One Step Closer To The Moon With The Artemis Program! 🌙
One Step Closer to the Moon with the Artemis Program! 🌙

The past couple of weeks have been packed with milestones for our Artemis program — the program that will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon!

Artemis I will be an integrated, uncrewed test of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System (SLS) rocket before we send crewed flights to the Moon.

On March 2, 2021, we completed stacking the twin SLS solid rocket boosters for the Artemis I mission. Over several weeks, workers with NASA's Exploration Ground Systems used one of five massive cranes to place 10 booster segments and nose assemblies on the mobile launcher inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida.
On March 18, 2021, we completed our Green Run hot fire test for the SLS core stage at Stennis Space Center in Mississippi. The core stage includes the flight computers, four RS-25 engines, and enormous propellant tanks that hold more than 700,000 gallons of super cold propellant. The test successfully ignited the core stage and produced 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The next time the core stage lights up will be when Artemis I launches on its mission to the Moon!

In coming days, engineers will examine the data and determine if the stage is ready to be refurbished, prepared for shipment, and delivered to KSC where it will be integrated with the twin solid rocket boosters and the other rocket elements.
We are a couple steps closer to landing boots on the Moon!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Sergioballester-blog and Others
Going the Distance... In Space
On April 17, NASA's New Horizons crossed a rare deep-space milestone – 50 astronomical units from the Sun, or 50 times farther from the Sun than Earth is. New Horizons is just the fifth spacecraft to reach this great distance, following the legendary Voyagers 1 and 2 and Pioneers 10 and 11. It’s almost 5 billion miles (7.5 billion kilometers) away; a remote region where a signal radioed from NASA's largest antennas on Earth, even traveling at the speed of light, needs seven hours to reach the far-flung spacecraft.
To celebrate reaching 50 AU, the New Horizons team compiled a list of 50 facts about the mission. Here are just a few of them; you'll find the full collection at: http://pluto.jhuapl.edu/News-Center/Fifty-Facts.php.

New Horizons is the first – and so far, only – spacecraft to visit Pluto. New Horizons sped through the Pluto system on July 14, 2015, providing a history-making close-up view of the dwarf planet and its family of five moons.
New Horizons is carrying some of the ashes of Pluto’s discoverer, Clyde Tombaugh. In 1930, the amateur astronomer spotted Pluto in a series of telescope images at Lowell Observatory in Arizona, making him the first American to discover a planet.

The “Pluto Not Yet Explored” U.S. stamp that New Horizons carries holds the Guinness World Record for the farthest traveled postage stamp. The stamp was part of a series created in 1991, when Pluto was the last unexplored planet in the solar system.

Dispatched at 36,400 miles per hour (58, 500 kilometers per hour) on January 19, 2006, New Horizons is still the fastest human-made object ever launched from Earth.
As the spacecraft flew by Jupiter’s moon Io, in February 2007, New Horizons captured the first detailed movie of a volcano erupting anywhere in the solar system except Earth.

New Horizons’ radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) – its nuclear battery – will provide enough power to keep the spacecraft operating until the late-2030s.

Measurements of the universe’s darkness using New Horizons data found that the universe is twice as bright as predicted – a major extragalactic astronomy discovery!

New Horizons’ Venetia Burney Student Dust Counter is the first student-built instrument on any NASA planetary mission – and is providing unprecedented insight into the dust environment in the outer solar system.

New Horizons is so far away, that even the positons of the stars look different than what we see from Earth. This view of an "alien sky" allowed scientists to make stereo images of the nearest stars against the background of the galaxy.

Arrokoth – the official name the mission team proposed for the Kuiper Belt object New Horizons explored in January 2019 – is a Native American term that means “sky” in the Powhatan/Algonquin language.

Stay tuned in to the latest New Horizons updates on the mission website and follow NASA Solar System on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
This impressive storm captured by Geoff Green over West Australia in August 2018, gives you an idea of the huge frequency at which lightning happen in an extreme weather event
Instagram: wonders_of_the_cosmos
Perseverance: Amazing descent & landing video taken by the rover’s EDL cameras.










Jupiter Descending
Download Software Used to Get Rovers to the Red Planet
Watching our Perseverance rover safely land on the surface of Mars is the kind of historic feat that gets our adventure-loving hearts racing.

Launching and landing rovers on Mars requires overcoming challenges like defying gravity on two planets, surviving the extreme heat of atmospheric entry, and avoiding rocky obstacles. This takes more than just rocket science – it takes incredible software too.
Did you know that some of the same tried and tested software that helped ensure a safe arrival for Perseverance (and its predecessor, Curiosity) can be downloaded – by you...for free...right now?

Our 2021-22 Software Catalog is full of codes made for space that can be used by entrepreneurs, teachers, gamers, or just about anyone. Whether you are curious about the Martian atmosphere, want to visualize the inside of a volcano, or have an application we’ve never even considered, our software may be able to help. Check out our full site, updated regularly with the latest codes available for download.
Here are a few examples of what you could do with our software!
1. Simulate the Martian atmosphere to prepare spacecrafts for landing

To prepare for exactly what a spacecraft will face on landing day, no matter the location scientists choose, we created software that simulates the Martian atmosphere. The code, Mars (GRAM), is now available to anyone.
We also have a version that simulates Earth's atmosphere, allowing users (especially those in the world of drone design) a way to replicate and design for, potentially dangerous conditions without ever stepping away from the computer.
2. Explore the Red Planet virtually from home with help from the Curiosity rover team
Originally developed for scientists and engineers working on the Curiosity rover mission, OnSight allowed the team a virtual way to walk on and look around Mars. Using an immersive display, such as a virtual reality headset, scientists could see the Red Planet the way a rover would.
This software can also be used to provide virtual experiences of places here on Earth, such as caves and lava fields.
3. Dodge disasters with a risk management tool made for space missions

When preparing for complex space missions, like the upcoming Mars Sample Return mission, it’s crucial to examine how different elements, independently and collectively, impact the probability of success.
But risk management has become an important tool for businesses of all disciplines, from engineering to accounting – and the Space Mission Architecture and Risk Analysis Tool (SMART) could help.
Sound interesting? The NASA software catalog has these and more than 800 additional codes ready for download.
You can also follow our Technology Transfer program on Twitter to learn more about software and technology that can be put to use on Earth.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
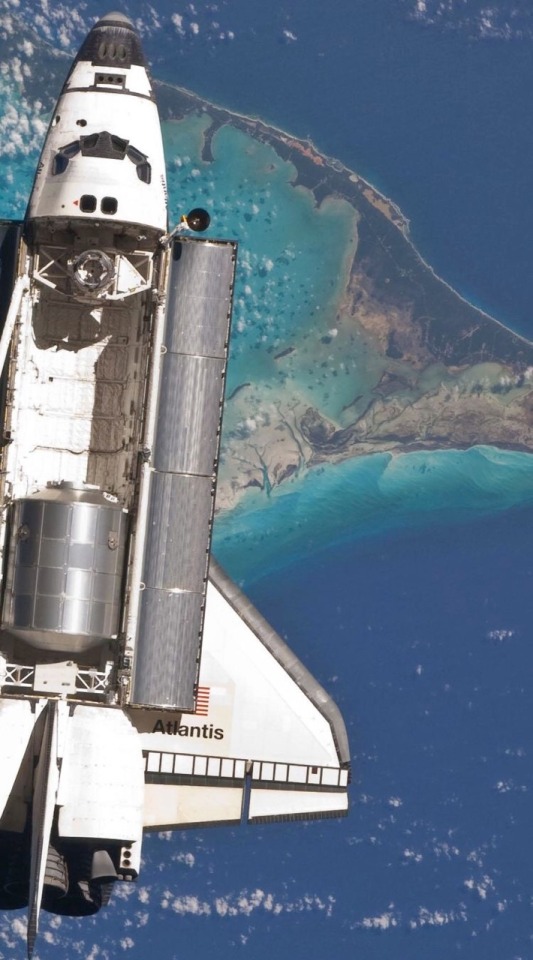

Shuttle Atlantis over the Bahamas. 🚀
The first palaeontologist on Mars

(Image: Artist’s impression of NASA’s Perseverance rover on Mars)
Today NASA’s Perseverance rover landed on Mars. I don’t usually talk astronomy on this blog, but this time it’s relevant because—as you might have read—Perseverance is more or less the first palaeontologist on Mars!
Let me explain.

(Image: Satellite topography map of Jezero Crater, the site where Perseverance landed)
The site where Perseverance is landing, Jezero Crater, is a meteor impact crater near Mars’s Equator (say that 10 times fast!). It has evidence of a delta—the geomorphic feature that occurs when running water enters a large body of water. Orbital analyses also suggest it’s filled with carbonate rock—the kind that tend to deposit at the bottom of bodies of water.
Jezero Crater is not filled with water today. But the evidence strongly suggests it once was. If we’re going to find evidence of life on Mars, this is a good place to start looking.
Microbial fossils
When you think of fossils, most people think of giant T. rex skeletons, or frozen woolly mammoths, or neanderthal skulls. Maybe you’ve been around the block a bit, and you think about corals, or plant fossils, or tiny fossil shells. But some of the most common and important fossils on Earth are even tinier. Microbial fossils are commonly made by bacteria, archaea, and the like.

(Image: A cross-section of a stromatolite fossil, showing the multiple layers)
Some of the earliest fossils on earth are called stromatolites. They occur when bacterial colonies grow together in a mat—then, over time, sediment deposits over the colony, and the bacteria form another layer on top of the previous layer. Over time, many layers can be formed.

(Image: Helium Ion Microscopy image of iron oxide filaments formed by bacteria)
Although we breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide, many microbes are not quite so restricted, and can breathe anything from sulphur to iron to methane or ammonia. When they do this, they often leave behind solid waste products, such as the above iron oxide filaments, that give away their presence. We can tell these apart from normal minerals in a number of ways, including by the relative proportions of different isotopes in them.

(Image: Schematic digram showing how molecular fossils form and are studied)
However, some of the most important fossils are molecular fossils. Living organisms produce a variety of different organic molecules; even long after the bodies of these organisms decay, those molecules can stay behind in an altered form for millions or even billions of years. If we’re looking for evidence of life on Mars, this might be our best bet.
Enter Perseverance

(Image: Diagram of Perseverance rover showing different instruments)
The Perseverance rover is overall similar in design to the Curiosity rover that landed in 2012, but there are some key differences—and most relevant here is that it’s a geological powerhouse. It’s got a number of instruments designed to carry out detailed geologic investigations:
RIMFAX is a ground-penetrating Radar unit. Like normal Radar, it works by sending radio waves into the ground; different materials affect the radio waves differently, as do transitions between different materials. This will allow us to, for the first time, study the geology of Mars below the surface to get an idea of what has been going on down there.

(Image: This is the kind of result produced by ground-penetrating radar—a rough image of the stratigraphy below the surface.)
PIXL (Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry) shoots x-rays at samples and examines how they fluoresce in reaction. This allows for the detection of the elemental composition of a sample—helping us better understand the geology of the area, and potentially detect signatures of life.
SuperCam is a multi-function laser spectrometer that uses four different spectroscopy methods to examine the composition of samples. They all work in similar ways—essentially, different molecules react to laser stimulation differently, and different amounts of energy are required to make different molecules vibrate. The way that these molecules react can help us identify their composition, and the hope is that this may allow us to detect molecular fossils (these methods allow us to detect molecular fossils on Earth!)
SHERLOC (Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals) is another spectroscopic instrument—this one, however, is more precise, and optimised for detecting trace biosignatures in samples. It works similar to the above, using an ultraviolet laser to scan a 7 × 7 mm zone for evidence of organic compounds.
In addition to studying samples in situ, Perseverance will package small samples and leave them behind on Mars. A planned future mission will collect these packaged samples and launch them into space, where an orbiter will collect them and—hopefully—return them to Earth. This would be the first time that samples have ever been recovered from Mars, and would go a long way in increasing our understanding of the Martian environment and geology.
There’s no way of knowing yet what Perseverance will find—but even the fact that a robot palaeontologist is on Mars is incredibly exciting. Here’s to many years of discovery!

Ocean on the moon Europa
Scientists' consensus is that a layer of liquid water exists beneath Europa's surface, and that heat from tidal flexing allows the subsurface ocean to remain liquid.

Europa's surface temperature averages about 110 K (−160 °C; −260 °F) at the equator and only 50 K (−220 °C; −370 °F) at the poles, keeping Europa's icy crust as hard as granite. The first hints of a subsurface ocean came from theoretical considerations of tidal heating (a consequence of Europa's slightly eccentric orbit and orbital resonance with the other Galilean moons). Galileo imaging team members argue for the existence of a subsurface ocean from analysis of Voyager and Galileo images.

The most dramatic example is "chaos terrain", a common feature on Europa's surface that some interpret as a region where the subsurface ocean has melted through the icy crust.
The thin-ice model suggests that Europa's ice shell may be only a few kilometers thick. However, most planetary scientists conclude that this model considers only those topmost layers of Europa's crust that behave elastically when affected by Jupiter's tides.

The Hubble Space Telescope acquired an image of Europa in 2012 that was interpreted to be a plume of water vapour erupting from near its south pole The image suggests the plume may be 200 km (120 mi) high, or more than 20 times the height of Mt. Everest.
Life?
So far, there is no evidence that life exists on Europa, but Europa has emerged as one of the most likely locations in the Solar System for potential habitability. Life could exist in its under-ice ocean, perhaps in an environment similar to Earth's deep-ocean hydrothermal vents. Even if Europa lacks volcanic hydrothermal activity, a 2016 NASA study found that Earth-like levels of hydrogen and oxygen could be produced through processes related to serpentinization and ice-derived oxidants, which do not directly involve volcanism.

In 2015, scientists announced that salt from a subsurface ocean may likely be coating some geological features on Europa, suggesting that the ocean is interacting with the seafloor. This may be important in determining if Europa could be habitable. The likely presence of liquid water in contact with Europa's rocky mantle has spurred calls to send a probe there.
Missions

Europa Clipper is an interplanetary mission in development by NASA comprising an orbiter. Set for a launch in October 2024, the spacecraft is being developed to study the Galilean moon Europa through a series of flybys while in orbit around Jupiter.

The Europa Lander is a proposed astrobiology mission concept by NASA to Europa, an icy moon of Jupiter. If funded and developed as a large strategic science mission, it would be launched in 2027 to complement the studies by the Europa Clipper orbiter mission and perform analyses on site. NASA's budget for fiscal year 2021 neither mandates nor allocates any funds to the mission leaving its future uncertain.
The objectives of the mission are to search for biosignatures at the subsurface ≈10 cm, to characterize the composition of non-ice near-subsurface material, and determine the proximity of liquid water and recently erupted material near the lander's location.
source




jupiter

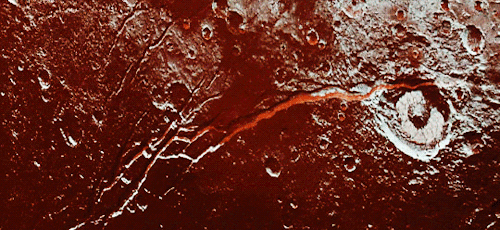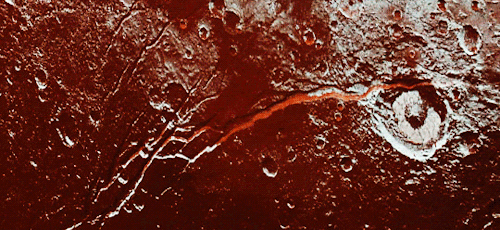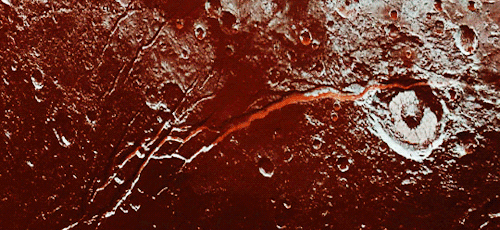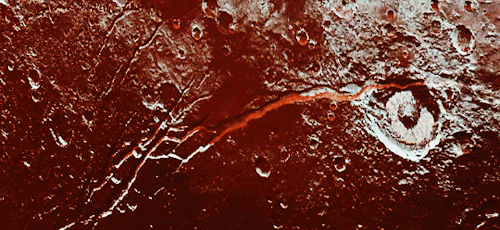

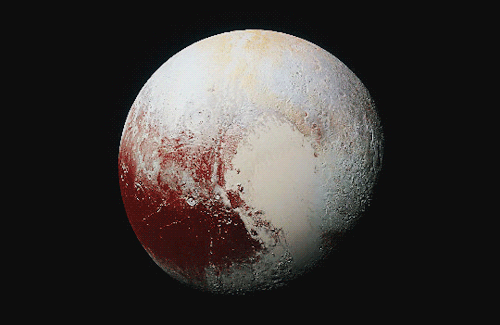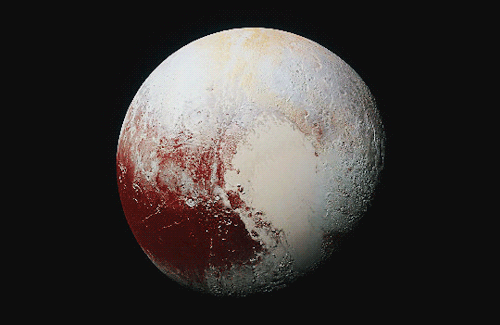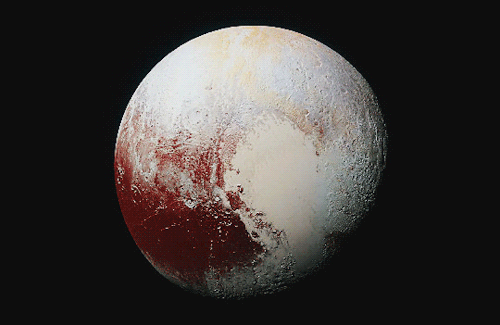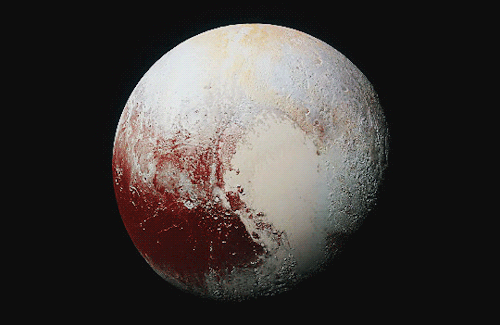


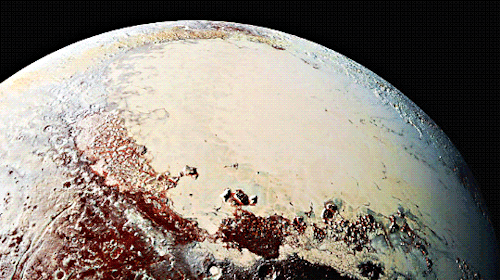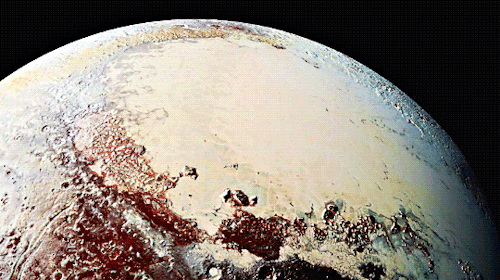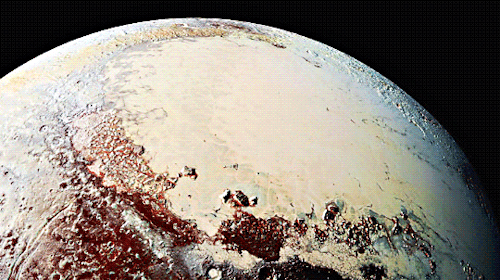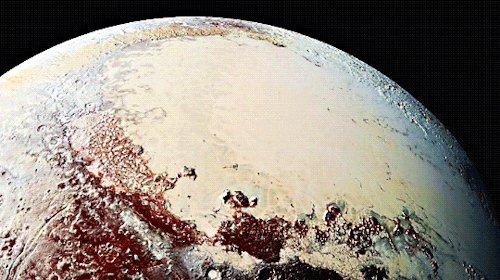



Pluto as seen from NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft ; Its heart-shaped sea is filled with poisonous ice.
-
 pendragyn reblogged this · 1 year ago
pendragyn reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 loudninstant liked this · 2 years ago
loudninstant liked this · 2 years ago -
 13-orbit liked this · 3 years ago
13-orbit liked this · 3 years ago -
 ownervirgin reblogged this · 3 years ago
ownervirgin reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 0rions-belt liked this · 3 years ago
0rions-belt liked this · 3 years ago -
 dclaure-blog1 liked this · 3 years ago
dclaure-blog1 liked this · 3 years ago -
 mrclaw61 liked this · 3 years ago
mrclaw61 liked this · 3 years ago -
 peopleessay liked this · 4 years ago
peopleessay liked this · 4 years ago -
 fuckingkissinger liked this · 4 years ago
fuckingkissinger liked this · 4 years ago -
 candyland20bp1 liked this · 4 years ago
candyland20bp1 liked this · 4 years ago -
 writernotyetauthor liked this · 4 years ago
writernotyetauthor liked this · 4 years ago -
 pinkiepieaddict reblogged this · 4 years ago
pinkiepieaddict reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 aestesianobilis reblogged this · 4 years ago
aestesianobilis reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 aestesianobilis liked this · 4 years ago
aestesianobilis liked this · 4 years ago -
 aestheticaadvent reblogged this · 4 years ago
aestheticaadvent reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 aestheticaadvent liked this · 4 years ago
aestheticaadvent liked this · 4 years ago -
 anthigua liked this · 4 years ago
anthigua liked this · 4 years ago -
 ellatheneonlight liked this · 4 years ago
ellatheneonlight liked this · 4 years ago -
 shybirdstuff liked this · 4 years ago
shybirdstuff liked this · 4 years ago -
 abbey67road liked this · 4 years ago
abbey67road liked this · 4 years ago -
 catyuy reblogged this · 4 years ago
catyuy reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 cconfusion liked this · 4 years ago
cconfusion liked this · 4 years ago -
 keyvawn liked this · 4 years ago
keyvawn liked this · 4 years ago -
 pressuredrightnow reblogged this · 4 years ago
pressuredrightnow reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 dragonfly-wings1 liked this · 4 years ago
dragonfly-wings1 liked this · 4 years ago -
 save-the-witch reblogged this · 4 years ago
save-the-witch reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 save-the-witch liked this · 4 years ago
save-the-witch liked this · 4 years ago -
 catyuy liked this · 4 years ago
catyuy liked this · 4 years ago -
 darthmelyanna reblogged this · 4 years ago
darthmelyanna reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 thegoddessawakening liked this · 4 years ago
thegoddessawakening liked this · 4 years ago -
 den1990 reblogged this · 4 years ago
den1990 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 shadow-king-club liked this · 4 years ago
shadow-king-club liked this · 4 years ago -
 soleilcentauri liked this · 4 years ago
soleilcentauri liked this · 4 years ago -
 aki213-blog liked this · 4 years ago
aki213-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 popcorn8784 liked this · 4 years ago
popcorn8784 liked this · 4 years ago -
 fay-the-ghost liked this · 4 years ago
fay-the-ghost liked this · 4 years ago -
 pxevx reblogged this · 4 years ago
pxevx reblogged this · 4 years ago