How Do We Know Light Is A Wave?
How do we know light is a wave?
Before I answer this question, I’ll need to briefly go over a wave property called superposition. Basically, superposition is the idea that two waves can be in the same position at the same time, and interfere with each other:
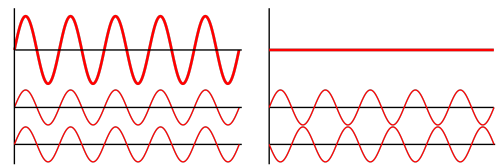
When the two waves add to each other and make a larger wave, we call this constructive interference. When the waves cancel each other out, we call this destructive interference.
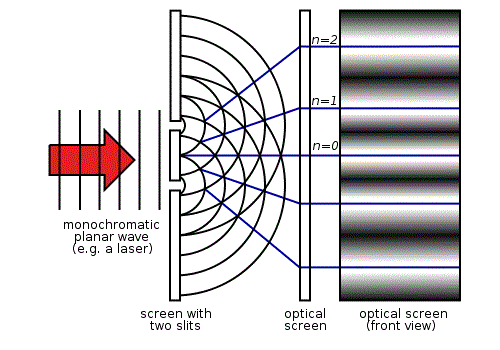
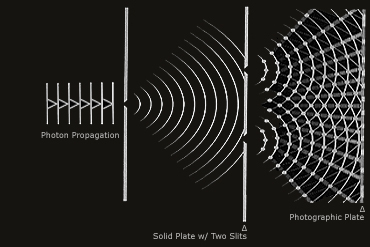
Now we’re going to move on to the Double Slit Experiment. Basically, you shine a beam of light at a piece of metal, cardboard, etc with two slits in it, with a surface behind it where you can see the light hit it.
If light is a wave, what we’d expect to see would be an interference pattern created by the light from the first slit interfering with light from the second slit, which is exactly what we see. It’s a pattern of constructive interference (brighter regions) and destructive interference (darker regions), looking like this:
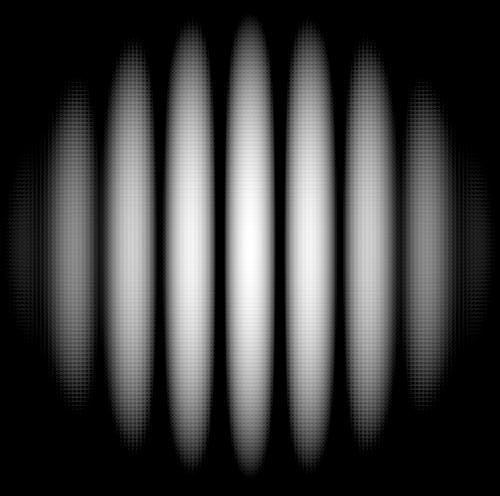

These images are helpful:
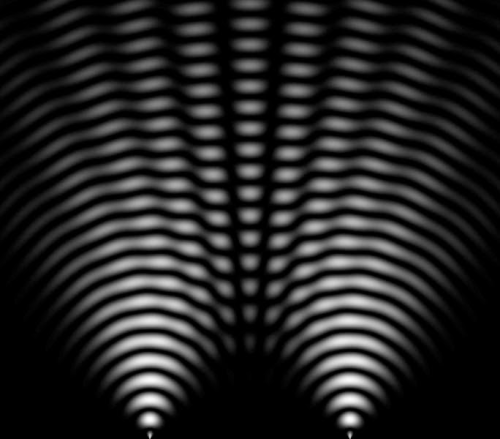
that is how we know light acts as a wave!!
More Posts from Astrotidbits-blog and Others
Hydra 3K Medium Mech da Marco Marozzi

Observing the Skies Above by Kirby Wright on Flickr.


The Usborne Book of the Future




Blackmagic URSA 4K Digital Cinema Camera
And now that one special, prestigious piece of gear has finally arrived to round off the years of camera development and take you to the vertiginous peaks of unbelievable footage quality and extreme equipment versatility: the recently released Blackmagic URSA 4K Digital Cinema Camera is the ultimate camera for professional film crews and keen solo cameramen looking to revolutionize their filming sessions.

Orbital Symphony

ham radio.
Fun Facts About Mars

Mars is a cold desert world, and is the fourth planet from the sun. It is half the diameter of Earth and has the same amount of dry land. Like Earth, Mars has seasons, polar ice caps, volcanoes, canyons and weather, but its atmosphere is too thin for liquid water to exist for long on the surface. There are signs of ancient floods on the Red Planet, but evidence for water now exists mainly in icy soil and thin clouds.

Earth has one, Mars has two…moons of course! Phobos (fear) and Deimos (panic) are the Red Planet’s two small moons. They are named after the horses that pulled the chariot of the Greek war god Ares, the counterpart to the Roman war god Mars.

The diameter of Mars is 4220 miles (6792 km). That means that the Red Planet is twice as big as the moon, but the Earth is twice as big as Mars.

Since Mars has less gravity than Earth, you would weigh 62% less than you do here on our home planet. Weigh yourself here on the Planets App. What’s the heaviest thing you’ve ever lifted? On Mars, you could have lifted more than twice that! Every 10 pounds on Earth only equals 4 pounds on the Red Planet. Find out why HERE.

Mass is the measurement of the amount of matter something contains. Mars is about 1/10th of the mass of Earth.

Mars and Earth are at their closest point to each other about every two years, with a distance of about 33 million miles between them at that time. The farthest that the Earth and Mars can be apart is: 249 million miles. This is due to the fact that both Mars and Earth have elliptical orbits and Mars’ orbit is tilted in comparison with the Earth’s. They also orbit the sun at different rates.

The temperature on Mars can be as high as 70 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius) or as low as about –225 degrees Fahrenheit (-153 degrees Celsius). How hot or cold the surface varies between day and night and among seasons. Mars is colder than Earth because it is farther from the sun.

You know that onions have layers, but did you know that Mars has layers too? Like Earth, Mars has a crust, a mantle and a core. The same stuff even makes up the planet layers: iron and silicate.

Ever wonder why it’s so hard launching things to space? It’s because the Earth has a log of gravity! Gravity makes things have weight, and the greater the gravity, the more it weights. On Mars, things weigh less because the gravity isn’t as strong.

Take a deep breath. What do you think you just breathed in? Mostly Nitrogen, about a fifth of that breath was Oxygen and the rest was a mix of other gases. To get the same amount of oxygen from one Earth breath, you’d have to take around 14,500 breaths on Mars! With the atmosphere being 100 times less dense, and being mostly carbon dioxide, there’s not a whole lot of oxygen to breathe in.

Mars has about 15% of Earth’s volume. To fill Earth’s volume, it would take over 6 Mars’ volumes.
For more fun Mars facts, visit HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com





NASA’s Cassini spacecraft is set to make its first dive through the narrow gap between Saturn and its rings on April 26, 2017. Because that gap is a region no spacecraft has ever explored, Cassini will use its dish-shaped high-gain antenna (13 feet or 4 meters across) as a protective shield while passing through the ring plane. No particles larger than smoke particles are expected, but the precautionary measure is being taken on the first dive. The Cassini team will use data collected by one of the spacecraft’s science instruments (the Radio and Plasma Wave Subsystem, or RPWS) to ascertain the size and density of ring particles in the gap in advance of future dives. As a result of its antenna-forward orientation, the spacecraft will be out of contact with Earth during the dive.
Below is a list of milestones expected to occur during the event, if all goes as planned:
– 5 p.m. PDT (8 p.m. EDT) on April 25: Cassini is approaching Saturn over the planet’s northern hemisphere in advance of its first of 22 planned dives through the gap between the planet and its rings.
– 1:34 a.m. PDT (4:34 a.m. EDT) on April 26: As it passes from north to south over Saturn, Cassini begins a 14-minute turn to point its high-gain antenna into the direction of oncoming ring particles. In this orientation, the antenna acts as a protective shield for Cassini’s instruments and engineering systems.
– 2 a.m. PDT (5 a.m. EDT) on April 26: Cassini crosses the ring plane during its dive between the rings and Saturn. The spacecraft’s science instruments are collecting data, but Cassini is not in contact with Earth at this time.
– No earlier than around midnight PDT on April 26 (3 a.m. EDT on April 27): Earth has its first opportunity to regain contact with Cassini as the giant, 230-foot (70-meter) Deep Space Network antenna at Goldstone, California, listens for the spacecraft’s radio signal.

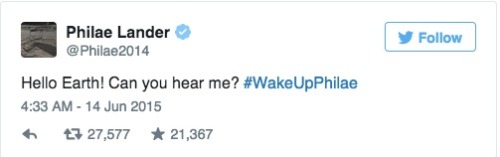
Comet lander Philae wakes up: How it happened and what’s next
By Lauren Raab
Philae, the first spacecraft to land on a comet, surprised and delighted scientists this weekend by waking up and reestablishing contact with Earth, seven months after running out of power. It “spoke” for more than a minute, according to the European Space Agency, and it’s expected to be able to continue gathering information and sending it home.
Here’s a look at what the lander has done so far and what will happen next.
Continue Reading.
-
 adookeran liked this · 1 year ago
adookeran liked this · 1 year ago -
 ercombeaugink liked this · 1 year ago
ercombeaugink liked this · 1 year ago -
 bug-s0da liked this · 2 years ago
bug-s0da liked this · 2 years ago -
 lovealesia liked this · 2 years ago
lovealesia liked this · 2 years ago -
 depressednostalgia liked this · 4 years ago
depressednostalgia liked this · 4 years ago -
 oxxxxc1zzzzzzzzzzzzz7 reblogged this · 4 years ago
oxxxxc1zzzzzzzzzzzzz7 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 oxxxxc1zzzzzzzzzzzzz7 liked this · 4 years ago
oxxxxc1zzzzzzzzzzzzz7 liked this · 4 years ago