Sean Bienvenidos, Japonistasarqueológicos, A Una Nueva Entrega De Arqueología Nipona, Una Vez Dicho



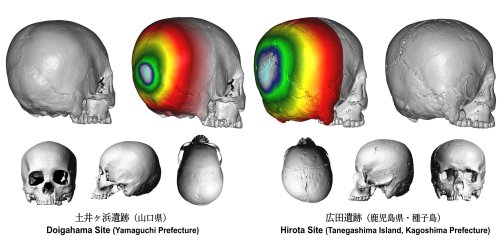
Sean bienvenidos, japonistasarqueológicos, a una nueva entrega de arqueología nipona, una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos qué empezamos. - En esta ocasión vamos a hablar, de cómo se deformaba el cráneo de forma antropogénica en el sitio arqueológico de Hirota en Tanegashima, localizado en la prefectura de Kagoshima. El yacimiento data del periodo yayoi 400 al 250 d.c - La deformación craneal ya se daba en muchas culturas de América, con motivos religiosos y sociales y posiblemente aquí podremos hallar el mismo caso similar o parecido, al ser un hallazgo reciente todavía faltan muchos estudios para ello. ¿Qué opinan ustedes al respecto? ¿Conocían este lugar? - En el caso de las culturas Americanas, le ponían cuerdas para alargar el cráneo¿Practicaban las mismas actividades? Quien sabe lo que nos depara el futuro, esta publicación está hecha con intenciones científica-divulgativa para transmitir conocimiento al mundo. - Espero que os guste y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones, que pasen una buena semana.
-
Welcome, Japanese archaeologists, to a new installment of Japanese archaeology, having said that, make yourself comfortable and let's start.
-
On this occasion we are going to talk about how the skull was deformed in an anthropogenic way in the archaeological site of Hirota in Tanegashima, located in the Kagoshima prefecture. The site dates from the Yayoi period 400 to 250 AD
-
Cranial deformation already occurred in many cultures in America, for religious and social reasons and possibly here we can find the same or similar case, as it is a recent finding, many studies are still missing for it. What do you think about it? Did you know this place? - In the case of American cultures, they used ropes to lengthen the skull. Did they practice the same activities? Who knows what the future holds for us, this publication is made with scientific-informative intentions to transmit knowledge to the world. - I hope you like it and see you in future publications, have a good week.Welcome, Japanese archaeologists, to a new installment of Japanese archaeology, having said that, make yourself comfortable and let's start.
-
On this occasion we are going to talk about how the skull was deformed in an anthropogenic way in the archaeological site of Hirota in Tanegashima, located in the Kagoshima prefecture. The site dates from the Yayoi period 400 to 250 AD
-
Cranial deformation already occurred in many cultures in America, for religious and social reasons and possibly here we can find the same or similar case, as it is a recent finding, many studies are still missing for it. What do you think about it? Did you know this place?
-
In the case of American cultures, they used ropes to lengthen the skull. Did they practice the same activities? Who knows what the future holds for us, this publication is made with scientific-informative intentions to transmit knowledge to the world. - I hope you like it and see you in future publications, have a good week.
-
日本の考古学者の皆さん、日本の考古学の新しい記事へようこそ。そうは言っても、気を楽にして始めましょう。
-
今回は、鹿児島県種子島の広田遺跡で、人為的に頭蓋骨がどのように変形されたのかについてお話します。この遺跡は、弥生時代、西暦 400 年から 250 年に遡ります。 頭蓋骨の変形は、宗教的および社会的理由により、アメリカの多くの文化ですでに発生しており、おそらくここでも同じまたは類似の症例が見つかる可能性があります。これは最近の発見であるため、多くの研究がまだ不足しています。あなたはそれについてどう思いますか?この場所を知っていましたか? - アメリカ文化の場合、頭蓋骨を伸ばすためにロープを使用していましたが、同じ活動を行っていたのでしょうか?私たちの将来がどうなるかは誰にもわかりませんが、この出版物は、知識を世界に伝えるという科学的有益な意図を持って作成されています。
-
気に入っていただければ幸いです。今後の出版物でお会いできることを願っています。良い一週間をお過ごしください
More Posts from Noticiasarquelogicasjaponesas and Others




Sean bienvenidos mis queridos fanáticosarqueológicos a una nueva entrega de prehistoria Japónesa en esta ocasión nos trasladamos a la pregunta ¿Cuándo se originó el sintoísmo?. - Aunque parezca raro es una religión que se conformo durante el periódo Jōmon (17.500-300), para ser exactos a finales de dicho período y continua hasta nuestros días los dioses del sintoísmo, se les llama Kamis ( dios) ya que para los japoneses todo tenía un dios las montañas, ríos. - El sintoísmo tiene influencias chinas, coreanas de hay que tenga similitudes con el taoísmo, ¿Qué dos libros recogen la categoría de los Kamis? Son el Kojiki(713d.c) y el Nihonshoki(720d.c). - Espero que os guste y nos vemos en una próxima públicacion un cordial saludo. 🇯🇵 私の愛する考古学ファンを日本の先史時代の新作に歓迎します。今回は、神道がいつ始まったのかという質問に移ります。 - 奇妙に思えるかもしれませんが、縄文時代(17500-300)に形成された宗教であり、正確にはその時代の終わりに、今日まで神道の神であり、カミス(神)と呼ばれています。 日本人にとって、山や川にはすべて神がいました。 - 神道は中国、韓国の影響を受けており、道教との類似点があります。 カミスのカテゴリーに分類される2冊の本は何ですか? こうじき(713d.c)と日本書紀(720d.c)です。 - よろしくお願いします。次の出版物で心からのご挨拶を申し上げます。 🇬🇧 Welcome my dear archaeological fans to a new installment of Japanese prehistory, this time we move to the question, when did Shintoism originate? - Although it may seem strange, it is a religion that was formed during the Jōmon period (17500-300), to be exact at the end of that period and continues to this day the gods of Shintoism, they are called Kamis (god) since for the Japanese everything the mountains and rivers had a god. - Shintoism has Chinese, Korean influences, and there are similarities with Taoism. What two books are classified under the category of the Kamis? They are the Kojiki (713d.c) and the Nihonshoki (720d.c). - I hope you like it and see you in a next publication a cordial greeting.
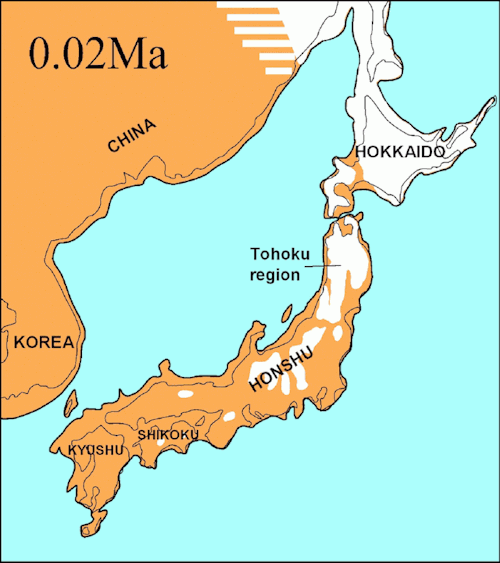
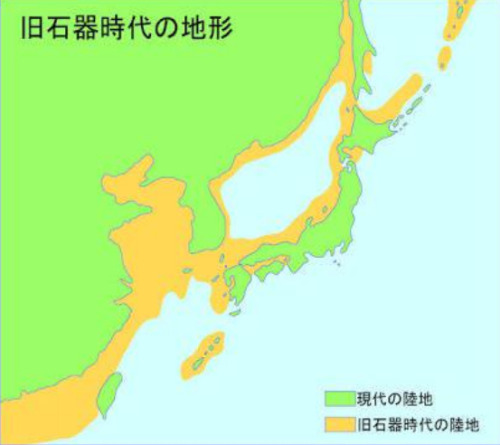
Capítulo 4: El origen de un país y su prehistoria, un paseo por la historia del país del sol naciente. - El Pleistoceno: ¿Cómo era el clima en el pleistoceno a través de los registros? Los testigos geológicos y los foraminíferos que nos permiten saber cómo era el clima en aquella época, en Japón era muy húmedo y muy frío, hay que tener en cuenta que las temperaturas actuales no son las mismas que hace 1.2 millones de años. ¿Es verdad, que los humanos en el pleistoceno extinguieron a mucha megafauna? Lo cual es una verdad a medias, ya que el ser humano fue una de las muchas causas, por el hecho de que como las temperaturas fueron uno de los factores claves en sus extinciones, por el hecho de que si una especie necesita de determinada para sobrevivir y el ser humano y el clima acaban con ella, pues, hay tenemos el golpe de gracia. Se sabe que en Hokkaido había Mamuts. El territorio Nippo, estaba unido al continente chino y correano en la zona sur por el estrecho de Tsushima o también denominado Paleo - Honshu y al norte por la isla de Sanjin. Como veíamos en el capítulo anterior, ¿Cómo se llaman las placas tectónicas que forman el archipiélago? Está compuesta por cuatro, Placa del Pasifico, EuroAsiática y NorteAmericana. Esto jugará, un papel fundamental, en la conformación del archipiélago japonés. Como ya mencione en el capítulo 3, posiblemente serían un conjunto de pequeñas islas que se fueron cambiando hasta conformar lo que vemos actualmente como Japón. - Mientras unas se indican, otras emergen y así a la inversa, esto deja registros geológicos. Algunas prefecturas donde se han encontrado restos humanos: prefecturas de Hyogo Shizuoka. - Chapter 4: The origin of a country and its prehistory, a walk through the history of the country of the rising sun. - The Pleistocene: What was the climate like in the Pleistocene across records? The geological witnesses and foraminifera that allow us to know what the climate was like at that time, in Japan it was very humid and very cold, we must take into account that current temperatures are not the same as 1.2 million years ago. Is it true that humans in the Pleistocene extinct many megafauna? Which is a half truth, since the human being was one of the many causes, due to the fact that since temperatures were one of the key factors in their extinctions, due to the fact that if a species needs a certain amount to survive and the human being and the climate put an end to it, well, there we have the coup de grace. It is known that there were Mammoths in Hokkaido. The Nippo territory was joined to the Chinese and Correan continent in the south by the Strait of Tsushima or also called Paleo-Honshu and to the north by the island of Sanjin. - As we saw in the previous chapter, what are the names of the tectonic plates that form the archipelago? It is made up of four, Pacific, Euro-Asian and North American Plates. This will play a fundamental role in the formation of the Japanese archipelago. As I already mentioned in chapter 3, they were possibly a set of small islands that changed until they formed what we currently see as Japan. While some are indicated, others emerge and so on, this leaves geological records. Some prefectures where human remains have been found: Hyogo Shizuoka prefectures. - 第4章 国の成り立ちと先史、日出ずる国の歴史を歩く。 - 更新世: 記録に残る更新世の気候はどのようなものでしたか? 地質学的証拠と有孔虫は、当時の日本がどのような気候であったかを知ることを可能にします。日本は非常に湿気が多く、非常に寒かったため、現在の気温は 120 万年前と同じではないことを考慮する必要があります。 更新世の人類が多くの巨大動物を絶滅させたというのは本当ですか? これは半分真実です。なぜなら、温度が絶滅の重要な要因の1つであるという事実、そして種が生き残るためにある程度の量が必要であるという事実のため、人間は多くの原因の1つであるからです。人間と気候がそれに終止符を打ったのです。まあ、ここで私たちは幸運をもたらしました。 北海道にはマンモスがいたことが知られています。 日豊領土は、南は対馬海峡、または古本州とも呼ばれ、北は三津島によって中国大陸とコレリア大陸につながっていました。 - 前の章で見たように、列島を形成する構造プレートの名前は何ですか? 太平洋プレート、ヨーロッパ・アジアプレート、北米プレートの4枚で構成されています。 それは日本列島の形成に根本的な役割を果たします。 第 3 章ですでに述べたように、それらはおそらく、私たちが現在日本として見ているものを形成するまでに変化した小さな島の集まりであった可能性があります。 示されているものもあれば、出現しているものもあり、これにより地質学的記録が残ります。 人骨が発見された都道府県: 兵庫県 静岡県。 -




Sean bienvenidos japonistasarqueológicos a una nueva entrega en esta ocasión os hago una introducción a la serie de Japón y su arqueología para él Jōmon ya os la iré subiendo de cada periodo prehistórico. - ¿En cuántas partes se divide el periodo Jōmon? Su estructura se clasifica en 6 partes: 1 Edad temprana. 2 Temprano. 3 Periodo temprano (4000-300 a.c) 4 Medio temprano ( 3000-2000 a.c) 5 Tardío (2000-1000 a.c) 6 Período Tardío(1000-300 d.c) - Espero que os haya gustado y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones. - Welcome japonistasarqueológicos to a new installment. This time I'll introduce you to the series of Japan and its archaeology for the Jōmon, and I'll upload it for each prehistoric period. - How many parts is the Jōmon period divided into? Its structure is classified into 6 parts: 1 Early Age. 2 Early. 3 Early Period (4000-300 BC) 4 Early Middle (3000-2000 BC) 5 Late (2000-1000 BC) 6 Late Period (1000-300 AD) - I hope you liked it and see you in future posts. - 日本考古学の専門家へようこそ。今回は縄文に関する日本とその考古学のシリーズを先史時代ごとにアップロードします。 - 縄文時代はいくつに分かれていますか?その構造は次の 6 つの部分に分類されます。 1 幼少期。 2 早い。 3 初期 (紀元前 4000 ~ 300 年) 4 中期初期(紀元前 3000 ~ 2000 年) 5 後期 (紀元前 2000 ~ 1000 年) 6 後期 (西暦 1000 ~ 300 年) - 気に入っていただければ幸いです。今後の投稿でお会いしましょう。

Una espada con alma propia./自らの魂を宿した剣。/A sword with its own soul. La katana o (sable japonés) japonesa es un elemento, único en el mundo, porque para los samuráis la espada era su alma y perderla era todo un deshonor. La katana japonesa surge el siglo VIII, periodo Heian, pero en el periodo entre el 1192 y el 1336, durante el periodo Kamakura, la producción de espadas se amplió bastante. - 日本刀は世界でも類を見ない要素です。サムライにとって刀は魂であり、それを失うことは完全な不名誉だからです。 日本刀は平安時代の8世紀に誕生しましたが、鎌倉時代の1192年から1336年にかけて刀剣の生産は大幅に拡大しました。 - The Japanese katana or (Japanese sword) is an element, unique in the world, because for the samurai the sword was their soul and losing it was a complete dishonor. The Japanese katana emerged in the 8th century, Heian period, but in the period between 1192 and 1336, during the Kamakura period, the production of swords expanded considerably.


Sean bienvenidos, japonistasarqueológicos a una nueva entrega, de arqueología en la que comentaremos, cómo era vivir hace 2000 años en el período Yayoi, una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos que empezamos. — En el emplazamiento, podréis vivir la experiencia de como si estuvierais en las viviendas, de dicho periodo, las recreaciones de los almacenes y los santuarios de las ruinas de toro se han reducido a una escala de aproximada al 80 % las paredes representan la naturaleza, de la época y de su estilo de vida. Siéntete como si hubieras viajado en el tiempo al pueblo Toro del período Yayoi, con nuestra máquina del tiempo, ya que puede ser una experiencia inolvidable, para todas las edades, porque la vida no ha cambiado en 2000 a 3000 años. — Espero que os guste y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones, que pasen una buena semana.
-
日本の考古学者諸君、ようこそ考古学の新連載へ。2000年前の弥生時代の暮らしとはどんなものだったのかについて語り合おう。 - 遺跡では、当時の住居がどのようなものであったかを体験することができます。トロ遺跡の倉庫や神社を約80%の縮尺で再現し、壁で当時の自然や生活様式を表現しています。まるでタイムマシンで弥生時代の登呂集落にタイムスリップしたかのような体験は、2000年から3000年経っても変わらない暮らしの中で、世代を問わず忘れられない思い出になることだろう。 - それでは、また次回もお楽しみに。
-
Welcome, Japanese archaeologists, to a new instalment of archaeology in which we will discuss what it was like to live 2000 years ago in the Yayoi period, so make yourselves comfortable and let's get started. - At the site, you can experience what it was like to live in the dwellings of that period, the recreations of the warehouses and shrines of the toro ruins have been reduced to a scale of about 80% and the walls represent the nature of the period and its lifestyle. Feel as if you have travelled back in time to the Toro village of the Yayoi period, with our time machine, as it can be an unforgettable experience, for all ages, because life has not changed in 2000 to 3000 years. - I hope you like it and see you in future publications, have a nice week.
詳しくは/more information:
https://www.shizuoka-toromuseum.jp/guide/admission/
Capítulo 4: El origen de un país y su prehistoria, un paseo por la historia del país del sol naciente. - El Pleistoceno: ¿Cómo era el clima en el pleistoceno a través de los registros? Los testigos geológicos y los foraminíferos que nos permiten saber cómo era el clima en aquella época, en Japón era muy húmedo y muy frío, hay que tener en cuenta que las temperaturas actuales no son las mismas que hace 1.2 millones de años. ¿Es verdad, que los humanos en el pleistoceno extinguieron a mucha megafauna? Lo cual es una verdad a medias, ya que el ser humano fue una de las muchas causas, por el hecho de que como las temperaturas fueron uno de los factores claves en sus extinciones, por el hecho de que si una especie necesita de determinada para sobrevivir y el ser humano y el clima acaban con ella, pues, hay tenemos el golpe de gracia. Se sabe que en Hokkaido había Mamuts. El territorio Nippo, estaba unido al continente chino y correano en la zona sur por el estrecho de Tsushima o también denominado Paleo - Honshu y al norte por la isla de Sanjin. Como veíamos en el capítulo anterior, ¿Cómo se llaman las placas tectónicas que forman el archipiélago? Está compuesta por cuatro, Placa del Pasifico, EuroAsiática y NorteAmericana. Esto jugará, un papel fundamental, en la conformación del archipiélago japonés. Como ya mencione en el capítulo 3, posiblemente serían un conjunto de pequeñas islas que se fueron cambiando hasta conformar lo que vemos actualmente como Japón. - Mientras unas se indican, otras emergen y así a la inversa, esto deja registros geológicos. Algunas prefecturas donde se han encontrado restos humanos: prefecturas de Hyogo Shizuoka. - Chapter 4: The origin of a country and its prehistory, a walk through the history of the country of the rising sun. - The Pleistocene: What was the climate like in the Pleistocene across records? The geological witnesses and foraminifera that allow us to know what the climate was like at that time, in Japan it was very humid and very cold, we must take into account that current temperatures are not the same as 1.2 million years ago. Is it true that humans in the Pleistocene extinct many megafauna? Which is a half truth, since the human being was one of the many causes, due to the fact that since temperatures were one of the key factors in their extinctions, due to the fact that if a species needs a certain amount to survive and the human being and the climate put an end to it, well, there we have the coup de grace. It is known that there were Mammoths in Hokkaido. The Nippo territory was joined to the Chinese and Correan continent in the south by the Strait of Tsushima or also called Paleo-Honshu and to the north by the island of Sanjin. - As we saw in the previous chapter, what are the names of the tectonic plates that form the archipelago? It is made up of four, Pacific, Euro-Asian and North American Plates. This will play a fundamental role in the formation of the Japanese archipelago. As I already mentioned in chapter 3, they were possibly a set of small islands that changed until they formed what we currently see as Japan. While some are indicated, others emerge and so on, this leaves geological records. Some prefectures where human remains have been found: Hyogo Shizuoka prefectures. - 第4章 国の成り立ちと先史、日出ずる国の歴史を歩く。 - 更新世: 記録に残る更新世の気候はどのようなものでしたか? 地質学的証拠と有孔虫は、当時の日本がどのような気候であったかを知ることを可能にします。日本は非常に湿気が多く、非常に寒かったため、現在の気温は 120 万年前と同じではないことを考慮する必要があります。 更新世の人類が多くの巨大動物を絶滅させたというのは本当ですか? これは半分真実です。なぜなら、温度が絶滅の重要な要因の1つであるという事実、そして種が生き残るためにある程度の量が必要であるという事実のため、人間は多くの原因の1つであるからです。人間と気候がそれに終止符を打ったのです。まあ、ここで私たちは幸運をもたらしました。 北海道にはマンモスがいたことが知られています。 日豊領土は、南は対馬海峡、または古本州とも呼ばれ、北は三津島によって中国大陸とコレリア大陸につながっていました。 - 前の章で見たように、列島を形成する構造プレートの名前は何ですか? 太平洋プレート、ヨーロッパ・アジアプレート、北米プレートの4枚で構成されています。 それは日本列島の形成に根本的な役割を果たします。 第 3 章ですでに述べたように、それらはおそらく、私たちが現在日本として見ているものを形成するまでに変化した小さな島の集まりであった可能性があります。 示されているものもあれば、出現しているものもあり、これにより地質学的記録が残ります。 人骨が発見された都道府県: 兵庫県 静岡県。 -




Una espada con alma propia./自らの魂を宿した剣。/A sword with its own soul. La katana o (sable japonés) japonesa es un elemento, único en el mundo, porque para los samuráis la espada era su alma y perderla era todo un deshonor. La katana japonesa surge el siglo VIII, periodo Heian, pero en el periodo entre el 1192 y el 1336, durante el periodo Kamakura, la producción de espadas se amplió bastante. - 日本刀は世界でも類を見ない要素です。サムライにとって刀は魂であり、それを失うことは完全な不名誉だからです。 日本刀は平安時代の8世紀に誕生しましたが、鎌倉時代の1192年から1336年にかけて刀剣の生産は大幅に拡大しました。 - The Japanese katana or (Japanese sword) is an element, unique in the world, because for the samurai the sword was their soul and losing it was a complete dishonor. The Japanese katana emerged in the 8th century, Heian period, but in the period between 1192 and 1336, during the Kamakura period, the production of swords expanded considerably.







Sean Bienvenidos, japonistasarqueologicos a una nueva entrega sintética, en la cual mencionaremos una de las muchas obras de Hiroshige, del cual ya hablamos en una publicación, pero no publique ninguna obra, ahora llego el momento dicho esto pónganse cómodos que empezamos. - Características Año: 1852 - 1858 Título: Itsukushima in Aki Province. Estilo: Ukiyo-e - Espero que os haya gustado os deseo una feliz semana y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones de Japón. - ようこそ、ジャポニスタサルケオロジコスの新しい合成配信へ。その中で、広重の多くの作品の一つを紹介します。その作品については、すでに出版物で話していますが、私は作品を出版していません。今、その時が来ました。そう言って、あなた自身を快適にして、始めましょう。 - 特徴 年:1852年~1858年 タイトル:安芸国厳島(あきこくいつくしま 様式:浮世絵 - お気に召していただけたなら幸いです。今週もよろしくお願いします。また、今後の日本の出版物でお会いしましょう。 - Welcome, japonistasarqueologicos to a new synthetic delivery, in which we will mention one of the many works of Hiroshige, of which we already spoke in a publication, but I did not publish any work, now the time has come, having said that, make yourselves comfortable and let's begin. - Features Year: 1852 - 1858 Title: Itsukushima in Aki Province. Style: Ukiyo-e - I hope you liked it, I wish you a happy week and see you in future Japan publications.

Sean bienvenidos, japonistasarqueologos, a una nueva entrega en esta ocasión comentaremos de por qué en Japón se come poca carne, una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos que empezamos. - Seguramente todos pensemos, que en Japón se come carne y no otro tipo de alimentos, ya que eso sería un estereotipo alimenticio. Para empezar el tema hay que entender que la geografía juega un papel muy importante en todo esto porque hay pocos focos donde los japoneses puedan tener el ganado, por el hecho de que su país es muy accidentado geográficamente hablando, el 90% de la carne es importada como otros muchos productos porque Japón escasean muchos de ellos. - En su territorio crían pollos y la Wagyu que es la más conocida y más cara del mundo, además, Japón es el segundo mayor importador de carne de cerdo del mundo, llegando a importar unas 923.835 toneladas de carne en 2020. Por eso comer carne en Japón es muy cara, hay platos con carne, pero no os creáis que hay muchos, al contrario de los que hay más son de: pescado, arroz, verduras, es decir los brotes de soja, el arroz les sale más barato por poner algunos ejemplos y los lácteos es otro de los productos que son muy caros. Su dieta es una de las más sanas del mundo y eso se ve en su población la más longeva del mundo, llegando a los 100 años, aparte de un gran equilibrio alimenticio, aplicado a una buena filosofía. - En esta publicación no he hablado de la influencia Yankee en Japón, pero qué país no tiene su influencia de su asquerosa comida chatarra, normal que sean el país con más problemas de obesidad del mundo. Espero que os haya gustado y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones que pasen una buena semana. - ジャポニスタ・サルケオロゴスの皆さん、ようこそ!今回は、なぜ日本では肉をあまり食べないのかについてコメントします。 - 日本では肉を食べ、他の種類の食べ物は食べない。というのも、日本の国土は地理的に非常に起伏に富んでいるため、日本人が家畜を飼うことができる場所はほとんどない。 - さらに、日本は世界第2位の豚肉輸入国であり、2020年には約92万3,835トンの肉を輸入する。そのため、日本で肉を食べるのは非常に高価である。肉を使った料理はあるが、その数はそれほど多くない。彼らの食生活は世界で最も健康的なもののひとつであり、そのことは、優れた哲学に基づいた栄養バランスの良さとは別に、世界で最も長寿で100歳に達する彼らの人口にも表れている。 - 本書では、日本におけるヤンキーの影響については触れなかったが、ジャンクフードの影響を受けていない国があるだろうか?それでは、また次の記事でお会いしましょう。 - Welcome, japonistasarqueologos, to a new installment in this occasion we will comment on why in Japan they eat little meat, having said that, make yourselves comfortable and let's get started. - Surely we all think that in Japan they eat meat and not other types of food, since that would be a food stereotype. To begin the subject we must understand that geography plays a very important role in all this because there are few places where the Japanese can keep livestock, due to the fact that their country is very rugged geographically speaking, 90% of the meat is imported like many other products because Japan has a shortage of many of them. - On its territory they raise chickens and Wagyu which is the best known and most expensive in the world, in addition, Japan is the second largest importer of pork in the world, importing some 923,835 tonnes of meat in 2020. That is why eating meat in Japan is very expensive, there are dishes with meat, but do not think that there are many, on the contrary there are more: fish, rice, vegetables, i.e. bean sprouts, rice is cheaper to give some examples and dairy products is another of the products that are very expensive. Their diet is one of the healthiest in the world and this can be seen in their population, the longest in the world, reaching 100 years of age, apart from a great nutritional balance, applied to a good philosophy. - In this publication I have not talked about the Yankee influence in Japan, but what country does not have its influence of its disgusting junk food, it is normal that they are the country with more obesity problems in the world. I hope you liked it and see you in the next posts have a nice week.
-
 rfpreiwaphase liked this · 11 months ago
rfpreiwaphase liked this · 11 months ago -
 repera23 liked this · 1 year ago
repera23 liked this · 1 year ago -
 bear-pattern-hamster liked this · 1 year ago
bear-pattern-hamster liked this · 1 year ago -
 noticiasarquelogicasjaponesas reblogged this · 1 year ago
noticiasarquelogicasjaponesas reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 naser1963 liked this · 1 year ago
naser1963 liked this · 1 year ago -
 curiokhan0113 liked this · 1 year ago
curiokhan0113 liked this · 1 year ago -
 rodolfo9999 liked this · 1 year ago
rodolfo9999 liked this · 1 year ago -
 50littlepotatogremlinsinurpantry liked this · 1 year ago
50littlepotatogremlinsinurpantry liked this · 1 year ago -
 u-nobu liked this · 1 year ago
u-nobu liked this · 1 year ago -
 manyrattos liked this · 1 year ago
manyrattos liked this · 1 year ago -
 asteroideasbellybuttons liked this · 1 year ago
asteroideasbellybuttons liked this · 1 year ago -
 hiromusicarts-blog liked this · 1 year ago
hiromusicarts-blog liked this · 1 year ago -
 sicks93 liked this · 1 year ago
sicks93 liked this · 1 year ago -
 noticiasarquelogicasjaponesas reblogged this · 1 year ago
noticiasarquelogicasjaponesas reblogged this · 1 year ago

238 posts









