I’m Really Intrigued About This Shipping Thing And Who I Would Match Haha...Can I Have An Outer Banks
I’m really intrigued about this shipping thing and who I would match haha...Can I have an Outer Banks ship? My icon is actually me! I’m a straight female, 5’5 with mid length brown hair and brown eyes. I love older music like 70s rock bands but also love pop/rock music for driving with the windows down like Taylor Swift or Avril Lavigne. I’m from South Carolina and I love Kayaking and Paddle Boarding I also like just reading a good book. The most important thing to me is a sense of adventure!
outer banks

i ship you with john b!
• you and john b go on adventures all the time. there isn’t a mountain or hiking trail you two haven’t gone on. you guys also sneak into a lot of abandoned places.
• he also would teach you how to surf. he’s not the best teacher, but you get the hang of it anyway.
• naps in the twinkie>
• him laying his head in your lap while you read
• i feel like he might listen to the same music you do
• screaming complicated by avril with the windows down and full volume
More Posts from Mousoudi20 and Others
Chart-Topping Space Images From 2019 You Won’t Want to Miss
From the first-ever image of a black hole, to astronaut Christina Koch breaking the record for the longest single spaceflight by a woman – 2019 was full of awe-inspiring events!
As we look forward to a new decade, we’ve taken ten of our top Instagram posts and put them here for your viewing pleasure. With eight out of ten being carousels, be sure to click on each title to navigate to the full post.
1. First-Ever Black Hole Image Makes History

In a historic feat by the Event horizon Telescope and National Science Foundation, an image of a black hole and its shadow was captured for the first time. At a whopping 3.4 million likes, this image takes home the gold as our most loved photo of 2019. Several of our missions were part of a large effort to observe this black hole using different wavelengths of light and collect data to understand its environment. Here’s a look at our Chandra X-Ray Observatory’s close-up of the core of the M87 galaxy with the imaged black hole at its center.
2. Hubble Celebrates 29 Years of Dazzling Discoveries


When you wish upon a star… Hubble captures it from afar ✨On April 18, 2019 our Hubble Space Telescope celebrated 29 years of dazzling discoveries, serving as a window to the wonders of worlds light-years away.
Hubble continues to observe the universe in near-ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared light. Over the past 29 years, it has captured the farthest views ever taken of the evolving universe, found planet-forming disks around nearby stars and identified the first supermassive black hole in the heart of a neighboring galaxy. Want more? Enjoy the full 10 photo Instagram carousel here.
3. Stars and Stripes in Space for Flag Day


Patriotism was in the air June 14 for Flag Day, and coming in at number three in our most liked Instagram line up is a carousel of our stars and stripes in space! One of the most iconic images from the Apollo 11 missions is of Buzz Aldrin saluting the American flag on the surface of the Moon. But did you know that over the years, five more flags joined the one left by Apollo 11 – and that many other flags have flown onboard our spacecraft? Scroll through the full carousel for flag day here.
4. Spitzer Celebrates its Super Sweet 16!


Since 2003, our Spitzer Space Telescope has been lifting the veil on the wonders of the cosmos, from our own solar system to faraway galaxies, using infrared light! Thanks to Spitzer, we’ve confirm the presence of seven rocky, Earth-size planets, received weather maps of hot, gaseous exoplanets and discovered a hidden ring around Saturn. In honor of Spitzer’s Sweet 16 in space, enjoy 16 jaw-dropping images from its mission here.
5. Earth as Seen Through Our Astronauts’ Eyes Show Perspective Changing Views

“That’s here. That’s home. That’s us.” – Carl Sagan
Seeing Earth from space can alter an astronauts’ cosmic perspective, a mental shift known as the “Overview Effect.” First coined by space writer Frank White in 1987, the Overview Effect is described as a feeling of awe for our home planet and a sense of responsibility for taking care of it. See Earth from the vantage point of our astronauts in a carousel of perspective-changing views here.
6. Astronaut Christina Koch Breaks Records With 300 Days in Space


Astronaut Christina Koch (@Astro_Christina) set a record Dec. 28, 2019 for the longest single spaceflight by a woman, eclipsing the former record of 288 days set by Peggy Whitson. Her long-duration mission is helping us learn how to keep astronauts healthy for deep space exploration to the Moon and Mars. Congrats to Christina on reaching new heights! Join in the celebration and view few photos she captured from her vantage point aboard the Space Station here.
7. Our Beautiful Planet – The Only Place We Know to Harbor Life – From Space


Earth is special. It’s the only place in the universe that we know contains life.
On July 7, 2019, two million people joined us in celebrating its beauty with a jaw dropping carousel of our home planet, as captured by crew members aboard the International Space Station. Bright blue oceans, glowing city lights and ice-capped mountain peaks come to life in a collection of breathtaking images, found here.
8. A Moon Even Sinatra Couldn’t Help But Sing About

Every 29 days our Moon turns over a new leaf, and on May, 18 we saw a very special one of its faces. Appearing opposite the Sun at 5:11 p.m. EDT, the world looked up to find a Blue Moon! Though the Moon didn’t actually look blue, the site of one is kind of rare. They occur on average about every two-and-a-half years when a season ends up having four full moons instead of three. Click through a carousel of high-definition lunar phases here.
9. The Majesty of Hubble Imagery … From Your Backyard


On December 23, a new gallery of Hubble Space Telescope images highlighting celestial objects visible to amateur and professional astronomers alike was released. All of the objects are from a collection known as the Caldwell catalog, which includes 109 interesting objects visible in amateur-sized telescopes in both the northern and southern skies. Flip through the jaw-dropping carousel here, and learn more about how you can study the night sky with Hubble here.
10. The Moon Gets Sassy

Nobody:
The Moon: “Y'all on the way yet?” 👀
We’re working on it, Moon. Under the Artemis program, we’re sending the first woman and the next man to walk on your surface by 2024. Find out how we’re doing it here.

For more pictures like these, follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/nasa/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How Do We Learn About a Planet’s Atmosphere?
The first confirmation of a planet orbiting a star outside our solar system happened in 1995. We now know that these worlds – also known as exoplanets – are abundant. So far, we’ve confirmed more than 4000. Even though these planets are far, far away, we can still study them using ground-based and space-based telescopes.
Our upcoming James Webb Space Telescope will study the atmospheres of the worlds in our solar system and those of exoplanets far beyond. Could any of these places support life? What Webb finds out about the chemical elements in these exoplanet atmospheres might help us learn the answer.
How do we know what’s in the atmosphere of an exoplanet?
Most known exoplanets have been discovered because they partially block the light of their suns. This celestial photo-bombing is called a transit.

During a transit, some of the star’s light travels through the planet’s atmosphere and gets absorbed.

The light that survives carries information about the planet across light-years of space, where it reaches our telescopes.
(However, the planet is VERY small relative to the star, and VERY far away, so it is still very difficult to detect, which is why we need a BIG telescope to be sure to capture this tiny bit of light.)
So how do we use a telescope to read light?

Stars emit light at many wavelengths. Like a prism making a rainbow, we can separate light into its separate wavelengths. This is called a spectrum. Learn more about how telescopes break down light here.

Visible light appears to our eyes as the colors of the rainbow, but beyond visible light there are many wavelengths we cannot see.
Now back to the transiting planet…
As light is traveling through the planet’s atmosphere, some wavelengths get absorbed.

Which wavelengths get absorbed depends on which molecules are in the planet’s atmosphere. For example, carbon monoxide molecules will capture different wavelengths than water vapor molecules.

So, when we look at that planet in front of the star, some of the wavelengths of the starlight will be missing, depending on which molecules are in the atmosphere of the planet.

Learning about the atmospheres of other worlds is how we identify those that could potentially support life…

…bringing us another step closer to answering one of humanity’s oldest questions: Are we alone?

Watch the full video where this method of hunting for distant planets is explained:
To learn more about NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, visit the website, or follow the mission on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Text and graphics credit Space Telescope Science Institute
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
We Like Big Rockets and We Cannot Lie: Saturn V vs. SLS
On this day 50 years ago, human beings embarked on a journey to set foot on another world for the very first time.

At 9:32 a.m. EDT, millions watched as Apollo astronauts Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins lifted off from Launch Pad 39A at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, flying high on the most powerful rocket ever built: the mighty Saturn V.

As we prepare to return humans to the lunar surface with our Artemis program, we’re planning to make history again with a similarly unprecedented rocket, the Space Launch System (SLS). The SLS will be our first exploration-class vehicle since the Saturn V took American astronauts to the Moon a decade ago. With its superior lift capability, the SLS will expand our reach into the solar system, allowing astronauts aboard our Orion spacecraft to explore multiple, deep-space destinations including near-Earth asteroids, the Moon and ultimately Mars.

So, how does the Saturn V measure up half a century later? Let’s take a look.
Mission Profiles: From Apollo to Artemis
Saturn V

Every human who has ever stepped foot on the Moon made it there on a Saturn V rocket. The Saturn rockets were the driving force behind our Apollo program that was designed to land humans on the Moon and return them safely back to Earth.

Developed at our Marshall Space Flight Center in the 1960s, the Saturn V rocket (V for the Roman numeral “5”) launched for the first time uncrewed during the Apollo 4 mission on November 9, 1967. One year later, it lifted off for its first crewed mission during Apollo 8. On this mission, astronauts orbited the Moon but did not land. Then, on July 16, 1969, the Apollo 11 mission was the first Saturn V flight to land astronauts on the Moon. In total, this powerful rocket completed 13 successful missions, landing humans on the lunar surface six times before lifting off for the last time in 1973.
Space Launch System (SLS)

Just as the Saturn V was the rocket of the Apollo generation, the Space Launch System will be the driving force behind a new era of spaceflight: the Artemis generation.

During our Artemis missions, SLS will take humanity farther than ever before. It is the vehicle that will return our astronauts to the Moon by 2024, transporting the first woman and the next man to a destination never before explored – the lunar South Pole. Over time, the rocket will evolve into increasingly more powerful configurations to provide the foundation for human exploration beyond Earth’s orbit to deep space destinations, including Mars.
SLS will take flight for the first time during Artemis 1 where it will travel 280,000 miles from Earth – farther into deep space than any spacecraft built for humans has ever ventured.
Size: From Big to BIGGER
Saturn V

The Saturn V was big.
In fact, the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center is one of the largest buildings in the world by volume and was built specifically for assembling the massive rocket. At a height of 363 feet, the Saturn V rocket was about the size of a 36-story building and 60 feet taller than the Statue of Liberty!
Space Launch System (SLS)

Measured at just 41 feet shy of the Saturn V, the initial SLS rocket will stand at a height of 322 feet. Because this rocket will evolve into heavier lift capacities to facilitate crew and cargo missions beyond Earth’s orbit, its size will evolve as well. When the SLS reaches its maximum lift capability, it will stand at a height of 384 feet, making it the tallest rocket in the world.
Power: Turning Up the Heat
Saturn V
For the 1960s, the Saturn V rocket was a beast – to say the least.
Fully fueled for liftoff, the Saturn V weighed 6.2 million pounds and generated 7.6 million pounds of thrust at launch. That is more power than 85 Hoover Dams! This thrust came from five F-1 engines that made up the rocket’s first stage. With this lift capability, the Saturn V had the ability to send 130 tons (about 10 school buses) into low-Earth orbit and about 50 tons (about 4 school buses) to the Moon.
Space Launch System (SLS)

Photo of SLS rocket booster test
Unlike the Saturn V, our SLS rocket will evolve over time into increasingly more powerful versions of itself to accommodate missions to the Moon and then beyond to Mars.
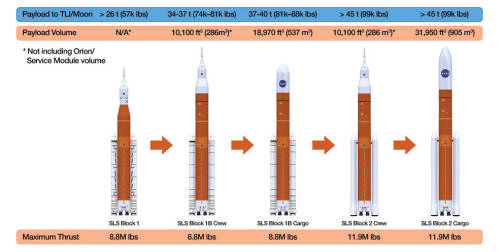
The first SLS vehicle, called Block 1, will weigh 5.75 million pounds and produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust at time of launch. That’s 15 percent more than the Saturn V produced during liftoff! It will also send more than 26 tons beyond the Moon. Powered by a pair of five-segment boosters and four RS-25 engines, the rocket will reach the period of greatest atmospheric force within 90 seconds!

Following Block 1, the SLS will evolve five more times to reach its final stage, Block 2 Cargo. At this stage, the rocket will provide 11.9 million pounds of thrust and will be the workhorse vehicle for sending cargo to the Moon, Mars and other deep space destinations. SLS Block 2 will be designed to lift more than 45 tons to deep space. With its unprecedented power and capabilities, SLS is the only rocket that can send our Orion spacecraft, astronauts and large cargo to the Moon on a single mission.
Build: How the Rockets Stack Up
Saturn V

The Saturn V was designed as a multi-stage system rocket, with three core stages. When one system ran out of fuel, it separated from the spacecraft and the next stage took over. The first stage, which was the most powerful, lifted the rocket off of Earth’s surface to an altitude of 68 kilometers (42 miles). This took only 2 minutes and 47 seconds! The first stage separated, allowing the second stage to fire and carry the rest of the stack almost into orbit. The third stage placed the Apollo spacecraft and service module into Earth orbit and pushed it toward the Moon. After the first two stages separated, they fell into the ocean for recovery. The third stage either stayed in space or crashed into the Moon.
Space Launch System (SLS)
Much like the Saturn V, our Space Launch System is also a multi-stage rocket. Its three stages (the solid rocket boosters, core stage and upper stage) will each take turns thrusting the spacecraft on its trajectory and separating after each individual stage has exhausted its fuel. In later, more powerful versions of the SLS, the third stage will carry both the Orion crew module and a deep space habitat module.
A New Era of Space Exploration
Just as the Saturn V and Apollo era signified a new age of exploration and technological advancements, the Space Launch System and Artemis missions will bring the United States into a new age of space travel and scientific discovery.
Join us in celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 Moon landing and hear about our future plans to go forward to the Moon and on to Mars by tuning in to a special two-hour live NASA Television broadcast at 1 p.m. ET on Friday, July 19. Watch the program at www.nasa.gov/live.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
What would happen if I go into a black hole? Do you think I would disappear forever or would I still exist inside the black hole?

50 years ago, three Apollo astronauts rode this 363 foot tall rocket, the Saturn V, embarking on one of the greatest missions of mankind – to step foot on another world. On July 20, 1969, astronauts Buzz Aldrin, Michael Collins and Neil Armstrong made history when they arrived at the Moon. Thanks to the Saturn V rocket, we were able to complete this epic feat, returning to the lunar surface a total of six times. The six missions that landed on the Moon returned a wealth of scientific data and almost 400 kilograms of lunar samples.
In honor of this historic launch, the National Air and Space Museum is projecting the identical rocket that took our astronauts to the Moon on the Washington Monument in Washington, D.C.
This week, you can watch us salute our Apollo 50th heroes and look forward to our next giant leap for future missions to the Moon and Mars. Tune in to a special two-hour live NASA Television broadcast at 1 p.m. ET on Friday, July 19. Watch the program at www.nasa.gov/live.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Want to Send Your Art to the International Space Station?!
For children ages 4-12, we’re hosting an art contest! Get the details:





We are working with Boeing and SpaceX to build human spaceflight systems, like rockets and spacecraft, to take astronauts to the International Space Station. These companies will fly astronauts to orbit around Earth while we focus on plans to explore deeper into our solar system.

Get out your art supplies and use your creative imagination to show us the present and future of traveling in space!

There are no grocery stores in space, but there may soon be farms. Very small farms that are important to a crew conducting a mission to deep space. That’s because our astronauts will need to grow some of their own food. Researchers on Earth and astronauts on the International Space Station are already showing what is needed to grow robust plants in orbit.

What would you take to space? Astronaut Suni Williams took a cutout of her dog, Gorbie, on her first mission to the International Space Station.

Kids 4 to 12, draw what you would take and enter it in our Children’s Artwork Calendar contest! Your entry could be beamed to the space station!


Go to http://go.nasa.gov/2fvRLNf for more information about the competition’s themes, rules and deadlines plus the entry form.


Get your parent’s permission, of course!
Email your entry form and drawing to us at: ksc-connect2ccp@mail.nasa.gov

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
There is a little bit of RF for fusion in the latest @ANSYS magazine Advantage ;)
https://t.co/SlhzaxPXsh
From #IBF19 Sergio Frattini, CEO @ASGsconductors
"The superconducting technology which has been developed in the #ITER project has led to a number of innovative systems in the fields of medicine and energy" @iterorg https://t.co/CCk9f1JXVP

hot
5 Ways the Moon Landing Changed Life on Earth
When Neil Armstrong took his first steps on the Moon 50 years ago, he famously said “that’s one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind.” He was referring to the historic milestone of exploring beyond our own planet — but there’s also another way to think about that giant leap: the massive effort to develop technologies to safely reach, walk on the Moon and return home led to countless innovations that have improved life on Earth.
Armstrong took one small step on the lunar surface, but the Moon landing led to a giant leap forward in innovations for humanity.
Here are five examples of technology developed for the Apollo program that we’re still using today:
1. Food Safety Standards
As soon as we started planning to send astronauts into space, we faced the problem of what to feed them — and how to ensure the food was safe to eat. Can you imagine getting food poisoning on a spacecraft, hundreds of thousands of miles from home?
We teamed up with a familiar name in food production: the Pillsbury Company. The company soon realized that existing quality control methods were lacking. There was no way to be certain, without extensive testing that destroyed the sample, that the food was free of bacteria and toxins.
Pillsbury revamped its entire food-safety process, creating what became the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point system. Its aim was to prevent food safety problems from occurring, rather than catch them after the fact. They managed this by analyzing and controlling every link in the chain, from the raw materials to the processing equipment to the people handling the food.
Today, this is one of the space program’s most far-reaching spinoffs. Beyond keeping the astronaut food supply safe, the Hazard Analysis and Critical Point system has also been adopted around the world — and likely reduced the risk of bacteria and toxins in your local grocery store.

2. Digital Controls for Air and Spacecraft
The Apollo spacecraft was revolutionary for many reasons. Did you know it was the first vehicle to be controlled by a digital computer? Instead of pushrods and cables that pilots manually adjusted to manipulate the spacecraft, Apollo’s computer sent signals to actuators at the flick of a switch.
Besides being physically lighter and less cumbersome, the switch to a digital control system enabled storing large quantities of data and programming maneuvers with complex software.
Before Apollo, there were no digital computers to control airplanes either. Working together with the Navy and Draper Laboratory, we adapted the Apollo digital flight computer to work on airplanes. Today, whatever airline you might be flying, the pilot is controlling it digitally, based on the technology first developed for the flight to the Moon.

3. Earthquake-ready Shock Absorbers
A shock absorber descended from Apollo-era dampers and computers saves lives by stabilizing buildings during earthquakes.
Apollo’s Saturn V rockets had to stay connected to the fueling tubes on the launchpad up to the very last second. That presented a challenge: how to safely move those tubes out of the way once liftoff began. Given how fast they were moving, how could we ensure they wouldn’t bounce back and smash into the vehicle?
We contracted with Taylor Devices, Inc. to develop dampers to cushion the shock, forcing the company to push conventional shock isolation technology to the limit.
Shortly after, we went back to the company for a hydraulics-based high-speed computer. For that challenge, the company came up with fluidic dampers—filled with compressible fluid—that worked even better. We later applied the same technology on the Space Shuttle’s launchpad.
The company has since adapted these fluidic dampers for buildings and bridges to help them survive earthquakes. Today, they are successfully protecting structures in some of the most quake-prone areas of the world, including Tokyo, San Francisco and Taiwan.

4. Insulation for Space
We’ve all seen runners draped in silvery “space blankets” at the end of marathons, but did you know the material, called radiant barrier insulation, was actually created for space?
Temperatures outside of Earth’s atmosphere can fluctuate widely, from hundreds of degrees below to hundreds above zero. To better protect our astronauts, during the Apollo program we invented a new kind of effective, lightweight insulation.
We developed a method of coating mylar with a thin layer of vaporized metal particles. The resulting material had the look and weight of thin cellophane packaging, but was extremely reflective—and pound-for-pound, better than anything else available.
Today the material is still used to protect astronauts, as well as sensitive electronics, in nearly all of our missions. But it has also found countless uses on the ground, from space blankets for athletes to energy-saving insulation for buildings. It also protects essential components of MRI machines used in medicine and much, much more.

Image courtesy of the U.S. Marines
5. Healthcare Monitors
Patients in hospitals are hooked up to sensors that send important health data to the nurse’s station and beyond — which means when an alarm goes off, the right people come running to help.
This technology saves lives every day. But before it reached the ICU, it was invented for something even more extraordinary: sending health data from space down to Earth.
When the Apollo astronauts flew to the Moon, they were hooked up to a system of sensors that sent real-time information on their blood pressure, body temperature, heart rate and more to a team on the ground.
The system was developed for us by Spacelabs Healthcare, which quickly adapted it for hospital monitoring. The company now has telemetric monitoring equipment in nearly every hospital around the world, and it is expanding further, so at-risk patients and their doctors can keep track of their health even outside the hospital.

Only a few people have ever walked on the Moon, but the benefits of the Apollo program for the rest of us continue to ripple widely.
In the years since, we have continued to create innovations that have saved lives, helped the environment, and advanced all kinds of technology.
Now we’re going forward to the Moon with the Artemis program and on to Mars — and building ever more cutting-edge technologies to get us there. As with the many spinoffs from the Apollo era, these innovations will transform our lives for generations to come.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 strangerthanfanfiction713 liked this · 4 years ago
strangerthanfanfiction713 liked this · 4 years ago -
 lovegooddarling liked this · 5 years ago
lovegooddarling liked this · 5 years ago -
 duck2005 liked this · 5 years ago
duck2005 liked this · 5 years ago -
 stassiebaebee liked this · 5 years ago
stassiebaebee liked this · 5 years ago -
 mousoudi20 reblogged this · 5 years ago
mousoudi20 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 mousoudi20 liked this · 5 years ago
mousoudi20 liked this · 5 years ago -
 poguegarbage reblogged this · 5 years ago
poguegarbage reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 daniiibananiii liked this · 5 years ago
daniiibananiii liked this · 5 years ago -
 thelovelydreamer17 liked this · 5 years ago
thelovelydreamer17 liked this · 5 years ago -
 poguegarbage reblogged this · 5 years ago
poguegarbage reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 poguegarbage liked this · 5 years ago
poguegarbage liked this · 5 years ago -
 fangirlfree liked this · 5 years ago
fangirlfree liked this · 5 years ago -
 kaatelyyynn liked this · 5 years ago
kaatelyyynn liked this · 5 years ago -
 simpforsomanypeople liked this · 5 years ago
simpforsomanypeople liked this · 5 years ago -
 kayleea122 liked this · 5 years ago
kayleea122 liked this · 5 years ago -
 supremestarkey reblogged this · 5 years ago
supremestarkey reblogged this · 5 years ago
