The Moon With The ISS Transitioning In Front Of It. Amazing View Considering The ISS Moves Over And

The Moon with the ISS transitioning in front of it. Amazing view considering the ISS moves over and past it in a matter of seconds.
More Posts from Sergioballester-blog and Others
Mars Helicopter: 6 Things to Know About Ingenuity

When our Perseverance Mars rover lands on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021, it will bring along the Ingenuity helicopter.
This small-but-mighty craft is a technology demonstration that will attempt the first powered, controlled flight on another planet. Its fuselage is about the size of a tissue box, and it weighs about 4 pounds (1.8 kg) on Earth. It started out six years ago as an implausible prospect and has now passed its Earthbound tests.
Here are six things to know about Ingenuity as it nears Mars:
1. Ingenuity is an experimental flight test.

This Mars helicopter is known as a technology demonstration, which is a project that aims to test a new capability for the first time with a limited scope. Previous technology demonstrations include Sojourner, the first Mars rover, and the Mars Cube One (MarCO) CubeStats that flew by Mars.
Ingenuity does not carry any science instruments and is not part of Perseverance’s science mission. The only objective for this helicopter is an engineering one – to demonstrate rotorcraft flight in the thin and challenging Martian atmosphere.
2. Mars won’t make it easy for Ingenuity.

Mars’ atmosphere is around 1% the density of Earth’s. Because of that lack of density, Ingenuity has rotor blades that are much larger and spin faster than a helicopter of Ingenuity’s mass here on our planet. It also must be extremely light to travel to Mars.
The Red Planet also has incredibly cold temperatures, with nights reaching minus 130 degrees Fahrenheit (-90 degrees Celsius) in Jezero Crater, where our rover and helicopter will land. Tests on Earth at the predicted temperatures indicate Ingenuity’s parts should work as designed, but the real test will be on Mars.
3. Ingenuity relies on Perseverance for safe passage to Mars and operations on the Martian surface.

Ingenuity is nestled sideways under Perseverance’s belly with a cover to protect the helicopter from debris during landing. The power system on the Mars 2020 spacecraft periodically charges Ingenuity’s batteries during the journey to the Red Planet.
In the first few months after landing, Perseverance will find a safe place for Ingenuity. Our rover will shed the landing cover, rotate the helicopter so its legs face the ground and gently drop it on the Martian surface.
4. Ingenuity is smart for a small robot.

NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory will not be able to control the helicopter with a joystick due to delays communicating with spacecraft across interplanetary distances. That means Ingenuity will make some of its own decisions based on parameters set by its engineering team on Earth.
During flight, Ingenuity will analyze sensor data and images of the terrain to ensure it stays on a flight path designed by project engineers.
5. The Ingenuity team counts success one step at a time.

Ingenuity’s team has a long list of milestones the helicopter must pass before it can take off and land in the Martian atmosphere.
Surviving the journey to and landing on Mars
Safely deploying onto the Martian surface from Perseverance’s belly
Autonomously keeping warm through those intensely cold Martian nights
Autonomously charging itself with its solar panel
Successfully communicating to and from the helicopter via the Mars Helicopter Base Station on Perseverance
6. If Ingenuity succeeds, future Mars exploration could include an ambitious aerial dimension.

The Mars helicopter intends to demonstrate technologies and first-of-its-kind operations needed for flying on Mars. If successful, these technologies and flight experience on another planet could pave the way for other advanced robotic flying vehicles.
Possible uses of a future helicopter on Mars include:
A unique viewpoint not provided by current orbiters, rovers or landers
High-definition images and reconnaissance for robots or humans
Access to terrain that is difficult for rovers to reach
Could even carry light but vital payloads from one site to another
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com


Orion Capsule interior. 🚀

It was time for their close-up. Two days ago Jupiter and Saturn passed a tenth of a degree from each other in what is known a Great Conjunction. Although the two planets pass each other on the sky every 20 years, this was the closest pass in nearly four centuries. Taken early in day of the Great Conjunction, the featured multiple-exposure combination captures not only both giant planets in a single frame, but also Jupiter's four largest moons (left to right) Callisto, Ganymede, Io, and Europa -- and Saturn's largest moon Titan.
Image Credit: Damian Peach
Download Software Used to Get Rovers to the Red Planet
Watching our Perseverance rover safely land on the surface of Mars is the kind of historic feat that gets our adventure-loving hearts racing.

Launching and landing rovers on Mars requires overcoming challenges like defying gravity on two planets, surviving the extreme heat of atmospheric entry, and avoiding rocky obstacles. This takes more than just rocket science – it takes incredible software too.
Did you know that some of the same tried and tested software that helped ensure a safe arrival for Perseverance (and its predecessor, Curiosity) can be downloaded – by you...for free...right now?

Our 2021-22 Software Catalog is full of codes made for space that can be used by entrepreneurs, teachers, gamers, or just about anyone. Whether you are curious about the Martian atmosphere, want to visualize the inside of a volcano, or have an application we’ve never even considered, our software may be able to help. Check out our full site, updated regularly with the latest codes available for download.
Here are a few examples of what you could do with our software!
1. Simulate the Martian atmosphere to prepare spacecrafts for landing

To prepare for exactly what a spacecraft will face on landing day, no matter the location scientists choose, we created software that simulates the Martian atmosphere. The code, Mars (GRAM), is now available to anyone.
We also have a version that simulates Earth's atmosphere, allowing users (especially those in the world of drone design) a way to replicate and design for, potentially dangerous conditions without ever stepping away from the computer.
2. Explore the Red Planet virtually from home with help from the Curiosity rover team
Originally developed for scientists and engineers working on the Curiosity rover mission, OnSight allowed the team a virtual way to walk on and look around Mars. Using an immersive display, such as a virtual reality headset, scientists could see the Red Planet the way a rover would.
This software can also be used to provide virtual experiences of places here on Earth, such as caves and lava fields.
3. Dodge disasters with a risk management tool made for space missions

When preparing for complex space missions, like the upcoming Mars Sample Return mission, it’s crucial to examine how different elements, independently and collectively, impact the probability of success.
But risk management has become an important tool for businesses of all disciplines, from engineering to accounting – and the Space Mission Architecture and Risk Analysis Tool (SMART) could help.
Sound interesting? The NASA software catalog has these and more than 800 additional codes ready for download.
You can also follow our Technology Transfer program on Twitter to learn more about software and technology that can be put to use on Earth.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

Arthur Strengthens, Moves Northward by NASA Goddard Photo and Video

An animation of Jupiter and Io by Nevan

Amazing Space Shuttle Shot. 🚀

Welcome to Mars, Percy!
February 18, 2021 - @nasa successfully landed its new robotic rover ‘Perseverance’ on Mars, a mission to directly study if there was ever life on the planet.

Cassini Spacecraft: Top Discoveries
Our Cassini spacecraft has been exploring Saturn, its stunning rings and its strange and beautiful moons for more than a decade.

Having expended almost every bit of the rocket propellant it carried to Saturn, operators are deliberately plunging Cassini into the planet to ensure Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration – in particular, the ice-covered, ocean-bearing moon Enceladus, but also Titan, with its intriguing pre-biotic chemistry.
Let’s take a look back at some of Cassini’s top discoveries:
Titan

Under its shroud of haze, Saturn’s planet-sized moon Titan hides dunes, mountains of water ice and rivers and seas of liquid methane. Of the hundreds of moons in our solar system, Titan is the only one with a dense atmosphere and large liquid reservoirs on its surface, making it in some ways more like a terrestrial planet.

Both Earth and Titan have nitrogen-dominated atmospheres – over 95% nitrogen in Titan’s case. However, unlike Earth, Titan has very little oxygen; the rest of the atmosphere is mostly methane and traced amounts of other gases, including ethane.

There are three large seas, all located close to the moon’s north pole, surrounded by numerous smaller lakes in the northern hemisphere. Just one large lake has been found in the southern hemisphere.
Enceladus

The moon Enceladus conceals a global ocean of salty liquid water beneath its icy surface. Some of that water even shoots out into space, creating an immense plume!

For decades, scientists didn’t know why Enceladus was the brightest world in the solar system, or how it related to Saturn’s E ring. Cassini found that both the fresh coating on its surface, and icy material in the E ring originate from vents connected to a global subsurface saltwater ocean that might host hydrothermal vents.

With its global ocean, unique chemistry and internal heat, Enceladus has become a promising lead in our search for worlds where life could exist.
Iapetus

Saturn’s two-toned moon Iapetus gets its odd coloring from reddish dust in its orbital path that is swept up and lands on the leading face of the moon.

The most unique, and perhaps most remarkable feature discovered on Iapetus in Cassini images is a topographic ridge that coincides almost exactly with the geographic equator. The physical origin of the ridge has yet to be explained…

It is not yet year whether the ridge is a mountain belt that has folded upward, or an extensional crack in the surface through which material from inside Iapetus erupted onto the surface and accumulated locally.
Saturn’s Rings

Saturn’s rings are made of countless particles of ice and dust, which Saturn’s moons push and tug, creating gaps and waves.

Scientists have never before studied the size, temperature, composition and distribution of Saturn’s rings from Saturn obit. Cassini has captured extraordinary ring-moon interactions, observed the lowest ring-temperature ever recorded at Saturn, discovered that the moon Enceladus is the source for Saturn’s E ring, and viewed the rings at equinox when sunlight strikes the rings edge-on, revealing never-before-seen ring features and details.
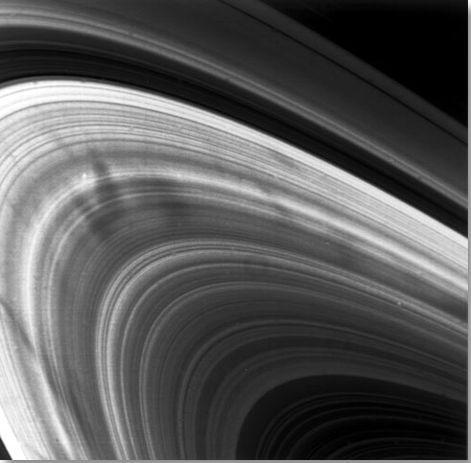
Cassini also studied features in Saturn’s rings called “spokes,” which can be longer than the diameter of Earth. Scientists think they’re made of thin icy particles that are lifted by an electrostatic charge and only last a few hours.
Auroras

The powerful magnetic field that permeates Saturn is strange because it lines up with the planet’s poles. But just like Earth’s field, it all creates shimmering auroras.

Auroras on Saturn occur in a process similar to Earth’s northern and southern lights. Particles from the solar wind are channeled by Saturn’s magnetic field toward the planet’s poles, where they interact with electrically charged gas (plasma) in the upper atmosphere and emit light.
Turbulent Atmosphere

Saturn’s turbulent atmosphere churns with immense storms and a striking, six-sided jet stream near its north pole.

Saturn’s north and south poles are also each beautifully (and violently) decorated by a colossal swirling storm. Cassini got an up-close look at the north polar storm and scientists found that the storm’s eye was about 50 times wider than an Earth hurricane’s eye.

Unlike the Earth hurricanes that are driven by warm ocean waters, Saturn’s polar vortexes aren’t actually hurricanes. They’re hurricane-like though, and even contain lightning. Cassini’s instruments have ‘heard’ lightning ever since entering Saturn orbit in 2004, in the form of radio waves. But it wasn’t until 2009 that Cassini’s cameras captured images of Saturnian lighting for the first time.

Cassini scientists assembled a short video of it, the first video of lightning discharging on a planet other than Earth.

Cassini’s adventure will end soon because it’s almost out of fuel. So to avoid possibly ever contaminating moons like Enceladus or Titan, on Sept. 15 it will intentionally dive into Saturn’s atmosphere.

The spacecraft is expected to lose radio contact with Earth within about one to two minutes after beginning its decent into Saturn’s upper atmosphere. But on the way down, before contact is lost, eight of Cassini’s 12 science instruments will be operating! More details on the spacecraft’s final decent can be found HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 wachsurfer2018 liked this · 4 years ago
wachsurfer2018 liked this · 4 years ago -
 dopestatesmangardenprofesso-blog liked this · 4 years ago
dopestatesmangardenprofesso-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 sergioballester-blog reblogged this · 4 years ago
sergioballester-blog reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 sergioballester-blog liked this · 4 years ago
sergioballester-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 john2267 liked this · 4 years ago
john2267 liked this · 4 years ago -
 shinigamiamaya liked this · 4 years ago
shinigamiamaya liked this · 4 years ago -
 16fahri liked this · 6 years ago
16fahri liked this · 6 years ago -
 6mostlynaturals9 liked this · 6 years ago
6mostlynaturals9 liked this · 6 years ago -
 mcain1813 liked this · 6 years ago
mcain1813 liked this · 6 years ago -
 notisaidthechicken liked this · 6 years ago
notisaidthechicken liked this · 6 years ago -
 yisnin liked this · 6 years ago
yisnin liked this · 6 years ago -
 metalzoic liked this · 6 years ago
metalzoic liked this · 6 years ago -
 jeebssred liked this · 6 years ago
jeebssred liked this · 6 years ago -
 fagdykefrank liked this · 6 years ago
fagdykefrank liked this · 6 years ago -
 sableshard liked this · 6 years ago
sableshard liked this · 6 years ago -
 on4theride liked this · 6 years ago
on4theride liked this · 6 years ago -
 zaffrefennec liked this · 6 years ago
zaffrefennec liked this · 6 years ago -
 oorts-and-clouds reblogged this · 6 years ago
oorts-and-clouds reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 knightpunk liked this · 6 years ago
knightpunk liked this · 6 years ago -
 dragonflames2061 liked this · 6 years ago
dragonflames2061 liked this · 6 years ago -
 alfonsomx liked this · 6 years ago
alfonsomx liked this · 6 years ago -
 hyunjinslongblackhair liked this · 6 years ago
hyunjinslongblackhair liked this · 6 years ago -
 brianmayislongaway reblogged this · 6 years ago
brianmayislongaway reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 brianmayislongaway liked this · 6 years ago
brianmayislongaway liked this · 6 years ago -
 dailymusemaniac liked this · 6 years ago
dailymusemaniac liked this · 6 years ago -
 smol-mermaid liked this · 6 years ago
smol-mermaid liked this · 6 years ago -
 transeliot reblogged this · 6 years ago
transeliot reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 deluision liked this · 6 years ago
deluision liked this · 6 years ago -
 too-tired-to-life liked this · 6 years ago
too-tired-to-life liked this · 6 years ago -
 watchergush55 liked this · 6 years ago
watchergush55 liked this · 6 years ago -
 the-fire-bubble reblogged this · 6 years ago
the-fire-bubble reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 the-fire-bubble liked this · 6 years ago
the-fire-bubble liked this · 6 years ago -
 alysettenymphaneth liked this · 6 years ago
alysettenymphaneth liked this · 6 years ago -
 milamaiart liked this · 6 years ago
milamaiart liked this · 6 years ago -
 ri-torno reblogged this · 6 years ago
ri-torno reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 mutato-nomine-music liked this · 6 years ago
mutato-nomine-music liked this · 6 years ago