Astrotidbits-blog - Astrotidbits.info

More Posts from Astrotidbits-blog and Others
Titan Touchdown
On Jan. 14, 2005, ESA’s Huygens probe made its descent to the surface of Saturn’s hazy moon, Titan. Carried to Saturn by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, Huygens made the most distant landing ever on another world, and the only landing on a body in the outer solar system. This video uses actual images taken by the probe during its two-and-a-half hour fall under its parachutes.

NASA’s Cassini spacecraft is set to make its first dive through the narrow gap between Saturn and its rings on April 26, 2017. Because that gap is a region no spacecraft has ever explored, Cassini will use its dish-shaped high-gain antenna (13 feet or 4 meters across) as a protective shield while passing through the ring plane. No particles larger than smoke particles are expected, but the precautionary measure is being taken on the first dive. The Cassini team will use data collected by one of the spacecraft’s science instruments (the Radio and Plasma Wave Subsystem, or RPWS) to ascertain the size and density of ring particles in the gap in advance of future dives. As a result of its antenna-forward orientation, the spacecraft will be out of contact with Earth during the dive.
Below is a list of milestones expected to occur during the event, if all goes as planned:
– 5 p.m. PDT (8 p.m. EDT) on April 25: Cassini is approaching Saturn over the planet’s northern hemisphere in advance of its first of 22 planned dives through the gap between the planet and its rings.
– 1:34 a.m. PDT (4:34 a.m. EDT) on April 26: As it passes from north to south over Saturn, Cassini begins a 14-minute turn to point its high-gain antenna into the direction of oncoming ring particles. In this orientation, the antenna acts as a protective shield for Cassini’s instruments and engineering systems.
– 2 a.m. PDT (5 a.m. EDT) on April 26: Cassini crosses the ring plane during its dive between the rings and Saturn. The spacecraft’s science instruments are collecting data, but Cassini is not in contact with Earth at this time.
– No earlier than around midnight PDT on April 26 (3 a.m. EDT on April 27): Earth has its first opportunity to regain contact with Cassini as the giant, 230-foot (70-meter) Deep Space Network antenna at Goldstone, California, listens for the spacecraft’s radio signal.

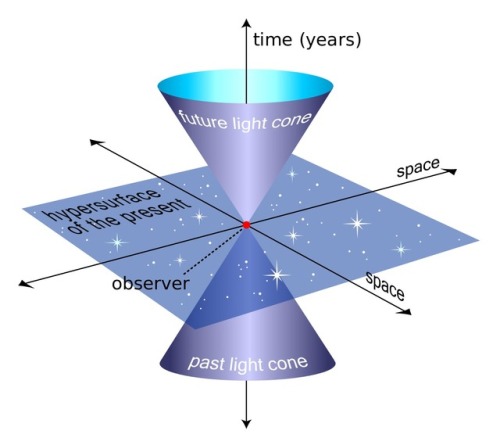

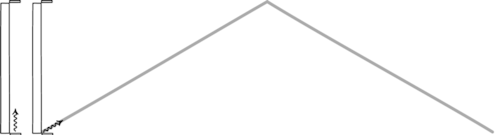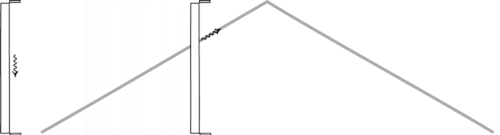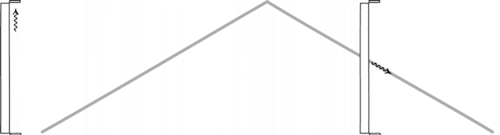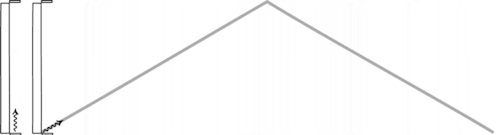

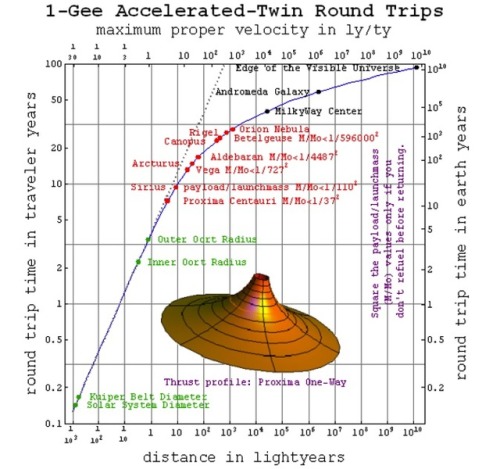
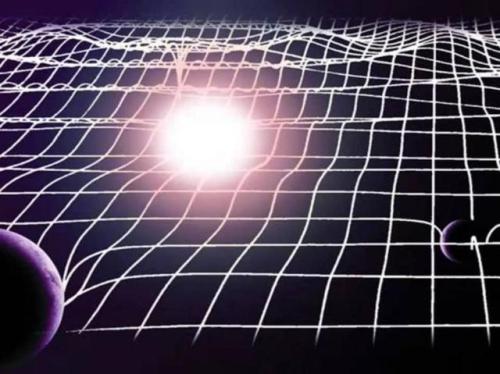
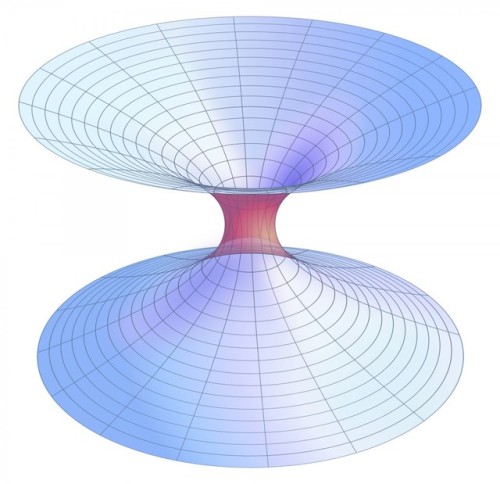

Is Time Travel Possible, According To Science?
“You can witness the evolution and destruction of humanity; the end of the Earth and Sun; the dissociation of our galaxy; the heat death of the Universe itself. So long as you have enough power in your space ship, you can travel as far into the future as you like.”
Have you ever wondered about time travel? Perhaps you have your destination in the far future, and want to see how it all turns out? Maybe you want to return to the past, and alter the future or present by your actions there? Or maybe you want to freeze time altogether? If you want to know whether it’s possible, the physics of relativity holds the answer. Special relativity allows us to control our motion through time by manipulating our motion through space. The more we move through space, the less we move through time, allowing us to travel as far as we want into the future, limited only by our energy available for space travel. But going to the past requires some specific solutions to general relativity, which may (or may not) describe our physical Universe.
What’s the status of traveling through time? Come get the scientific story (with a brand new podcast) today!
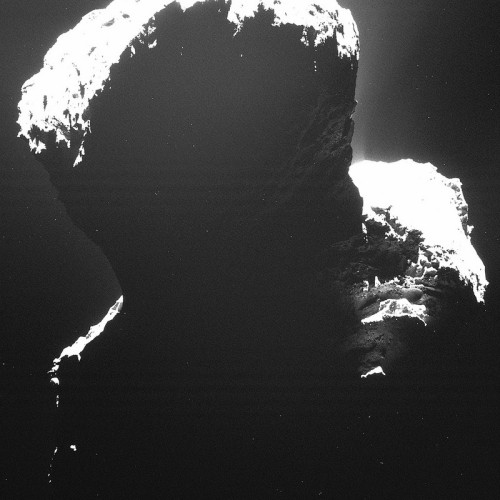
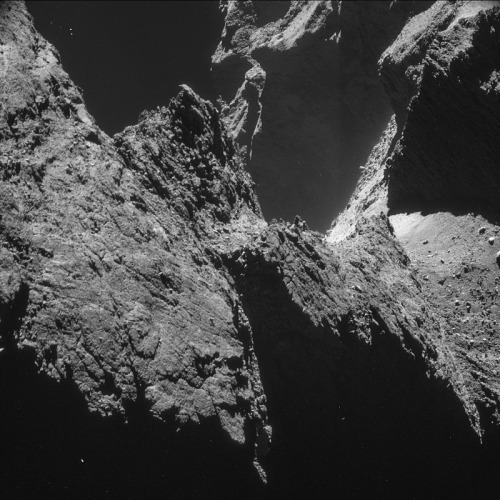
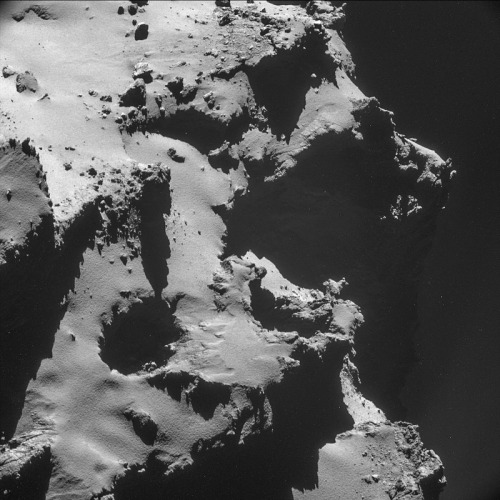
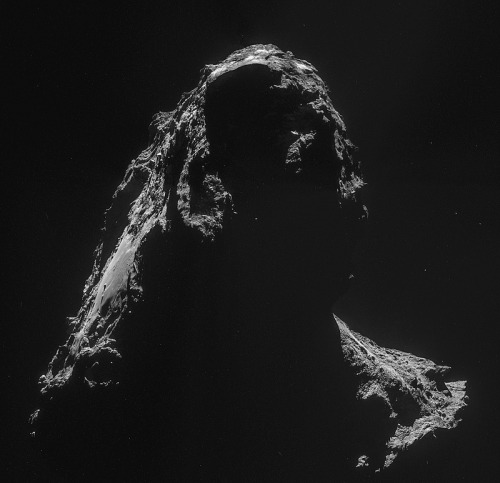
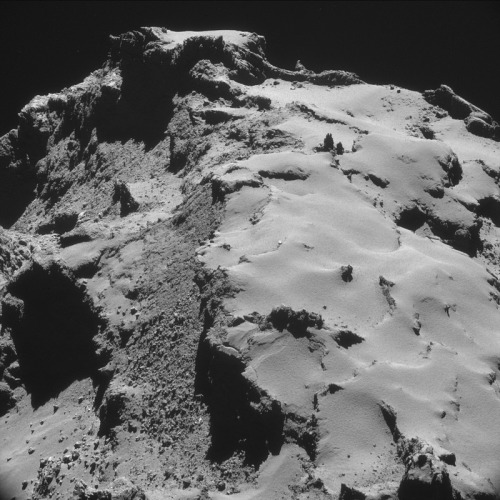
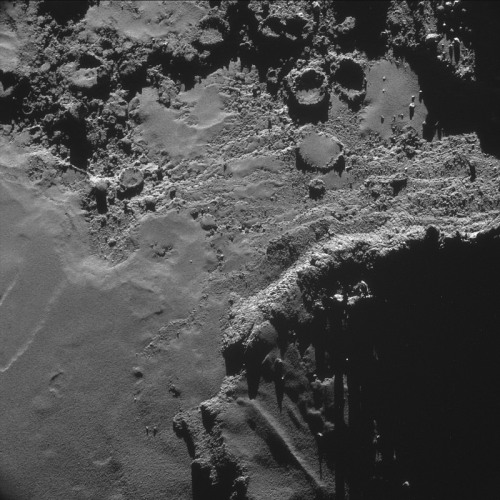
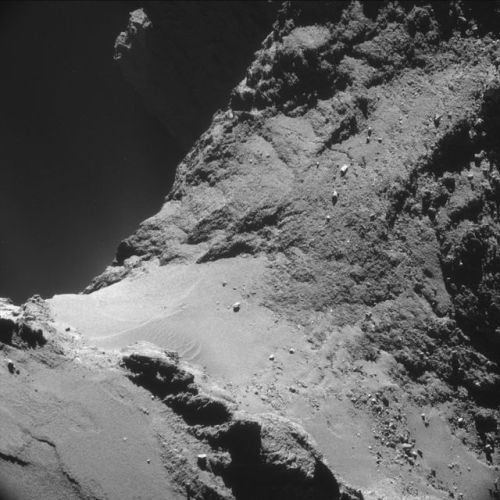





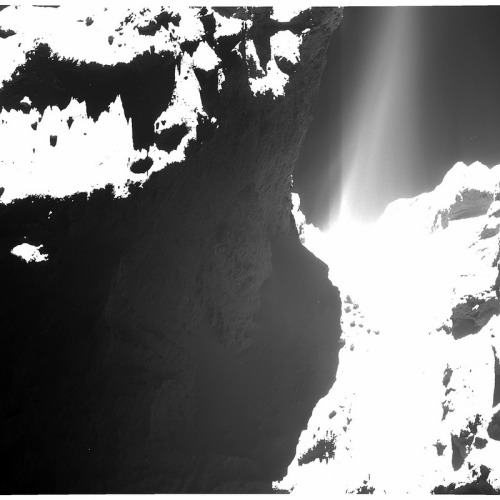


This is what a comet looks like, up close and personal.
PHOTOS FROM AN ALIEN WORLD.
I am so excited I can’t even. Source: ESA’s Flickr feed.

Solar
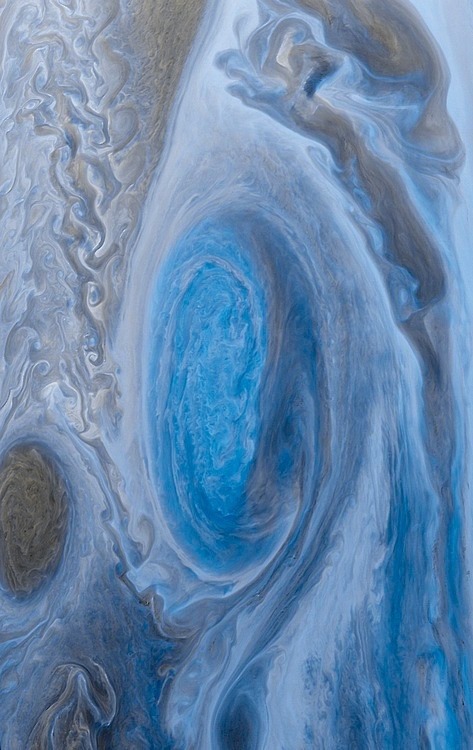

Jupiter’s Great Red Spot from Voyager 1 Color Inverted
What will become of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot? Recorded as shrinking since the 1930s, the rate of the Great Red Spot’s size appears to have accelerated just in the past few years. A hurricane larger than Earth, the Great Red Spot has been raging at least as long as telescopes could see it. Like most astronomical phenomena, the Great Red Spot was neither predicted nor immediately understood after its discovery. Although small eddies that feed into the storm system seem to play a role, a more full understanding of the gigantic storm cloud remains a topic of continued research, and may result in a better understanding of weather here on Earth. The above image is a digital enhancement of an image of Jupiter taken in 1979 by the Voyager 1 spacecraft as it zoomed by the Solar System’s largest planet. NASA’s Juno spacecraft is currently heading toward Jupiter and will arrive in 2016.
Image Credit: NASA, JPL; Digital processing: Björn Jónsson (IAAA), Color: thedemon-hauntedworld
“The images we see can only be “beautiful” or “real-looking” because they have been heavily processed, either by neural machinery or by code (in which case, both), operating below our threshold of consciousness. In the case of the software, this processing relies on norms and aesthetic judgments on the part of software engineers, so they are also unacknowledged collaborators in the image-making. There’s no such thing as a natural image; perhaps, too, there’s nothing especially artificial about the camera.” art in the age of machine intelligence — Artists and Machine Intelligence — Medium https://medium.com/artists-and-machine-intelligence/what-is-ami-ccd936394a83
(via mikerugnetta)










Cassini prepares for final orbital “Grand Finale” at Saturn.
Erik Wernquist, the same filmmaker who created 2014’s “Wanderers” and a stunning New Horizons promotional film in 2015, has created a new video highlighting NASA’s Cassini mission’s final days at Saturn. The Cassini spacecraft will begin its final series of orbits to cap a 13-year groundbreaking science mission known as the Grand Finale. For the first time ever in Cassini’s time at Saturn, the spacecraft will fly in between the planet’s rings and atmosphere. No spacecraft has ever before flown in this region of any of the solar system’s ringed planets. After 23 orbits, Cassini will dive into Saturn’s upper atmosphere September 15 where it will be destroyed. In 2008, mission managers explored a range of End of Mission scenarios that would protect Saturn’s moon’s from Earthly contaminants before ultimately deciding on atmospheric reentry. Cassini began her End of Mission manoeuvres on November 26, 2016, when it began the first of 20 ring-grazing orbits. A close flyby of Titan April 22 will alter the spacecraft’s trajectory to begin the first of 23 orbits in the Grand Finale, which will begin April 26.

Cassini launched from Earth on October 15, 1997, and entered Saturn orbit June 30, 2004. Six months later, on January 14, 2005, the European-built Huygens probe attached to the spacecraft landed on Titan, becoming the first probe to land in the outer solar system.
Originally scheduled for a four-year mission ending in 2008, Cassini received two mission extensions in 2008 and 2010, with the latter ending in 2017. With the spacecraft’s fuel reserves low, the Cassini team decided to end the mission. P/C: JPL/Erik Wernquist

open parachute during tests for Mars Science Laboratory
-
 cheffwed-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
cheffwed-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog liked this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 silvretspm liked this · 10 years ago
silvretspm liked this · 10 years ago -
 bigilsmyh reblogged this · 10 years ago
bigilsmyh reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 merrberry liked this · 11 years ago
merrberry liked this · 11 years ago -
 liveforthe-ephemeral liked this · 11 years ago
liveforthe-ephemeral liked this · 11 years ago -
 amikarat reblogged this · 11 years ago
amikarat reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 beautifully--bizzaree liked this · 11 years ago
beautifully--bizzaree liked this · 11 years ago -
 lzyixi reblogged this · 12 years ago
lzyixi reblogged this · 12 years ago -
 lzyixi liked this · 12 years ago
lzyixi liked this · 12 years ago -
 eatout1 reblogged this · 12 years ago
eatout1 reblogged this · 12 years ago -
 eatout1 liked this · 12 years ago
eatout1 liked this · 12 years ago -
 misterjordan reblogged this · 13 years ago
misterjordan reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 mermaids-and-alcohol reblogged this · 13 years ago
mermaids-and-alcohol reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 plasm0archives liked this · 13 years ago
plasm0archives liked this · 13 years ago -
 hell-inahandbasket liked this · 13 years ago
hell-inahandbasket liked this · 13 years ago -
 1126koharu liked this · 13 years ago
1126koharu liked this · 13 years ago -
 twona27 reblogged this · 13 years ago
twona27 reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 keepcalmandbestylish-blog reblogged this · 13 years ago
keepcalmandbestylish-blog reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 -grand-master- reblogged this · 13 years ago
-grand-master- reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 midnight-dweller reblogged this · 13 years ago
midnight-dweller reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 kvltvreshock-blog reblogged this · 13 years ago
kvltvreshock-blog reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 luisrobertovago reblogged this · 13 years ago
luisrobertovago reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 meltedpeach liked this · 13 years ago
meltedpeach liked this · 13 years ago -
 januarysouls reblogged this · 13 years ago
januarysouls reblogged this · 13 years ago