Look How Much The IPhone Camera Has Improved Over Time







Look how much the iPhone camera has improved over time
From the original iPhone to the iPhone 6, here’s how much the camera has evolved.
More Posts from Astrotidbits-blog and Others
http://player.vimeo.com/video/62255585
Comet Panstarrs captured in gorgeous time-lapse above the skies of Boulder, CO by Patrick Cullis. Lovely stuff.
Comets are mysterious frozen chunks of stellar and planetary debris, these dirty snowballs that wander in darkness until their tails are blown bright and wide by solar winds. Some follow paths so random and eccentric that they may pass a star only once, or perhaps not at all, instead floating through interstellar space, never to be known. But for those fleeting moments, like Panstarrs’ current passage, they are like icy candles lit for our enjoyment by the breath of the sun.
A song of ice and fire, indeed.
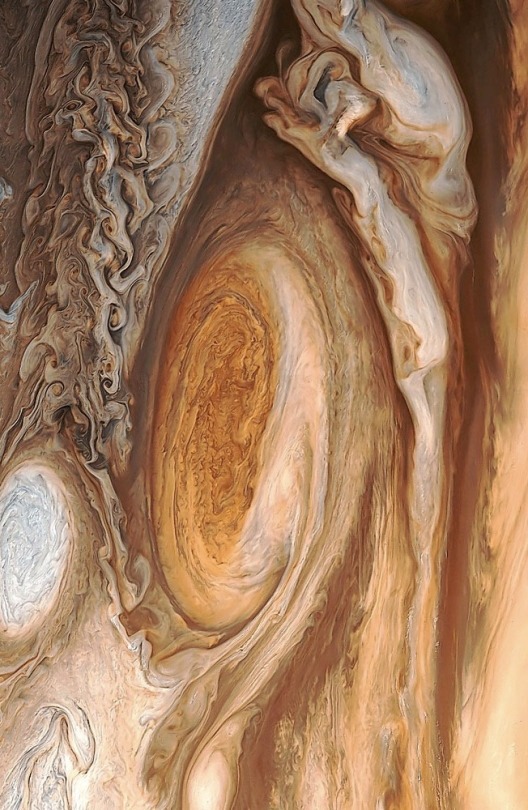

Great Red Spot of Jupiter










Cassini prepares for final orbital “Grand Finale” at Saturn.
Erik Wernquist, the same filmmaker who created 2014’s “Wanderers” and a stunning New Horizons promotional film in 2015, has created a new video highlighting NASA’s Cassini mission’s final days at Saturn. The Cassini spacecraft will begin its final series of orbits to cap a 13-year groundbreaking science mission known as the Grand Finale. For the first time ever in Cassini’s time at Saturn, the spacecraft will fly in between the planet’s rings and atmosphere. No spacecraft has ever before flown in this region of any of the solar system’s ringed planets. After 23 orbits, Cassini will dive into Saturn’s upper atmosphere September 15 where it will be destroyed. In 2008, mission managers explored a range of End of Mission scenarios that would protect Saturn’s moon’s from Earthly contaminants before ultimately deciding on atmospheric reentry. Cassini began her End of Mission manoeuvres on November 26, 2016, when it began the first of 20 ring-grazing orbits. A close flyby of Titan April 22 will alter the spacecraft’s trajectory to begin the first of 23 orbits in the Grand Finale, which will begin April 26.

Cassini launched from Earth on October 15, 1997, and entered Saturn orbit June 30, 2004. Six months later, on January 14, 2005, the European-built Huygens probe attached to the spacecraft landed on Titan, becoming the first probe to land in the outer solar system.
Originally scheduled for a four-year mission ending in 2008, Cassini received two mission extensions in 2008 and 2010, with the latter ending in 2017. With the spacecraft’s fuel reserves low, the Cassini team decided to end the mission. P/C: JPL/Erik Wernquist
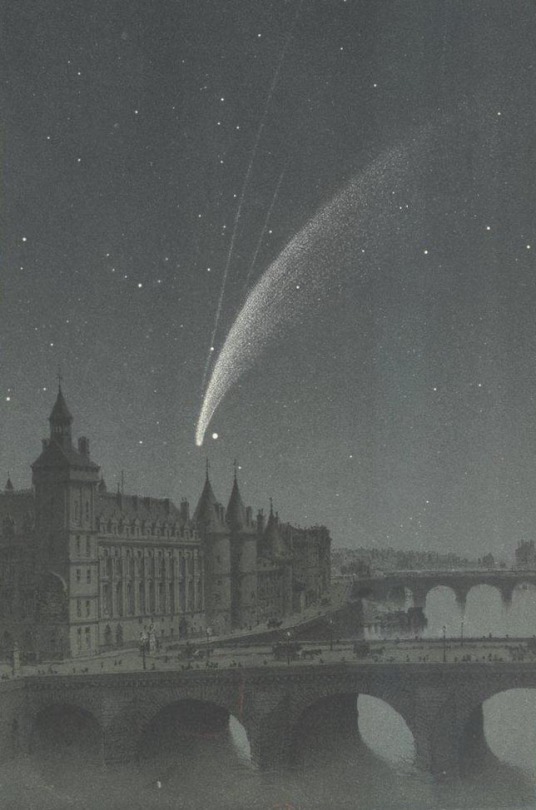

Amédée Guillemin, Les comètes (1875)
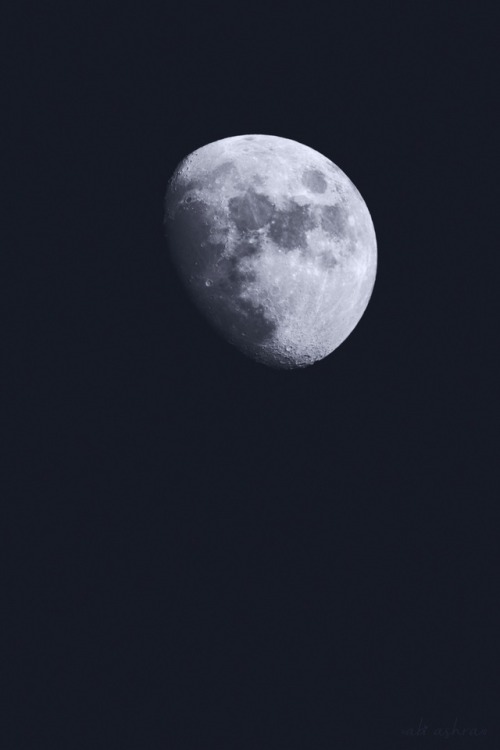

Gibbous by Abi Ashra (Tumblr)
What’s Up for March 2017?
What’s Up for March? The moon hides red star Aldebaran and crescents dazzle after dusk.

On March 4 the first quarter moon passes between Earth and the star Aldebaran, temporarily blocking our view of the star. This is called an occultation.

The occultation begins and concludes at different times, depending on where you are when you view it.

The event should be easy to see from most of the U.S., Mexico, most of Central America, the Western Caribbean and Bermuda.

Observers along a narrow path from Vancouver, British Columbia, to Hartford, Connecticut, will see the moon “graze” the star. The star will disappear and reappear repeatedly as hills and valleys on the moon alternately obscure and reveal it.

As seen from Earth, both Mercury and Venus have phases like our moon. That’s because they circle the sun inside Earth’s orbit.

Planets that orbit between Earth and the sun are known as inner or inferior planets.

Inferior planets can never be at “opposition,” which is when the planet and the sun are on opposite sides of Earth.

But inferior planets can be at “conjunction,” which is when a planet, the sun and Earth are all in a straight line.

Conjunction can happen once when the planet is on the opposite side of the sun from Earth and again when it’s on the same side of the sun as Earth.

When a planet is on the opposite side of the sun from Earth, we say it is at “superior conjunction.” As the planet moves out from behind the sun and gets closer to Earth, we see less and less of the lit side. We see phases, similar to our moon’s phases.

Mercury is at superior conjunction on March 6.

A few weeks later, the planet emerges from behind the sun and we can once again observe it. By the end of March we’ll see a last-quarter Mercury.

On April 20 Mercury reaches “inferior conjunction.”

Brilliant Venus is also racing toward its own inferior conjunction on March 25. Watch its crescent get thinner and thinner as the planet’s size appears larger and larger, because it is getting closer to Earth.

Finally, look for Jupiter to rise in the East. It will be visible all month long from late evening until dawn.

You can catch up on solar system missions and all of our missions at www.nasa.gov
Watch the full “What’s Up for March 2017″ video here:
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

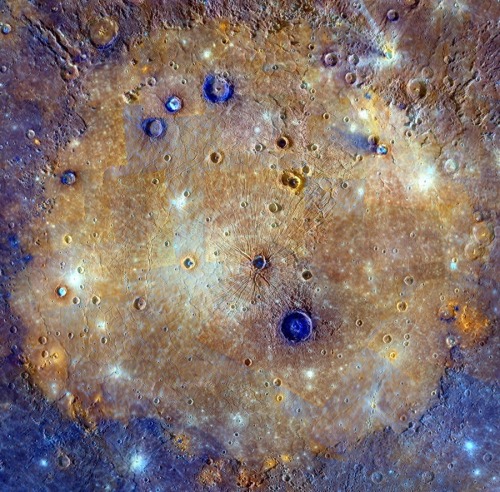
The sprawling Caloris basin on Mercury is one of the solar system’s largest impact basins, created during the early history of the solar system by the impact of a large asteroid-sized body. The multi-featured, fractured basin spans about 1,500 kilometers in this enhanced color mosaic based on image data from the Mercury-orbiting MESSENGER spacecraft. Mercury’s youngest large impact basin, Caloris was subsequently filled in by lavas that appear orange in the mosaic. Craters made after the flooding have excavated material from beneath the surface lavas. Seen as contrasting blue hues, they likely offer a glimpse of the original basin floor material. Analysis of these craters suggests the thickness of the covering volcanic lava to be 2.5-3.5 kilometers. Orange splotches around the basin’s perimeter are thought to be volcanic vents.
Image Credit: NASA, Johns Hopkins Univ. APL, Arizona State U., CIW

Saturn in Infrared from Cassini

Saturn’s moon, Daphnis, and Saturn’s rings.
-
 astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog liked this · 7 years ago
astrotidbits-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 silentniqhtz14 liked this · 8 years ago
silentniqhtz14 liked this · 8 years ago -
 zef-unicorn reblogged this · 9 years ago
zef-unicorn reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 yologadget liked this · 9 years ago
yologadget liked this · 9 years ago -
 shawnroscoe reblogged this · 9 years ago
shawnroscoe reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 shawnroscoe liked this · 9 years ago
shawnroscoe liked this · 9 years ago -
 umeclaire liked this · 9 years ago
umeclaire liked this · 9 years ago -
 emmaolbrantz liked this · 10 years ago
emmaolbrantz liked this · 10 years ago -
 younghipsterssince98 liked this · 10 years ago
younghipsterssince98 liked this · 10 years ago -
 zoct30 liked this · 10 years ago
zoct30 liked this · 10 years ago -
 limeturquoise825 reblogged this · 10 years ago
limeturquoise825 reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 queefking97 liked this · 10 years ago
queefking97 liked this · 10 years ago -
 jciari reblogged this · 10 years ago
jciari reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 tealcicada-sideblog liked this · 10 years ago
tealcicada-sideblog liked this · 10 years ago -
 wandering-jellyfish reblogged this · 10 years ago
wandering-jellyfish reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 omar135 liked this · 10 years ago
omar135 liked this · 10 years ago -
 t-e-r-r-y-o liked this · 10 years ago
t-e-r-r-y-o liked this · 10 years ago -
 premrasspaaeyaa liked this · 10 years ago
premrasspaaeyaa liked this · 10 years ago -
 fictionisbetterthanreallife reblogged this · 10 years ago
fictionisbetterthanreallife reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 reddevelopmentprint liked this · 10 years ago
reddevelopmentprint liked this · 10 years ago -
 etherealyhwh reblogged this · 10 years ago
etherealyhwh reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 shantemyton liked this · 10 years ago
shantemyton liked this · 10 years ago -
 grapefruitanarchy reblogged this · 10 years ago
grapefruitanarchy reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 snacktopia liked this · 10 years ago
snacktopia liked this · 10 years ago -
 lisalaysa liked this · 10 years ago
lisalaysa liked this · 10 years ago -
 littlejandthecity liked this · 10 years ago
littlejandthecity liked this · 10 years ago -
 where-the-ships-go liked this · 10 years ago
where-the-ships-go liked this · 10 years ago -
 nelsthefreek liked this · 10 years ago
nelsthefreek liked this · 10 years ago -
 princessbenjamin reblogged this · 10 years ago
princessbenjamin reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 bright-eyeddreamer liked this · 10 years ago
bright-eyeddreamer liked this · 10 years ago