Don’t Assume The Gender Of My HYDROGEN! Ok

don’t assume the gender of my HYDROGEN! ok
More Posts from Astrotidbits-blog and Others

SpaceX Plans to Send 2 Tourists Around Moon in 2018
“While the trip appears to be within the technical capabilities of SpaceX, industry observers wondered whether the company could pull it off as quickly as Mr. Musk indicated. “Dates are not SpaceX’s strong suit,” said Mary Lynne Dittmar, executive director of the Coalition for Deep Space Exploration. The Dragon 2 and Falcon Heavy are years behind schedule and have yet to fly.“It strikes me as risky,” Dr. Dittmar said, adding that autonomous systems are not infallible. “I find it extraordinary that these sorts of announcements are being made when SpaceX has yet to get crew from the ground to low-Earth orbit.””

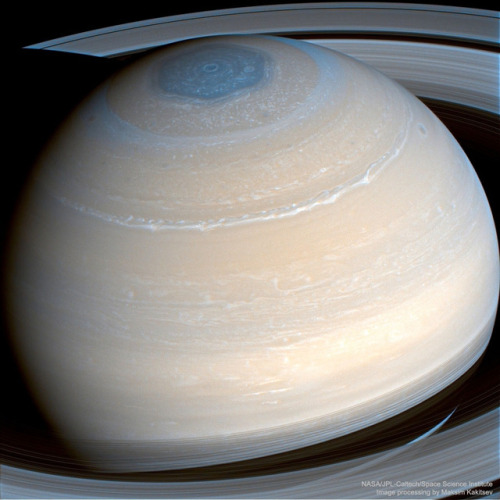
*Those razor-like shadows, they’re so black they look photoshopped
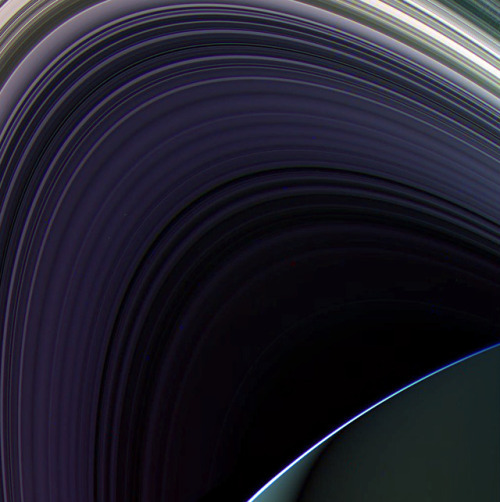

The rings of Saturn, observed by the Cassini space probe on May 3, 2017.

ASTRONOMERS CAPTURE BEST VIEW EVER OF DISINTEGRATING COMET
Astronomers have captured the sharpest, most detailed observations of a comet breaking apart 67 million miles from Earth, using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. The discovery is published online today in Astrophysical Journal Letters [http://apjl.aas.org].
In a series of images taken over three days in January 2016, Hubble showed 25 fragments consisting of a mixture of ice and dust that are drifting away from the comet at a pace equivalent to the walking speed of an adult, said David Jewitt, a professor in the UCLA departments of Earth, Planetary and Space Sciences; and Physics and Astronomy, who led the research team.
The images suggest that the roughly 4.5-billion-year-old comet, named 332P/Ikeya-Murakami, or Comet 332P, may be spinning so fast that material is ejected from its surface. The resulting debris is now scattered along a 3,000-mile-long trail, larger than the width of the continental United States.
These observations provide insight into the volatile behavior of comets as they approach the Sun and begin to vaporize, unleashing powerful forces.
“We know that comets sometimes disintegrate, but we don’t know much about why or how,” Jewitt said. “The trouble is that it happens quickly and without warning, so we don’t have much chance to get useful data. With Hubble’s fantastic resolution, not only do we see really tiny, faint bits of the comet, but we can watch them change from day to day. That has allowed us to make the best measurements ever obtained on such an object.”
The three-day observations show that the comet shards brighten and dim as icy patches on their surfaces rotate into and out of sunlight. Their shapes change, too, as they break apart. The icy relics comprise about four percent of the parent comet and range in size from roughly 65 feet wide to 200 feet wide. They are separating at only a few miles per hour as they orbit the Sun at more than 50,000 miles per hour.
The Hubble images show that the parent comet changes brightness frequently, completing a rotation every two to four hours. A visitor to the comet would see the Sun rise and set in as little as an hour, Jewitt said.
The comet is much smaller than astronomers thought, measuring only 1,600 feet across, about the length of five football fields.
Comet 332P was discovered in November 2010, after it surged in brightness and was spotted by two Japanese amateur astronomers.
Based on the Hubble data, the research team suggests that sunlight heated the surface of the comet, causing it to expel jets of dust and gas. Because the nucleus is so small, these jets act like rocket engines, spinning up the comet’s rotation, Jewitt said. The faster spin rate loosened chunks of material, which are drifting off into space. The research team calculated that the comet probably shed material over a period of months, between October and December 2015.
Jewitt suggests that some of the ejected pieces have themselves fallen to bits in a kind of cascading fragmentation. “We think these little guys have a short lifetime,” he said.
Hubble’s sharp vision also spied a chunk of material close to the comet, which may be the first salvo of another outburst. The remnant from still another flare-up, which may have occurred in 2012, is also visible. The fragment may be as large as Comet 332P, suggesting the comet split in two. But the remnant wasn’t spotted until Dec. 31, 2015, by a telescope in Hawaii.
That discovery prompted Jewitt and colleagues to request Hubble Space Telescope time to study the comet in detail.
“In the past, astronomers thought that comets die when they are warmed by sunlight, causing their ices to simply vaporize away,” Jewitt said. “But it’s starting to look like fragmentation may be more important. In comet 332P we may be seeing a comet fragmenting itself into oblivion.”
The researchers estimate that comet 332P contains enough mass for 25 more outbursts. “If the comet has an episode every six years, the equivalent of one orbit around the Sun, then it will be gone in 150 years,” Jewitt said. “It’s just the blink of an eye, astronomically speaking. The trip to the inner solar system has doomed it.”
The icy visitor hails from the Kuiper belt, a vast swarm of objects at the outskirts of our solar system. As the comet traveled across the system, it was deflected by the planets, like a ball bouncing around in a pinball machine, until Jupiter’s gravity set its current orbit, Jewitt said.


Milky Way & shooting stars.

Starry Night,
Vincent Van Gogh

Will Jupiter’s Great Red Spot turn into a wee red dot? by BOB KING
Watch out! One day it may just go away. Jupiter’s most celebrated atmospheric beauty mark, the Great Red Spot (GRS), has been shrinking for years. When I was a kid in the ’60s peering through my Edmund 6-inch reflector, not only was the Spot decidedly red, but it was extremely easy to see. Back then it really did span three Earths. Not anymore.
In the 1880s the GRS resembled a huge blimp gliding high above white crystalline clouds of ammonia and spanned 40,000 km (25, 000 miles) across. You couldn’t miss it even in those small brass refractors that were the standard amateur observing gear back in the day. Nearly one hundred years later in 1979, the Spot’s north-south extent has remained virtually unchanged, but it’s girth had shrunk to 25,000 km (15,535 miles) or just shy of two Earth diameters. Recent work done by expert astrophotographer Damian Peach using the WINJUPOS program to precisely measure the GRS in high resolution photos over the past 10 years indicates a continued steady shrinkage:
2003 Feb – 18,420km (11,445 miles)
2005 Apr – 18,000km (11,184)
2010 Sep – 17,624km (10,951)
2013 Jan – 16,954km (10,534)
2013 Sep – 15,894km (9,876)
2013 Dec – 15,302km (9,508) = 1.2 Earth diameters
If these figures stand up to professional scrutiny, it make one wonder how long the spot will continue to be a planetary highlight. It also helps explain why it’s become rather difficult to see in smaller telescopes in recent years. Yes, it’s been paler than normal and that’s played a big part, but combine pallor with a hundred-plus years of downsizing and it’s no wonder beginning amateur astronomers often struggle to locate the Spot in smaller telescopes. This observing season the Spot has developed a more pronounced red color, but unless you know what to look for, you may miss it entirely unless the local atmospheric seeing is excellent.
Not only has the Spot been shrinking, its rotation period has been speeding up. Older references give the period of one rotation at 6 days. John Rogers (British Astronomical Assn.) published a 2012 paper on the evolution of the GRS and discovered that between 2006 to 2012 – the same time as the Spot has been steadily shrinking – its rotation period has spun up to 4 days. As it shrinks, the storm appears to be conserving angular momentum by spinning faster the same way an ice skater spins up when she pulls in her arms.
Rogers also estimated a max wind speed of 300 mph, up from about 250 mph in 2006. Despite its smaller girth, this Jovian hurricane’s winds pack more punch than ever. Even more fascinating, the Great Red Spot may have even disappeared altogether from 1713 to 1830 before reappearing in 1831 as a long, pale “hollow”. According to Rogers, no observations or sketches of that era mention it. Surely something so prominent wouldn’t be missed. This begs the question of what happened in 1831. Was the “hollow” the genesis of a brand new Red Spot unrelated to the one first seen by astronomer Giovanni Cassini in 1665? Or was it the resurgence of Cassini’s Spot?
Clearly, the GRS waxes and wanes but exactly what makes it persist? By all accounts, it should have dissipated after just a few decades in Jupiter’s turbulent environment, but a new model developed by Pedram Hassanzadeh, a postdoctoral fellow at Harvard University, and Philip Marcus, a professor of fluid dynamics at the University of California-Berkeley, may help to explain its longevity. At least three factors appear to be at play:
* Jupiter has no land masses. Once a large storm forms, it can sustain itself for much longer than a hurricane on Earth, which plays itself out soon after making landfall.
* Eat or be eaten: A large vortex or whirlpool like the GRS can merge with and absorb energy from numerous smaller vortices carried along by the jet streams.
* In the Hassanzadeh and Marcus model, as the storm loses energy, it’s rejuvenated by vertical winds that transport hot and cold gases in and out of the Spot, restoring its energy. Their model also predicts radial or converging winds within the Spot that suck air from neighboring jet streams toward its center. The energy gained sustains the GRS.
If the shrinkage continues, “Great” may soon have to be dropped from the Red Spot’s title. In the meantime, Oval BA (nicknamed Red Spot Jr.) and about half the size of the GRS, waits in the wings. Located along the edge of the South Temperate Belt on the opposite side of the planet from the GRS, Oval BA formed from the merger of three smaller white ovals between 1998 and 2000. Will it give the hallowed storm a run for its money? We’ll be watching.
At left, photo of Jupiter’s enormous Great Red Spot in 1879 from Agnes Clerk’s Book ” A History of Astronomy in the 19th Century”. At right, Jupiter on Jan. 10, 2014. Credit: Damian Peach
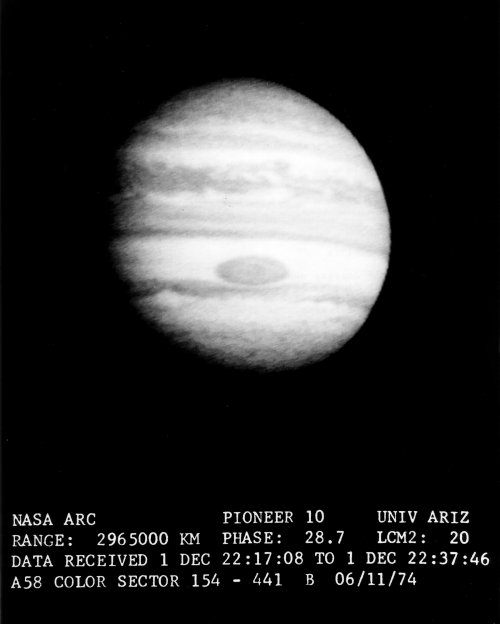

This view of Jupiter shows the giant planet’s cloud tops taken by the Pioneer 10 spacecraft as it flew past Jupiter. This view was taken from 2,695,000 kilometers (1,842,451 miles) away. It shows the 25,000 mile long Great Red Spot, which is large enough to swallow up several Earths. Individual cloud formations are visible in some detail. The bright zones appear to become split up into the detailed flow patterns of Jupiter’s atmosphere and clouds. The area surrounding the Spot in the bright South Tropical Zone, suggests a flow pattern about the Spot which is bulged toward the north by the Spot. The Spot may be a gigantic “permanent hurricane.” The gigantic cloud swirls are thousands or more miles across. Pioneer 10 flew past Jupiter in December 1974 and flew past the orbit of Pluto in 1987. A sister spacecraft, Pioneer 11 reached Jupiter in December 1975. The Pioneer Project was managed by NASA’s Ames Research Center, Mountain View, Calafornia. The spacecraft was built by TRW Systems.
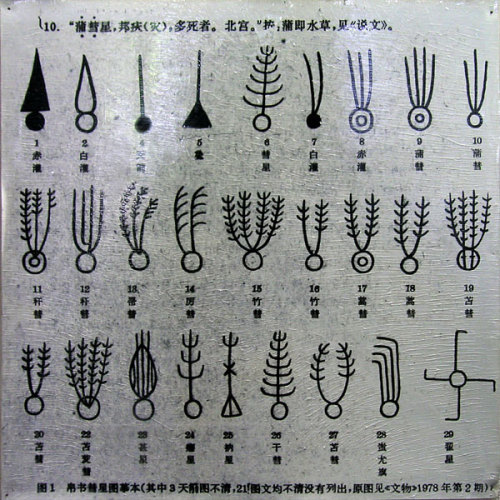

Comet shapes and characteristics from a Chinese silk book (Boshu) written during the Han dynasty (206 BC-22 AD)
-
 h1ph0p-hypn0515-t1g3r liked this · 6 years ago
h1ph0p-hypn0515-t1g3r liked this · 6 years ago -
 optecs liked this · 7 years ago
optecs liked this · 7 years ago -
 daffy-dutchboy reblogged this · 7 years ago
daffy-dutchboy reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 mallumnamuz-blog liked this · 7 years ago
mallumnamuz-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 mikeyperes liked this · 8 years ago
mikeyperes liked this · 8 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog liked this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 johnnyreyna liked this · 8 years ago
johnnyreyna liked this · 8 years ago -
 blog-dzepxich liked this · 8 years ago
blog-dzepxich liked this · 8 years ago -
 irr3alism liked this · 8 years ago
irr3alism liked this · 8 years ago -
 porcelinaofthevastocean01010101 reblogged this · 8 years ago
porcelinaofthevastocean01010101 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 dankcontent-only liked this · 8 years ago
dankcontent-only liked this · 8 years ago -
 infinitelifestory reblogged this · 8 years ago
infinitelifestory reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 theascendedhaveawoken liked this · 8 years ago
theascendedhaveawoken liked this · 8 years ago -
 alterbeing reblogged this · 8 years ago
alterbeing reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 alterbeing liked this · 8 years ago
alterbeing liked this · 8 years ago -
 cheap-bliss reblogged this · 8 years ago
cheap-bliss reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 turpentinedreams reblogged this · 8 years ago
turpentinedreams reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 t-rexsex reblogged this · 8 years ago
t-rexsex reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 b-eg reblogged this · 8 years ago
b-eg reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 u-the-artist reblogged this · 8 years ago
u-the-artist reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 metarecordings reblogged this · 8 years ago
metarecordings reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 reactshawn8869 reblogged this · 8 years ago
reactshawn8869 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mysticcollectioncandy liked this · 8 years ago
mysticcollectioncandy liked this · 8 years ago -
 billtavis liked this · 8 years ago
billtavis liked this · 8 years ago -
 photoniclabs reblogged this · 8 years ago
photoniclabs reblogged this · 8 years ago