Sergioballester-blog - Sin Título

More Posts from Sergioballester-blog and Others

Montage of Neptune and Triton by NASA on The Commons

Saturn by europeanspaceagency
Going the Distance... In Space
On April 17, NASA's New Horizons crossed a rare deep-space milestone – 50 astronomical units from the Sun, or 50 times farther from the Sun than Earth is. New Horizons is just the fifth spacecraft to reach this great distance, following the legendary Voyagers 1 and 2 and Pioneers 10 and 11. It’s almost 5 billion miles (7.5 billion kilometers) away; a remote region where a signal radioed from NASA's largest antennas on Earth, even traveling at the speed of light, needs seven hours to reach the far-flung spacecraft.
To celebrate reaching 50 AU, the New Horizons team compiled a list of 50 facts about the mission. Here are just a few of them; you'll find the full collection at: http://pluto.jhuapl.edu/News-Center/Fifty-Facts.php.

New Horizons is the first – and so far, only – spacecraft to visit Pluto. New Horizons sped through the Pluto system on July 14, 2015, providing a history-making close-up view of the dwarf planet and its family of five moons.
New Horizons is carrying some of the ashes of Pluto’s discoverer, Clyde Tombaugh. In 1930, the amateur astronomer spotted Pluto in a series of telescope images at Lowell Observatory in Arizona, making him the first American to discover a planet.

The “Pluto Not Yet Explored” U.S. stamp that New Horizons carries holds the Guinness World Record for the farthest traveled postage stamp. The stamp was part of a series created in 1991, when Pluto was the last unexplored planet in the solar system.

Dispatched at 36,400 miles per hour (58, 500 kilometers per hour) on January 19, 2006, New Horizons is still the fastest human-made object ever launched from Earth.
As the spacecraft flew by Jupiter’s moon Io, in February 2007, New Horizons captured the first detailed movie of a volcano erupting anywhere in the solar system except Earth.

New Horizons’ radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) – its nuclear battery – will provide enough power to keep the spacecraft operating until the late-2030s.

Measurements of the universe’s darkness using New Horizons data found that the universe is twice as bright as predicted – a major extragalactic astronomy discovery!

New Horizons’ Venetia Burney Student Dust Counter is the first student-built instrument on any NASA planetary mission – and is providing unprecedented insight into the dust environment in the outer solar system.

New Horizons is so far away, that even the positons of the stars look different than what we see from Earth. This view of an "alien sky" allowed scientists to make stereo images of the nearest stars against the background of the galaxy.

Arrokoth – the official name the mission team proposed for the Kuiper Belt object New Horizons explored in January 2019 – is a Native American term that means “sky” in the Powhatan/Algonquin language.

Stay tuned in to the latest New Horizons updates on the mission website and follow NASA Solar System on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Update your phones with our #CountdownToMars wallpapers, like this one, today: https://www.nasa.gov/feature/perseverance-mars-rover-wallpaper-images/
It's LANDING DAY for our Perseverance Mars Rover and her mission to search for ancient signs of life on the Red Planet!
Watch LIVE coverage today starting at 2:15pm ET (18:15 UTC):
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Landing Day for InSight by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center









The Planets (BBC) - Jupiter and Io
Download Software Used to Get Rovers to the Red Planet
Watching our Perseverance rover safely land on the surface of Mars is the kind of historic feat that gets our adventure-loving hearts racing.

Launching and landing rovers on Mars requires overcoming challenges like defying gravity on two planets, surviving the extreme heat of atmospheric entry, and avoiding rocky obstacles. This takes more than just rocket science – it takes incredible software too.
Did you know that some of the same tried and tested software that helped ensure a safe arrival for Perseverance (and its predecessor, Curiosity) can be downloaded – by you...for free...right now?

Our 2021-22 Software Catalog is full of codes made for space that can be used by entrepreneurs, teachers, gamers, or just about anyone. Whether you are curious about the Martian atmosphere, want to visualize the inside of a volcano, or have an application we’ve never even considered, our software may be able to help. Check out our full site, updated regularly with the latest codes available for download.
Here are a few examples of what you could do with our software!
1. Simulate the Martian atmosphere to prepare spacecrafts for landing

To prepare for exactly what a spacecraft will face on landing day, no matter the location scientists choose, we created software that simulates the Martian atmosphere. The code, Mars (GRAM), is now available to anyone.
We also have a version that simulates Earth's atmosphere, allowing users (especially those in the world of drone design) a way to replicate and design for, potentially dangerous conditions without ever stepping away from the computer.
2. Explore the Red Planet virtually from home with help from the Curiosity rover team
Originally developed for scientists and engineers working on the Curiosity rover mission, OnSight allowed the team a virtual way to walk on and look around Mars. Using an immersive display, such as a virtual reality headset, scientists could see the Red Planet the way a rover would.
This software can also be used to provide virtual experiences of places here on Earth, such as caves and lava fields.
3. Dodge disasters with a risk management tool made for space missions

When preparing for complex space missions, like the upcoming Mars Sample Return mission, it’s crucial to examine how different elements, independently and collectively, impact the probability of success.
But risk management has become an important tool for businesses of all disciplines, from engineering to accounting – and the Space Mission Architecture and Risk Analysis Tool (SMART) could help.
Sound interesting? The NASA software catalog has these and more than 800 additional codes ready for download.
You can also follow our Technology Transfer program on Twitter to learn more about software and technology that can be put to use on Earth.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

Shuttle Atlantis crew shot. 👨🏻🚀👩🏻🚀🚀
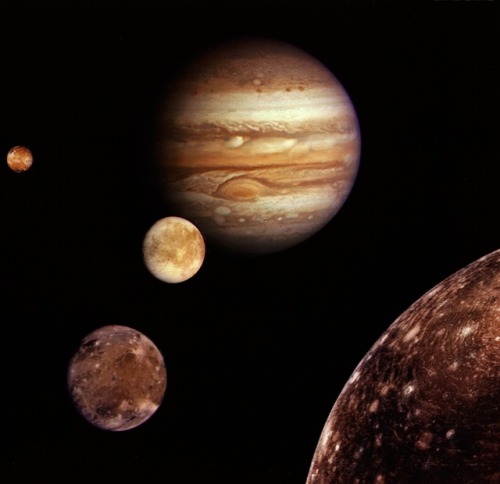
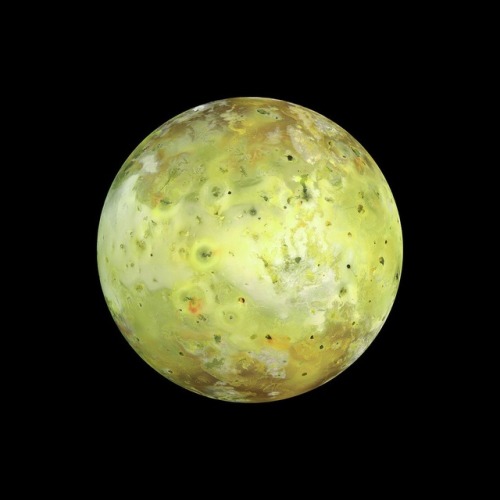
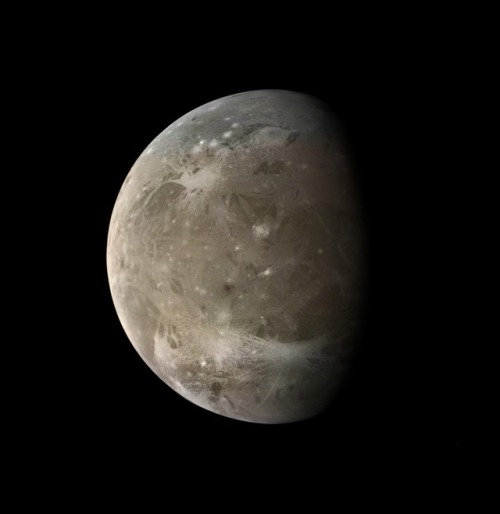
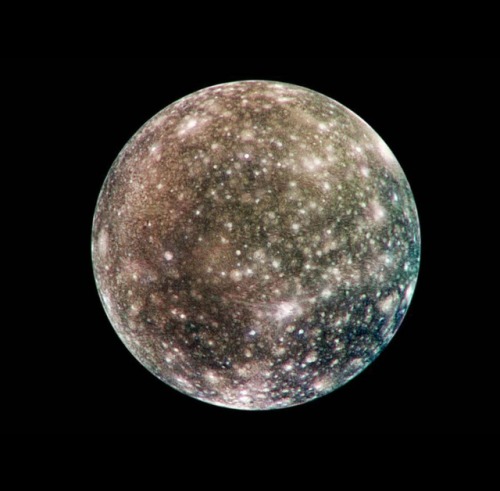


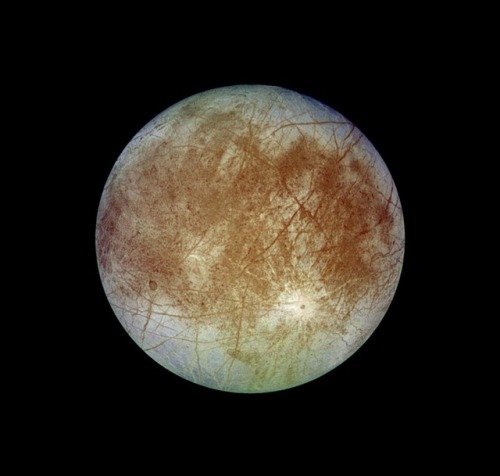


Galilean moons
The Galilean moons are the four largest moons of Jupiter — Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. They were first seen by Galileo Galilei in January 1610, and recognized by him as satellites of Jupiter in March 1610. They are the first objects found to orbit another planet. Their names derive from the lovers of Zeus. They are the first objects found to orbit another planet. Their names derive from the lovers of Zeus. They are among the largest objects in the Solar System with the exception of the Sun and the eight planets, with a radius larger than any of the dwarf planets.
Io is the fourth largest moon in the Solar System. With over 400 active volcanos, Io is the most geologically active object in the Solar System. Its surface is dotted with more than 100 mountains, some of which are taller than Earth’s Mount Everest. Unlike most satellites in the outer Solar System (which have a thick coating of ice), Io is primarily composed of silicate rock surrounding a molten iron or iron sulfide core. Although not proven, recent data from the Galileo orbiter indicate that Io might have its own magnetic field.
Europa the second of the four Galilean moons, is the second closest to Jupiter and the smallest at 3121.6 kilometers in diameter, which is slightly smaller than the Moon. The name comes from a mythical Phoenician noblewoman, Europa, who was courted by Zeus and became the queen of Crete, though the name did not become widely used until the mid-20th century. It has a smooth and bright surface, with a layer of water surrounding the mantle of the planet, thought to be 100 kilometers thick. The smooth surface includes a layer of ice, while the bottom of the ice is theorized to be liquid water. The apparent youth and smoothness of the surface have led to the hypothesis that a water ocean exists beneath it, which could conceivably serve as an abode for extraterrestrial life.
Ganymede is the largest moon in the Solar System, and is even bigger than the planet Mercury. It is the only satellite in the Solar System known to possess a magnetosphere, likely created through convection within the liquid iron core.
Callisto is the fourth and last Galilean moon, and is the second largest of the four, and at 4820.6 kilometers in diameter, it is the third largest moon in the Solar System, and barely smaller than Mercury, though only a third of the latter’s mass. It is named after the Greek mythological nymph Callisto, a lover of Zeus who was a daughter of the Arkadian King Lykaon and a hunting companion of the goddess Artemis. It is one of the most heavily cratered satellites in the Solar System, and one major feature is a basin around 3000 km wide called Valhalla.
source
image credit: NASA/JPL

by NASA’s Juno spacecraft.
-
 almalusasblog liked this · 3 years ago
almalusasblog liked this · 3 years ago -
 codinomecassius7 liked this · 4 years ago
codinomecassius7 liked this · 4 years ago -
 jernostrapig liked this · 4 years ago
jernostrapig liked this · 4 years ago -
 cowboymk69 liked this · 4 years ago
cowboymk69 liked this · 4 years ago -
 sergioballester-blog reblogged this · 4 years ago
sergioballester-blog reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 sergioballester-blog liked this · 4 years ago
sergioballester-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 roadking180 reblogged this · 4 years ago
roadking180 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 roadking180 liked this · 4 years ago
roadking180 liked this · 4 years ago -
 beca1959-stuff reblogged this · 4 years ago
beca1959-stuff reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 beca1959-stuff liked this · 4 years ago
beca1959-stuff liked this · 4 years ago -
 exploring2000 liked this · 4 years ago
exploring2000 liked this · 4 years ago -
 wachsurfer2018 liked this · 4 years ago
wachsurfer2018 liked this · 4 years ago -
 scienceandtechnologycompendium reblogged this · 5 years ago
scienceandtechnologycompendium reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 universallyhiphoplovelight liked this · 5 years ago
universallyhiphoplovelight liked this · 5 years ago -
 bitchilovemyfamily liked this · 5 years ago
bitchilovemyfamily liked this · 5 years ago -
 kryspychickin liked this · 5 years ago
kryspychickin liked this · 5 years ago -
 ashdudesworld reblogged this · 5 years ago
ashdudesworld reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ashdudesworld liked this · 5 years ago
ashdudesworld liked this · 5 years ago -
 cosmic-navel-gazin liked this · 5 years ago
cosmic-navel-gazin liked this · 5 years ago -
 di5app34r liked this · 5 years ago
di5app34r liked this · 5 years ago -
 tenebrobscuro reblogged this · 5 years ago
tenebrobscuro reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 tenebrobscuro liked this · 5 years ago
tenebrobscuro liked this · 5 years ago -
 wlfmn63 reblogged this · 5 years ago
wlfmn63 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 wlfmn63 liked this · 5 years ago
wlfmn63 liked this · 5 years ago -
 calmersoul reblogged this · 5 years ago
calmersoul reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 smilelilith liked this · 5 years ago
smilelilith liked this · 5 years ago -
 chronicallyrandom liked this · 5 years ago
chronicallyrandom liked this · 5 years ago -
 jsarzoza liked this · 5 years ago
jsarzoza liked this · 5 years ago -
 xxxpurplesz liked this · 5 years ago
xxxpurplesz liked this · 5 years ago -
 mv-world-wide liked this · 5 years ago
mv-world-wide liked this · 5 years ago -
 flasheande liked this · 5 years ago
flasheande liked this · 5 years ago -
 theghostofb reblogged this · 5 years ago
theghostofb reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 theghostofb liked this · 5 years ago
theghostofb liked this · 5 years ago -
 mellowunknowninternet liked this · 5 years ago
mellowunknowninternet liked this · 5 years ago -
 louseslayer liked this · 5 years ago
louseslayer liked this · 5 years ago -
 cicada-cicada liked this · 5 years ago
cicada-cicada liked this · 5 years ago -
 dininginthevoid reblogged this · 5 years ago
dininginthevoid reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 reddog1984 reblogged this · 5 years ago
reddog1984 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 cuckoldwanttobepnpcd liked this · 5 years ago
cuckoldwanttobepnpcd liked this · 5 years ago -
 mrstick39 liked this · 5 years ago
mrstick39 liked this · 5 years ago -
 anticrypt liked this · 5 years ago
anticrypt liked this · 5 years ago -
 catfatbitch liked this · 5 years ago
catfatbitch liked this · 5 years ago