The Final Stretch.


The final stretch.
More Posts from Mousoudi20 and Others

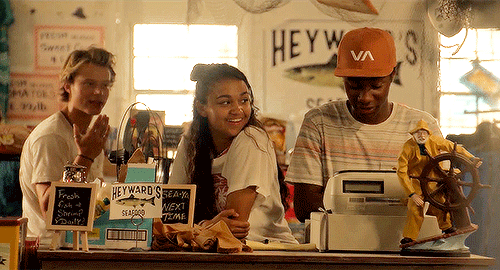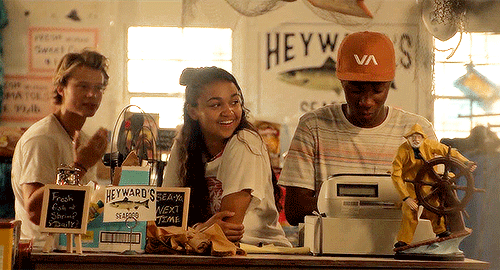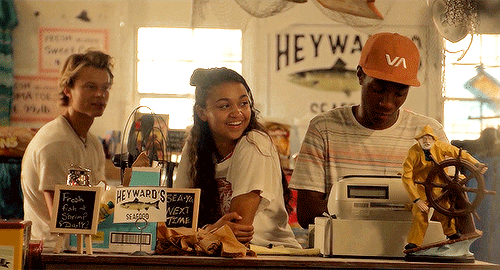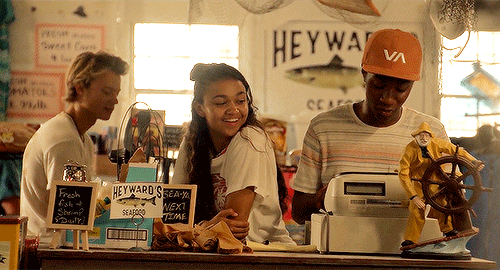

outer banks → places: heyward’s seafood

Prune your contact list yearlySome people say to do this once a quarter and if you have the time to do it, great, but I usually don’t. I find that the best time to get in touch with people that you haven’t spoken to in a while is to just send them a quick personal email or note once a year, at new years, wishing them a happy new year. Almost everyone celebrates it, it’s politically correct, and if you are lucky it can even rekindle a relationship long dormant, whether its business or pleasure.
Follow for more.
The Perseid Meteor Shower Is Here!

Image Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
The Perseids are at their peak this week!
The Perseid meteor shower, one of the biggest meteor showers of the year, will be at its brightest early in the morning on Wednesday, August 12. Read on for some tips on how to watch the night sky this week – and to find out: what exactly are the Perseids, anyway?

Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
Your best chance to spot the Perseids will be between 2 AM and dawn (local time) the morning of August 12. Find a dark spot, avoid bright lights (yes, that includes your phone) and get acclimated to the night sky.
Your eyes should be at peak viewing capacity after about 30 minutes; though the Moon may block out some of the dimmer meteors, you should still be able to see up to 15-20 an hour. If you’re not an early bird, you can try and take a look soon after sunset (around 9 PM) on the 11th, though you may not see as many Perseids then.

Credit: NASA/MEO
If it’s too cloudy, or too bright, to go skywatching where you are, you can try again Wednesday or Thursday night – or just stay indoors and watch the Perseids online!
Our Meteor Watch program will be livestreaming the Perseids from Huntsville, Alabama on Facebook (weather permitting), starting around 9 p.m. EDT on August 11 and continuing through sunrise.
So… why are they called the Perseids?
Because all of a meteor shower’s meteors have similar orbits, they appear to come from the same place in the sky – a point called the radiant.

The radiant for the Perseids, as you might guess from the name, is in the constellation Perseus, found near Aries and Taurus in the night sky.
But they’re not actually coming from Perseus, right?

Credit: NASA/Joel Kowsky
Right! The Perseids are actually fragments of the comet Swift-Tuttle, which orbits within our solar system.
If you want to learn more about the Perseids, visit our Watch the Skies blog or check out our monthly “What’s Up” video series. Happy viewing!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
I’m really intrigued about this shipping thing and who I would match haha...Can I have an Outer Banks ship? My icon is actually me! I’m a straight female, 5’5 with mid length brown hair and brown eyes. I love older music like 70s rock bands but also love pop/rock music for driving with the windows down like Taylor Swift or Avril Lavigne. I’m from South Carolina and I love Kayaking and Paddle Boarding I also like just reading a good book. The most important thing to me is a sense of adventure!
outer banks

i ship you with john b!
• you and john b go on adventures all the time. there isn’t a mountain or hiking trail you two haven’t gone on. you guys also sneak into a lot of abandoned places.
• he also would teach you how to surf. he’s not the best teacher, but you get the hang of it anyway.
• naps in the twinkie>
• him laying his head in your lap while you read
• i feel like he might listen to the same music you do
• screaming complicated by avril with the windows down and full volume

The International Space Station Through the Eyes of Little Earth!
Currently, six humans are living and working on the International Space Station, which orbits 250 miles above our planet at 17,500mph. Accompanying their mission is a zero-g indicator, informally known as “Little Earth”.
Greetings fellow Earthlings! Curious about my first week on the International Space Station? What does a normal day look like when you’re living and working hundreds of miles above Earth? Take a look at some photos from my first week, when I was still learning the ropes from my new roommates!
Welcome Ceremony
Talk about a warm welcome! I arrived on March 3, 2019 when the SpaceX Crew Dragon docked to the Space Station for the first time. This historic mission marked the first time a commercially built American spacecraft intended for human spaceflight docked to the orbital lab. Though un-crewed, Dragon was carrying two very important passengers – my space travel companion Ripley and myself, Astronaut Little Earth. During my three-day introduction to the station, two Expedition 59 astronauts, Anne McClain and David Saint-Jacques, taught me what it takes to be a Space Station crew member!
Earth Watching

First thing’s first – the VIEW. After the traditional hatch opening welcome ceremony, I was off to the Cupola Observational Module. Designed for the observation of operations outside the station, this module’s six side windows also provide spectacular views of our Mother Earth! My roommate Anne McClain introduced me to the beautiful vantage point of space. Clearly, I was a little star-struck.
Space Suit Sizing

Next, it was time to get to work – lending a hand with Anne McClain’s space suit sizing. Did you know you actually grow in zero gravity? Astronaut McClain has grown two inches on her current mission in space. Crew members must account for this change in growth to know if different components need to be switched out of their individual spacesuit for a better fit. When pressurized and filled with oxygen, the spacesuits become stiff objects around the astronauts inside, making it critical they fit comfortably. These spacesuits are essentially mini spacecraft that provide protection and a means of survival for the astronauts as they venture outside the space station and into the harsh environment of space.
Space Coffee!

One Café Latte, please! I was thrilled to find out that even in space, the morning begins with a pick me up. Due to microgravity, liquids tend to get sticky and cling to the wall of cups, making these plastic pouches and straws necessary for consumption. Astronauts in 2015 got an upgrade to their morning cup of joe thanks to SpaceX, Lavazza and the Italian Space Agency. Named the ISSpresso, a microgravity coffee maker has brought authentic Italian espresso with zero-G coffee cups onto the International Space Station.
Emergency Mask Donning

Fueled up and ready for the day, my next agenda item was emergency preparedness practice. There is no 9-1-1 in space, and three events that could pose a dangerous threat to the Space Station include a fire, a depressurization event or an ammonia breakout. Here, Canadian Astronaut David Saint-Jacques and I practiced emergency mask donning in the unlikely event of an ammonia leak into the station’s atmosphere.
Preventative Maintenance

From astronaut to astro-plumber, I traded my mask for goggles with Astronaut Anne McClain during a briefing on plumbing routine maintenance. Because the International Space Station never returns to Earth, the crew is trained to regularly inspect, replace and clean parts inside the station.
Daily Exercise

Talk about staying healthy! After a busy day, Astronaut McClain and I continued to hit the ground running, literally. Crew members are required to work out daily for about two hours to help keep their heart, bones and muscles strong in zero gravity. The harness McClain is wearing is very much like a backpacking harness, designed to evenly distribute weight across her upper body and is attached to a system of bungees and cords. Depending on the tension in these attachments, a specific load of pressure is applied to her body onto the machine.
Strength Training in Zero-G

Watch out, deadlift going on. Running isn’t the only gym exercise they have onboard; strength training is also incorporated into the daily exercise regime.
Robotics Operations: Canadarm2

You can look, just don’t touch they told me. Whoops. This was a definite highlight, my Canadarm 2 briefing. That black nob by my hand is the translational hand controller. It operates the up and down function of the 57.7-foot-long robotic arm. The Canadarm2 lends a literal helping hand with many station functions, using a “hand” known as a Latching End Effector to perform tasks such as in orbit maintenance, moving supplies and performing “cosmic catches”.
Crew Group Dinner

Whew, you work up a big appetite working on the Space Station. Ending the day, I was introduced to a crew favorite, group dinner! Astronauts and cosmonauts from around the world come together on the orbital lab and bring with them a variety of cultures and … food! Though each country is responsible for feeding its own members, when on board the astronauts can share as they please. A new friend of mine, Paxi from the European Space Agency, welcomed my visit and we split a delicious space-shrimp cocktail.
And that’s a wrap to a busy first week aboard the International Space Station! Learn more about what it means to live and work aboard the International Space Station, and click here to see if you have what it takes to become a NASA Astronaut. Until next time!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

50 years ago, three Apollo astronauts rode this 363 foot tall rocket, the Saturn V, embarking on one of the greatest missions of mankind – to step foot on another world. On July 20, 1969, astronauts Buzz Aldrin, Michael Collins and Neil Armstrong made history when they arrived at the Moon. Thanks to the Saturn V rocket, we were able to complete this epic feat, returning to the lunar surface a total of six times. The six missions that landed on the Moon returned a wealth of scientific data and almost 400 kilograms of lunar samples.
In honor of this historic launch, the National Air and Space Museum is projecting the identical rocket that took our astronauts to the Moon on the Washington Monument in Washington, D.C.
This week, you can watch us salute our Apollo 50th heroes and look forward to our next giant leap for future missions to the Moon and Mars. Tune in to a special two-hour live NASA Television broadcast at 1 p.m. ET on Friday, July 19. Watch the program at www.nasa.gov/live.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
#IBF2019 participants on tour at #ITER. Here in the Assembly Hall where the two giant tools stand ready to assemble the vacuum vessel sectors. #fusionenergy #WeAreITER https://t.co/MLh2Z7gbr3



Retro. Modern. Iconic. That’s the worm.
#TheWormIsBack
Our beloved symbol of exploration will fly once again, just in time to mark the return of human spaceflight on American rockets from American soil. The retired logo is making its comeback on on SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket that will take flight later this year when we #LaunchAmerica once again.
The NASA insignia, or “meatball,” seen in our profile image, was quite difficult to reproduce with 1970s technology. In 1975, enter the sleek, simple design you see above! The world knew it as “the worm.” For a period of time we were able to thrive with both the worm and the meatball. However, in 1992, the 1970s brand was retired - except on clothing and other souvenir items - in favor of the original late 1950s graphic.
Image Credit: NASA/SpaceX
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
We Like Big Rockets and We Cannot Lie: Saturn V vs. SLS
On this day 50 years ago, human beings embarked on a journey to set foot on another world for the very first time.

At 9:32 a.m. EDT, millions watched as Apollo astronauts Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins lifted off from Launch Pad 39A at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, flying high on the most powerful rocket ever built: the mighty Saturn V.

As we prepare to return humans to the lunar surface with our Artemis program, we’re planning to make history again with a similarly unprecedented rocket, the Space Launch System (SLS). The SLS will be our first exploration-class vehicle since the Saturn V took American astronauts to the Moon a decade ago. With its superior lift capability, the SLS will expand our reach into the solar system, allowing astronauts aboard our Orion spacecraft to explore multiple, deep-space destinations including near-Earth asteroids, the Moon and ultimately Mars.

So, how does the Saturn V measure up half a century later? Let’s take a look.
Mission Profiles: From Apollo to Artemis
Saturn V

Every human who has ever stepped foot on the Moon made it there on a Saturn V rocket. The Saturn rockets were the driving force behind our Apollo program that was designed to land humans on the Moon and return them safely back to Earth.

Developed at our Marshall Space Flight Center in the 1960s, the Saturn V rocket (V for the Roman numeral “5”) launched for the first time uncrewed during the Apollo 4 mission on November 9, 1967. One year later, it lifted off for its first crewed mission during Apollo 8. On this mission, astronauts orbited the Moon but did not land. Then, on July 16, 1969, the Apollo 11 mission was the first Saturn V flight to land astronauts on the Moon. In total, this powerful rocket completed 13 successful missions, landing humans on the lunar surface six times before lifting off for the last time in 1973.
Space Launch System (SLS)

Just as the Saturn V was the rocket of the Apollo generation, the Space Launch System will be the driving force behind a new era of spaceflight: the Artemis generation.

During our Artemis missions, SLS will take humanity farther than ever before. It is the vehicle that will return our astronauts to the Moon by 2024, transporting the first woman and the next man to a destination never before explored – the lunar South Pole. Over time, the rocket will evolve into increasingly more powerful configurations to provide the foundation for human exploration beyond Earth’s orbit to deep space destinations, including Mars.
SLS will take flight for the first time during Artemis 1 where it will travel 280,000 miles from Earth – farther into deep space than any spacecraft built for humans has ever ventured.
Size: From Big to BIGGER
Saturn V

The Saturn V was big.
In fact, the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center is one of the largest buildings in the world by volume and was built specifically for assembling the massive rocket. At a height of 363 feet, the Saturn V rocket was about the size of a 36-story building and 60 feet taller than the Statue of Liberty!
Space Launch System (SLS)

Measured at just 41 feet shy of the Saturn V, the initial SLS rocket will stand at a height of 322 feet. Because this rocket will evolve into heavier lift capacities to facilitate crew and cargo missions beyond Earth’s orbit, its size will evolve as well. When the SLS reaches its maximum lift capability, it will stand at a height of 384 feet, making it the tallest rocket in the world.
Power: Turning Up the Heat
Saturn V
For the 1960s, the Saturn V rocket was a beast – to say the least.
Fully fueled for liftoff, the Saturn V weighed 6.2 million pounds and generated 7.6 million pounds of thrust at launch. That is more power than 85 Hoover Dams! This thrust came from five F-1 engines that made up the rocket’s first stage. With this lift capability, the Saturn V had the ability to send 130 tons (about 10 school buses) into low-Earth orbit and about 50 tons (about 4 school buses) to the Moon.
Space Launch System (SLS)

Photo of SLS rocket booster test
Unlike the Saturn V, our SLS rocket will evolve over time into increasingly more powerful versions of itself to accommodate missions to the Moon and then beyond to Mars.
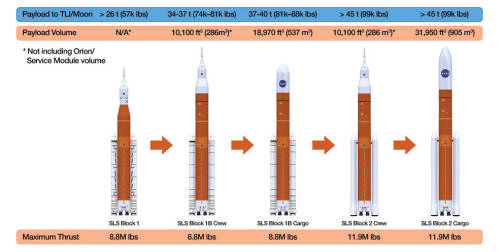
The first SLS vehicle, called Block 1, will weigh 5.75 million pounds and produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust at time of launch. That’s 15 percent more than the Saturn V produced during liftoff! It will also send more than 26 tons beyond the Moon. Powered by a pair of five-segment boosters and four RS-25 engines, the rocket will reach the period of greatest atmospheric force within 90 seconds!

Following Block 1, the SLS will evolve five more times to reach its final stage, Block 2 Cargo. At this stage, the rocket will provide 11.9 million pounds of thrust and will be the workhorse vehicle for sending cargo to the Moon, Mars and other deep space destinations. SLS Block 2 will be designed to lift more than 45 tons to deep space. With its unprecedented power and capabilities, SLS is the only rocket that can send our Orion spacecraft, astronauts and large cargo to the Moon on a single mission.
Build: How the Rockets Stack Up
Saturn V

The Saturn V was designed as a multi-stage system rocket, with three core stages. When one system ran out of fuel, it separated from the spacecraft and the next stage took over. The first stage, which was the most powerful, lifted the rocket off of Earth’s surface to an altitude of 68 kilometers (42 miles). This took only 2 minutes and 47 seconds! The first stage separated, allowing the second stage to fire and carry the rest of the stack almost into orbit. The third stage placed the Apollo spacecraft and service module into Earth orbit and pushed it toward the Moon. After the first two stages separated, they fell into the ocean for recovery. The third stage either stayed in space or crashed into the Moon.
Space Launch System (SLS)
Much like the Saturn V, our Space Launch System is also a multi-stage rocket. Its three stages (the solid rocket boosters, core stage and upper stage) will each take turns thrusting the spacecraft on its trajectory and separating after each individual stage has exhausted its fuel. In later, more powerful versions of the SLS, the third stage will carry both the Orion crew module and a deep space habitat module.
A New Era of Space Exploration
Just as the Saturn V and Apollo era signified a new age of exploration and technological advancements, the Space Launch System and Artemis missions will bring the United States into a new age of space travel and scientific discovery.
Join us in celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 Moon landing and hear about our future plans to go forward to the Moon and on to Mars by tuning in to a special two-hour live NASA Television broadcast at 1 p.m. ET on Friday, July 19. Watch the program at www.nasa.gov/live.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 relapserachel liked this · 3 years ago
relapserachel liked this · 3 years ago -
 alexsandra-world liked this · 4 years ago
alexsandra-world liked this · 4 years ago -
 perpetualkat liked this · 4 years ago
perpetualkat liked this · 4 years ago -
 halliote liked this · 4 years ago
halliote liked this · 4 years ago -
 derangedmutterings liked this · 4 years ago
derangedmutterings liked this · 4 years ago -
 barebellaw reblogged this · 4 years ago
barebellaw reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 heart-charming liked this · 4 years ago
heart-charming liked this · 4 years ago -
 hizerain liked this · 4 years ago
hizerain liked this · 4 years ago -
 hanaiyy liked this · 4 years ago
hanaiyy liked this · 4 years ago -
 i-hate-my-body-xx liked this · 4 years ago
i-hate-my-body-xx liked this · 4 years ago -
 mega-bigbouquetfox liked this · 4 years ago
mega-bigbouquetfox liked this · 4 years ago -
 superrichkiids liked this · 4 years ago
superrichkiids liked this · 4 years ago -
 kasuga707 liked this · 5 years ago
kasuga707 liked this · 5 years ago -
 stressedabouteverything liked this · 5 years ago
stressedabouteverything liked this · 5 years ago -
 kristin-luce liked this · 5 years ago
kristin-luce liked this · 5 years ago -
 strawbellmayr liked this · 5 years ago
strawbellmayr liked this · 5 years ago -
 eateraa liked this · 5 years ago
eateraa liked this · 5 years ago -
 pallasathena2002 liked this · 5 years ago
pallasathena2002 liked this · 5 years ago -
 milk-carton12 liked this · 5 years ago
milk-carton12 liked this · 5 years ago -
 loversandsisters liked this · 5 years ago
loversandsisters liked this · 5 years ago -
 acelizystudying reblogged this · 5 years ago
acelizystudying reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 acelizystudying liked this · 5 years ago
acelizystudying liked this · 5 years ago -
 czarnaanonimka liked this · 5 years ago
czarnaanonimka liked this · 5 years ago -
 szczesciegdziesczeka reblogged this · 5 years ago
szczesciegdziesczeka reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 novelaaaaaaaa liked this · 5 years ago
novelaaaaaaaa liked this · 5 years ago -
 bryluen liked this · 5 years ago
bryluen liked this · 5 years ago -
 bonnefilleparfaite liked this · 5 years ago
bonnefilleparfaite liked this · 5 years ago -
 vanessainstem liked this · 5 years ago
vanessainstem liked this · 5 years ago -
 kelsiegallagher liked this · 5 years ago
kelsiegallagher liked this · 5 years ago -
 bxbyporcelain liked this · 5 years ago
bxbyporcelain liked this · 5 years ago -
 lori-study reblogged this · 5 years ago
lori-study reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 rubyetadams liked this · 5 years ago
rubyetadams liked this · 5 years ago -
 mx-melancholic liked this · 5 years ago
mx-melancholic liked this · 5 years ago -
 ef-tu-brute liked this · 5 years ago
ef-tu-brute liked this · 5 years ago -
 grassrootskies liked this · 5 years ago
grassrootskies liked this · 5 years ago -
 studying-for-myself reblogged this · 5 years ago
studying-for-myself reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 baddecisions4-blog liked this · 5 years ago
baddecisions4-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 harukihatsune liked this · 5 years ago
harukihatsune liked this · 5 years ago -
 lerquw liked this · 5 years ago
lerquw liked this · 5 years ago -
 sanriosun liked this · 5 years ago
sanriosun liked this · 5 years ago -
 roadsandoceans liked this · 5 years ago
roadsandoceans liked this · 5 years ago
