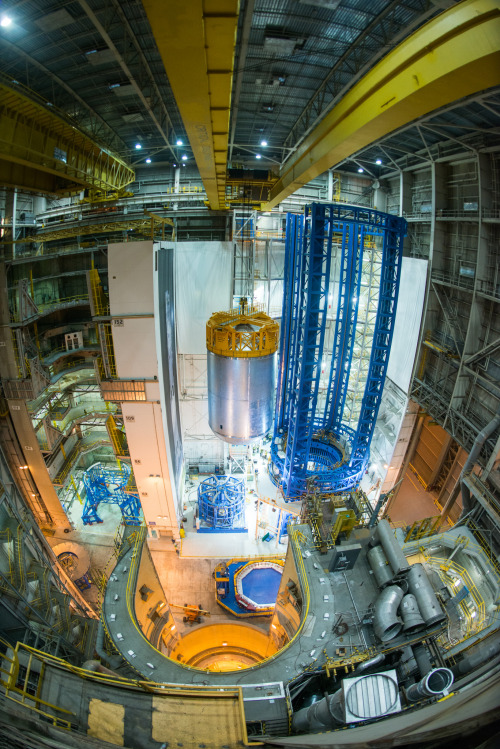




Liquid oxygen tank confidence weld complete on VAC
A liquid oxygen tank confidence article for NASA’s new rocket, the Space Launch System, completes final welding on the Vertical Assembly Center at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans.
A liquid oxygen tank confidence article for NASA’s new rocket, the Space Launch System, completes final welding on the Vertical Assembly Center at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans.
Scientists slow the speed of light
By Kenneth Macdonald
A team of Scottish scientists has made light travel slower than the speed of light.
They sent photons - individual particles of light - through a special mask. It changed the photons’ shape - and slowed them to less than light speed.
The photons remained travelling at the lower speed even when they returned to free space.
The experiment is likely to alter how science looks at light.
Continue Reading
-
 astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog liked this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 ohnokokko reblogged this · 9 years ago
ohnokokko reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 stillezerbricht-blog liked this · 9 years ago
stillezerbricht-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 p-u-r-e--i-m-a-g-i-n-a-t-i-o-n reblogged this · 10 years ago
p-u-r-e--i-m-a-g-i-n-a-t-i-o-n reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 p-u-r-e--i-m-a-g-i-n-a-t-i-o-n liked this · 10 years ago
p-u-r-e--i-m-a-g-i-n-a-t-i-o-n liked this · 10 years ago -
 prismilivein liked this · 10 years ago
prismilivein liked this · 10 years ago -
 rabidmonkeyut liked this · 10 years ago
rabidmonkeyut liked this · 10 years ago -
 kryptonitemind reblogged this · 10 years ago
kryptonitemind reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 groovypirate reblogged this · 10 years ago
groovypirate reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 viguy reblogged this · 10 years ago
viguy reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 bhawaniwasabi reblogged this · 10 years ago
bhawaniwasabi reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 twistedsickminded liked this · 10 years ago
twistedsickminded liked this · 10 years ago -
 steelskyline reblogged this · 10 years ago
steelskyline reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 steelskyline liked this · 10 years ago
steelskyline liked this · 10 years ago -
 jessicalilianne liked this · 10 years ago
jessicalilianne liked this · 10 years ago -
 iscykle liked this · 10 years ago
iscykle liked this · 10 years ago -
 thatjustlifeshesaid-blog1 liked this · 10 years ago
thatjustlifeshesaid-blog1 liked this · 10 years ago -
 thatjustlifeshesaid-blog1 reblogged this · 10 years ago
thatjustlifeshesaid-blog1 reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 burntsystems reblogged this · 10 years ago
burntsystems reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 siluetasysombras reblogged this · 10 years ago
siluetasysombras reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 strongpepper reblogged this · 10 years ago
strongpepper reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 darksource reblogged this · 10 years ago
darksource reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 beckit-g liked this · 10 years ago
beckit-g liked this · 10 years ago -
 ajisai-yatsurugi reblogged this · 10 years ago
ajisai-yatsurugi reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 welivelifelivid reblogged this · 10 years ago
welivelifelivid reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 marsinsane reblogged this · 10 years ago
marsinsane reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 dankshifty reblogged this · 10 years ago
dankshifty reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 40095 reblogged this · 10 years ago
40095 reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 momoscape-blog reblogged this · 10 years ago
momoscape-blog reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 eroseblossom reblogged this · 10 years ago
eroseblossom reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 bloodstainedblossom reblogged this · 10 years ago
bloodstainedblossom reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 dimens1ons reblogged this · 10 years ago
dimens1ons reblogged this · 10 years ago