New Day, New Series Of Photos. I’m Going To Try To Blog About The Planets Of The Solar System; First
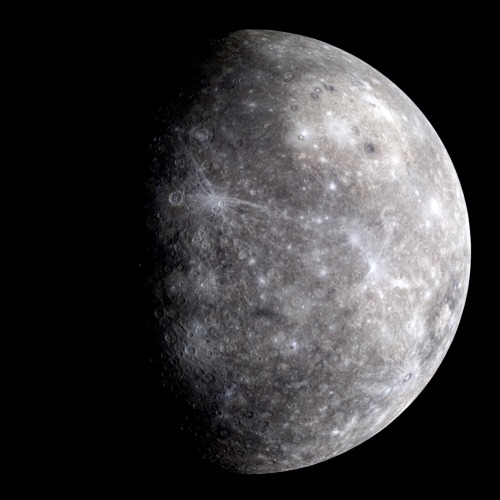
New day, new series of photos. I’m going to try to blog about the planets of the Solar System; First up is Mercury, which is the smallest and innermost planet. With a diameter ~4878km, it is smaller than some of the moons in the Solar System. The small planet in a 3:2 resonance with the sun, giving it a unique position where a single day takes 2 Mercurian years. It has the smallest tilt of any planet in the Solar System at just 1/30 of a degree.
Keep reading
More Posts from Astrotidbits-blog and Others


GoPro Hero 5

Drifting Memories
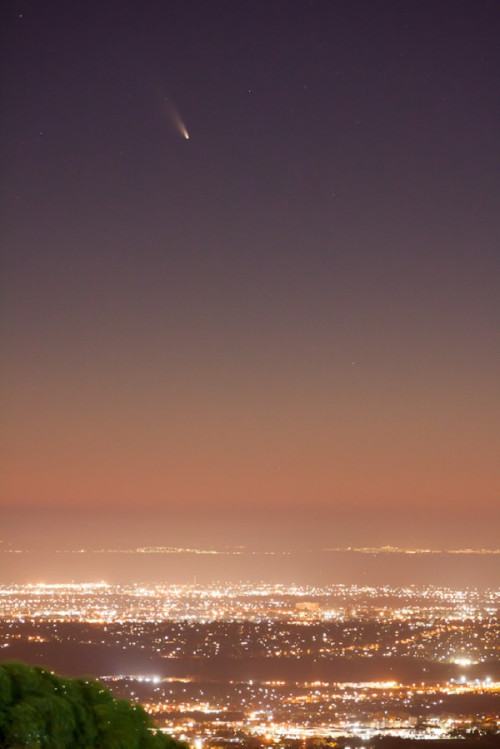

Comet PanSTARRS
Gorgeous picture of Comet PanSTARRS taken by Carl Gruber on March 2, 2013 at a mountain lookout in Melbourne.
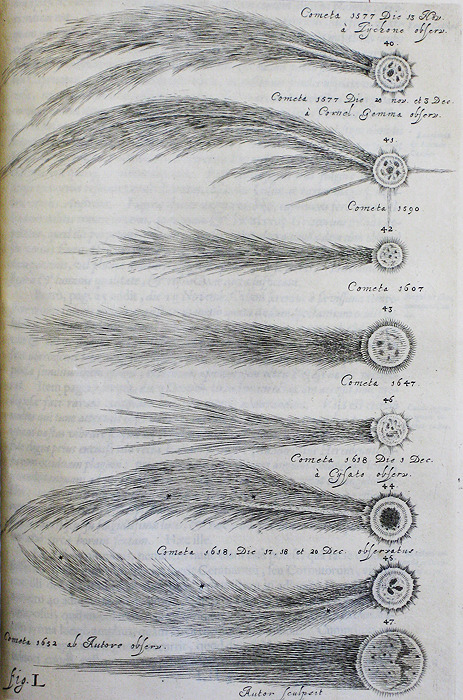
Johannes Hevelius, Cometographia (Danzig, 1668), Fig. L
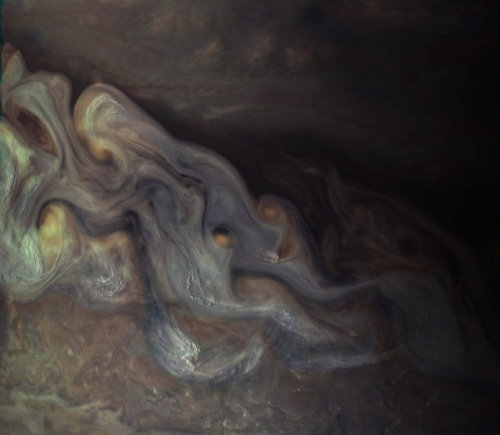

A close-up of an enhanced-color image of Jupiter’s clouds obtained by NASA’s Juno spacecraft.
NASA/SWRI/MSSS/Gerald Eichstädt/Seán Doran / New York Times
General Ham: CW Procedures/Abbreviations
Have I mentioned that the General Ham License Manual has a ton more information than the Technician manual? If I haven’t already, it’s true. It’s awesome.
So it’s a lot of work to spell out the full text of all words and phrases, so telegraphers developed an extensive set of abbreviations and procedural signals called prosigns. These are two letters sent together as a single character as indicated by an overbar. So the prosign AR is used to indicated “End of Message”.
And then there are abbreviations to shorten common words such as “AND” is “ES” and “GOING” is “GG” and “WEATHER” is “WX”.
Calling CQ on CW is about the same as on phone/voice. "DE" is an abbreviation used in place of “form” and the procedural signal K replaces “over”:
CQ CQ CQ DE W0TTV W0TTV W0TTV K
A response might look like the following:
W0TTV DE W1AW W1AW W1AW K
There’s no need to send the CQing station’s call more than once unless there’s interferences or the signal is weak. When signals are strong and clear, those responding to CQ may even just send their call once or twice.
Good idea is also to respond at the speed of the calling station but if you’re uncomfortable receiving at that speed, send the Q signal “QRS” (send slower) before the final K. Or if you want to go faster, QRQ.
Also adjust your transmitting frequency so that your signals is “zero beat” with the other signal so that you will be on the same frequency. This means the two signals produce the same audio tone in a receiver. Check the radio’s operating manual for instructions on how to zero beat another signal.
And once you’re in contact with another station, the prosign KN is used instead of K to prevent other stations from breaking in during the contact. It means “Only the station with whom I am in contact should respond”. When asked if you are ready to receive, “QRV” means “I’m ready to copy.” After receiving the message, “QSL” means "I acknowledge receipt.“
Then when it’s time to end the QSO, the prosign SK is used to let any listener know that the contact is completed: W1AW DE W0TTV SK and if you’re going off the air, add CL for closing station.
Phew!
@atdiy/@tymkrs
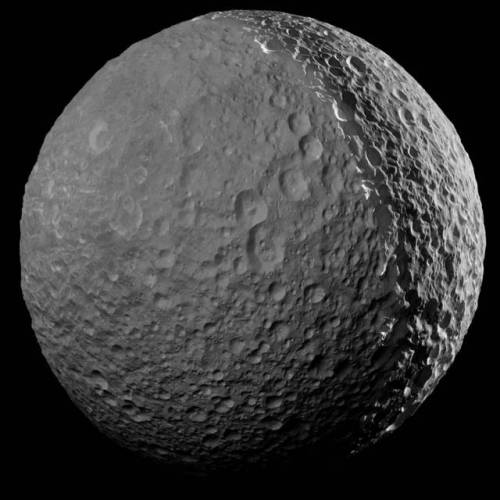



Cassini gets up close & personal with icy Mimas
The first two images show off the giant Herschel crater, a distinguishing feature of this moon. The second gives a better view of the mountain peak within the crater. The shadows cast by the crater and mountain peak give a glimpse into just how massive this crater truly is. The last image is one of the clearest images of Mimas to date.





For more on the Fermi Paradox and why alien life hasn’t found us yet. (Infographic via futurism)


NASA‘s Juno: spacecraft has successfully entered orbit around the gas giant Jupiter.
After five years and 1.7 billion miles the probe accomplish a risky braking manoeuvre in order for it to be hooked by Jupiter’s gravity. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California received the confirmation signal which confirmed Juno had finally entered orbit on July 4. Juno will begin a two-year mission of discovery which will help scientists better understand one of the largest objects in our solar system.
Using Juno’s complex array of cameras and sensors the team hope to answer some long-awaited questions including whether Jupiter actually has a solid core or if it really is just a swirling ball of gas. Another focus will be the Great Red Spot - a massive storm several times the size of Earth that has been raging on the surface of Jupiter for what appears to be hundreds of years. Juno is the fastest spacecraft to ever enter orbit around a planet, travelling at an astonishing 130,000mph by the time it reached the gas giant.
-
 kuroerinteira liked this · 6 years ago
kuroerinteira liked this · 6 years ago -
 eliana-hot24-blog liked this · 6 years ago
eliana-hot24-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 briny-space-explorer reblogged this · 6 years ago
briny-space-explorer reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 you-promised-me-the-world reblogged this · 6 years ago
you-promised-me-the-world reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 mrsjones1102 liked this · 6 years ago
mrsjones1102 liked this · 6 years ago -
 anabelledicapri liked this · 6 years ago
anabelledicapri liked this · 6 years ago -
 buzzingaround liked this · 6 years ago
buzzingaround liked this · 6 years ago -
 uneoeuvredartcatastrophique liked this · 6 years ago
uneoeuvredartcatastrophique liked this · 6 years ago -
 trez-lunas-blog liked this · 6 years ago
trez-lunas-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 starilyart liked this · 6 years ago
starilyart liked this · 6 years ago -
 universenerd1 liked this · 6 years ago
universenerd1 liked this · 6 years ago -
 novembermend liked this · 6 years ago
novembermend liked this · 6 years ago -
 electroinferno reblogged this · 6 years ago
electroinferno reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 electroinferno liked this · 6 years ago
electroinferno liked this · 6 years ago -
 cannibaldotcom liked this · 6 years ago
cannibaldotcom liked this · 6 years ago -
 swwan reblogged this · 7 years ago
swwan reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 swwan liked this · 7 years ago
swwan liked this · 7 years ago -
 tornike liked this · 7 years ago
tornike liked this · 7 years ago -
 hophorn reblogged this · 7 years ago
hophorn reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 blackberrycloud liked this · 7 years ago
blackberrycloud liked this · 7 years ago -
 donnytumbbear reblogged this · 7 years ago
donnytumbbear reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 donnytumbbear liked this · 7 years ago
donnytumbbear liked this · 7 years ago -
 doistillcare liked this · 7 years ago
doistillcare liked this · 7 years ago -
 stuttershock reblogged this · 7 years ago
stuttershock reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 nebraskadruid liked this · 7 years ago
nebraskadruid liked this · 7 years ago -
 horizondrifter liked this · 7 years ago
horizondrifter liked this · 7 years ago -
 audibleandvictorious reblogged this · 7 years ago
audibleandvictorious reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 nirobi1-blog liked this · 7 years ago
nirobi1-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 everybodyliesposts liked this · 7 years ago
everybodyliesposts liked this · 7 years ago -
 brettslagle liked this · 7 years ago
brettslagle liked this · 7 years ago -
 rain-in-the-slums liked this · 7 years ago
rain-in-the-slums liked this · 7 years ago -
 kvmilvhhvreth liked this · 7 years ago
kvmilvhhvreth liked this · 7 years ago -
 aliencatus-blog liked this · 8 years ago
aliencatus-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 valeria-16-06-04-blog liked this · 8 years ago
valeria-16-06-04-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 gothgirlclik liked this · 8 years ago
gothgirlclik liked this · 8 years ago -
 jewelvocado liked this · 8 years ago
jewelvocado liked this · 8 years ago -
 starlovely liked this · 8 years ago
starlovely liked this · 8 years ago -
 poetoftheshadow-and-knight-mer liked this · 8 years ago
poetoftheshadow-and-knight-mer liked this · 8 years ago -
 space-photos reblogged this · 8 years ago
space-photos reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 silvertrees liked this · 8 years ago
silvertrees liked this · 8 years ago