The Usborne Book Of The Future


The Usborne Book of the Future
More Posts from Astrotidbits-blog and Others
Solar System: 10 Things to Know This Week
State of the Solar System: 10 quick updates from around our galactic neighborhood.
1. Powered by the Sun

Fifty-nine years ago, Vanguard 1 launched to demonstrate a new spacecraft technology – solar power. We’ve been going farther and for longer ever since.
+More on Vanguard 1
2. Mapping Mercury

A big week in history for exploration of the innermost planet. On March 16, 1975, our Mariner 10 made its third and final flyby of Mercury. One day and 36 years later, MESSENGER became the first spacecraft to orbit Mercury. Next up: ESA’s BepiColumbo, undergoing testing now, is set to launch for Mercury in 2018.
+Missions to Mercury
3. Return to Venus

U.S. and Russian scientists are discussing a planned revival of the successful Venera program that revealed much about Venus in the 1960s, 70s and 80s. Meanwhile, Japan’s Akatsuki orbiter continues to study our sister planet.
+More on Venera-D
4. Rocket Power

Back on Earth 91 years ago (March 16, 1926), inventor and dreamer Robet Goddard changed the world forever with the first test of a liquid-fueled rocket. We’ve been going farther and faster ever since.
+More on Goddard
5. Moon Watch

Our Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) has been sending a steady stream of high-resolution images back to Earth for more than seven years.
+More on LRO
6. Busy Mars

There are currently five orbiters (Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, Mars Odyssey, MAVEN, ESA’s Mars Express and India’s Mars Orbiter Mission) and two rovers (Curiosity and Opportunity) exploring Mars, making it second only to Earth in the number of robotic spacecraft studying its secrets.
+Meet the Mars Fleet
7. Vote for Jupiter

Polls close today (March 20) so vote not to point a real spacecraft camera at Jupiter during the mission’s 5th perijove pass.
+Vote now
8. Science to the Last Second

In a little less than six months, our Cassini orbiter will plunge into Saturn as a spectacular finale to its 19-year mission – but not before it embarks on a completely new mission into unexplored space between Saturn and its mighty rings.
+More on Cassini’s Grand Finale
9. By George?

Happy belated birthday to Uranus, discovered on March 13, 1781 by William Herschel. The English astronomer wanted to name his discovery – the first planet discovered in recorded history – “Georgium Sidus” after England’s King George III. But he was overruled, and astronomer stuck with traditional mythological names – creating an opportunity for 263 years of student jokes at the expense of the ice giant planet’s name.
+More on Uranus
10. Go Farther

The round trip light time from Voyager 1 to Earth is more than 38 hours. Voyager 1 is almost 13 billion miles from our home planet.
+More on Voyager
Discover more lists of 10 things to know about our solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com


Come check us out for all your astronomy needs!!!
www.astrotidbits.com




Blackmagic URSA 4K Digital Cinema Camera
And now that one special, prestigious piece of gear has finally arrived to round off the years of camera development and take you to the vertiginous peaks of unbelievable footage quality and extreme equipment versatility: the recently released Blackmagic URSA 4K Digital Cinema Camera is the ultimate camera for professional film crews and keen solo cameramen looking to revolutionize their filming sessions.
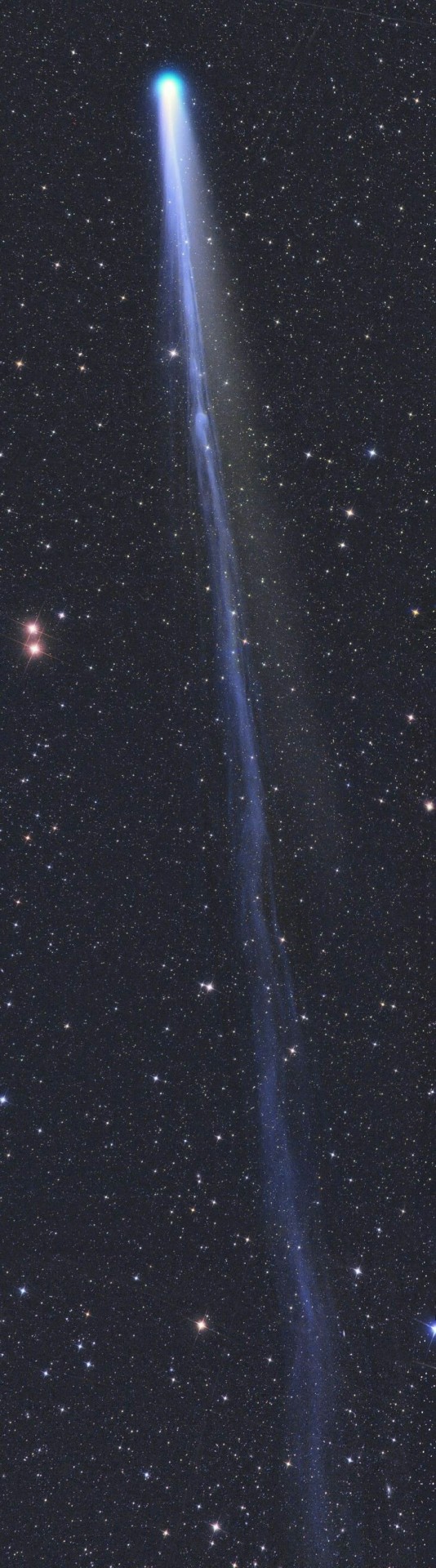

Comet Lovejoy C/2013 R1. Taken by Gerald Rhemann, December 2013.

The orbit of Jupiter protects the Earth from asteroids.
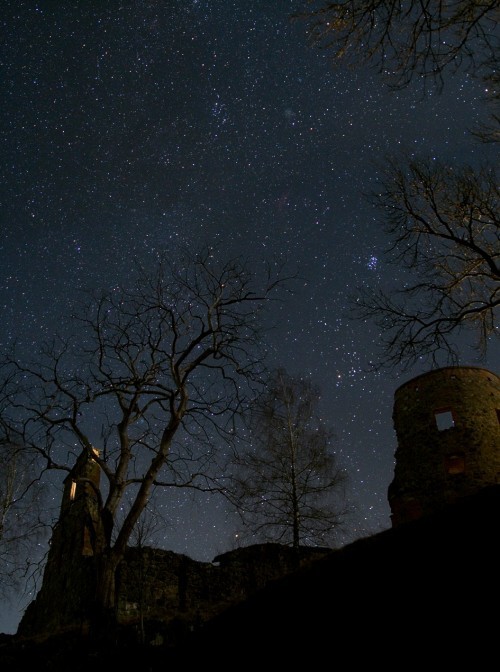

Starry Night Castle. Credit & Copyright: P-M Hedén
The Pleiades star cluster seems to lie just beyond the trees above a dark castle tower in this dramatic view. This starry sky also features bright star Aldebaran below the Pleiades and a small, faint, fuzzy cloud otherwise known as Comet Holmes near picture center at the top of the field. Starry Night Castle might be an appropriate name for the medieval castle ruin in the foreground. But its traditional name is Mörby Castle, found north of Stockholm, near lake Skedviken in Norrtälje, Sweden.









Saturn’s Moon, Enceladus, Is Our Closest Great Hope For Life Beyond Earth
“Cassini provided scientists with a wealth of data about Enceladus’ surface and the composition of its powerful plumes. This data showed evidence of a deep saltwater ocean with an energy source beneath Enceladus’ surface. The presence of water, warmth, and organic molecules are the necessary requirements for sustaining life as we know it. Water is proven to exist, while the tidal forces from Saturn provide the necessary heat. Based on observations of other bodies in the Solar System, Enceladus likely contains the raw ingredients for life as well. The suspected existence of all three hints at the possible presence of the precursors to amino acids in this vast subsurface ocean. Should we find extraterrestrial life on Enceladus – or in the geyser-like plumes erupting into space – the implications are almost incomprehensible.”
When you think about life beyond Earth, you likely think of it occurring on a somewhat Earth-like planet. A rocky world, with either a past or present liquid ocean atop the surface, seems ideal. But that might not even be where life on Earth originated! Deep beneath the Earth’s surface, geologically active hydrothermal vents currently support diverse colonies of life without any energy from the Sun. Saturn’s icy moon, Enceladus, has a subsurface ocean unlike any other world we’ve yet discovered. The tidal forces of Saturn itself provide the necessary heat, and also create cracks in the Enceladean surface, enabling massive geysers. This subsurface ocean rises hundreds of kilometers high, regularly resurfaces the world with a coat of fresh ice, and even creates the E-ring of Saturn. But most spectacularly, it may house actively living organisms, and could be the next-best world for life, after Earth, in the Solar System today.
Come get the full story on Enceladus, and welcome Starts With A Bang’s newest contributor, the remarkable Jesse Shanahan!

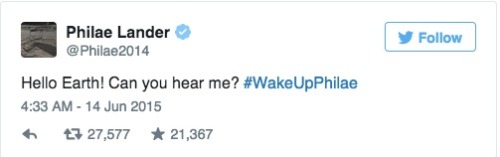
Comet lander Philae wakes up: How it happened and what’s next
By Lauren Raab
Philae, the first spacecraft to land on a comet, surprised and delighted scientists this weekend by waking up and reestablishing contact with Earth, seven months after running out of power. It “spoke” for more than a minute, according to the European Space Agency, and it’s expected to be able to continue gathering information and sending it home.
Here’s a look at what the lander has done so far and what will happen next.
Continue Reading.
-
 apexgrodd liked this · 2 years ago
apexgrodd liked this · 2 years ago -
 tom-tomorrow reblogged this · 4 years ago
tom-tomorrow reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 droidmom reblogged this · 5 years ago
droidmom reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ss82arts-movin-accounts liked this · 5 years ago
ss82arts-movin-accounts liked this · 5 years ago -
 anxvu liked this · 6 years ago
anxvu liked this · 6 years ago -
 destinedlife72 liked this · 6 years ago
destinedlife72 liked this · 6 years ago -
 blogquantumreality liked this · 7 years ago
blogquantumreality liked this · 7 years ago -
 ts26min liked this · 7 years ago
ts26min liked this · 7 years ago -
 joserubenrr-blog liked this · 7 years ago
joserubenrr-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 lynnie51 liked this · 7 years ago
lynnie51 liked this · 7 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog liked this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 walkingwithmountains reblogged this · 8 years ago
walkingwithmountains reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 cgbk10 liked this · 8 years ago
cgbk10 liked this · 8 years ago -
 dn3c liked this · 8 years ago
dn3c liked this · 8 years ago -
 haiifaa reblogged this · 8 years ago
haiifaa reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 letrounoire reblogged this · 8 years ago
letrounoire reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mvunirah reblogged this · 8 years ago
mvunirah reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mvunirah liked this · 8 years ago
mvunirah liked this · 8 years ago -
 enigmatic7-n reblogged this · 8 years ago
enigmatic7-n reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 papermillgraffiti liked this · 8 years ago
papermillgraffiti liked this · 8 years ago -
 thefoxwell liked this · 8 years ago
thefoxwell liked this · 8 years ago -
 i-like-thing reblogged this · 8 years ago
i-like-thing reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 longdickshawty liked this · 8 years ago
longdickshawty liked this · 8 years ago -
 redpandedu reblogged this · 8 years ago
redpandedu reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 xowatle liked this · 8 years ago
xowatle liked this · 8 years ago -
 jihyo-x reblogged this · 8 years ago
jihyo-x reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 rickowensn reblogged this · 8 years ago
rickowensn reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 david-bolin reblogged this · 8 years ago
david-bolin reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 danhon liked this · 8 years ago
danhon liked this · 8 years ago -
 realspaceships liked this · 8 years ago
realspaceships liked this · 8 years ago -
 domsantoleri reblogged this · 8 years ago
domsantoleri reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 domsantoleri liked this · 8 years ago
domsantoleri liked this · 8 years ago -
 wimagine liked this · 8 years ago
wimagine liked this · 8 years ago -
 mooblethecat reblogged this · 8 years ago
mooblethecat reblogged this · 8 years ago