Experiment Resolves Mystery About Wind Flows On Jupiter
Experiment resolves mystery about wind flows on Jupiter
Using a spinning table and a massive garbage can, geophysicist leads team in simulating the planet’s atmosphere
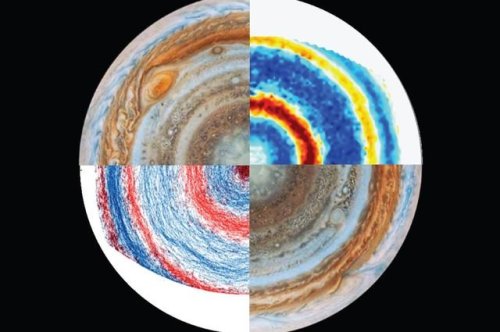
One mystery has been whether the jets exist only in the planet’s upper atmosphere – much like Earth’s own jet streams – or whether they plunge into Jupiter’s gaseous interior. If the latter is true, it could reveal clues about the planet’s interior structure and internal dynamics.
Now, UCLA geophysicist Jonathan Aurnou and collaborators in Marseille, France, have simulated Jupiter’s jets in the laboratory for the first time. Their work demonstrates that the winds likely extend thousands of miles below Jupiter’s visible atmosphere.
This research is published online in Nature Physics.
Keep reading
More Posts from Astrotidbits-blog and Others
Fun Facts About Mars

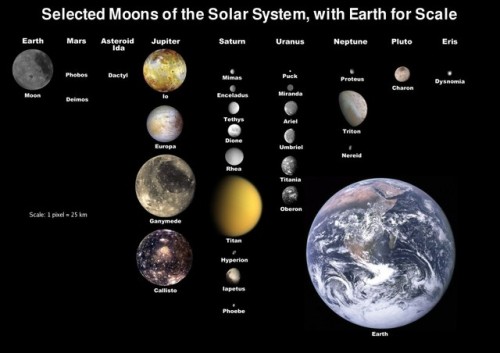
Mars is a cold desert world, and is the fourth planet from the sun. It is half the diameter of Earth and has the same amount of dry land. Like Earth, Mars has seasons, polar ice caps, volcanoes, canyons and weather, but its atmosphere is too thin for liquid water to exist for long on the surface. There are signs of ancient floods on the Red Planet, but evidence for water now exists mainly in icy soil and thin clouds.

Earth has one, Mars has two…moons of course! Phobos (fear) and Deimos (panic) are the Red Planet’s two small moons. They are named after the horses that pulled the chariot of the Greek war god Ares, the counterpart to the Roman war god Mars.

The diameter of Mars is 4220 miles (6792 km). That means that the Red Planet is twice as big as the moon, but the Earth is twice as big as Mars.

Since Mars has less gravity than Earth, you would weigh 62% less than you do here on our home planet. Weigh yourself here on the Planets App. What’s the heaviest thing you’ve ever lifted? On Mars, you could have lifted more than twice that! Every 10 pounds on Earth only equals 4 pounds on the Red Planet. Find out why HERE.

Mass is the measurement of the amount of matter something contains. Mars is about 1/10th of the mass of Earth.

Mars and Earth are at their closest point to each other about every two years, with a distance of about 33 million miles between them at that time. The farthest that the Earth and Mars can be apart is: 249 million miles. This is due to the fact that both Mars and Earth have elliptical orbits and Mars’ orbit is tilted in comparison with the Earth’s. They also orbit the sun at different rates.

The temperature on Mars can be as high as 70 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius) or as low as about –225 degrees Fahrenheit (-153 degrees Celsius). How hot or cold the surface varies between day and night and among seasons. Mars is colder than Earth because it is farther from the sun.

You know that onions have layers, but did you know that Mars has layers too? Like Earth, Mars has a crust, a mantle and a core. The same stuff even makes up the planet layers: iron and silicate.

Ever wonder why it’s so hard launching things to space? It’s because the Earth has a log of gravity! Gravity makes things have weight, and the greater the gravity, the more it weights. On Mars, things weigh less because the gravity isn’t as strong.

Take a deep breath. What do you think you just breathed in? Mostly Nitrogen, about a fifth of that breath was Oxygen and the rest was a mix of other gases. To get the same amount of oxygen from one Earth breath, you’d have to take around 14,500 breaths on Mars! With the atmosphere being 100 times less dense, and being mostly carbon dioxide, there’s not a whole lot of oxygen to breathe in.

Mars has about 15% of Earth’s volume. To fill Earth’s volume, it would take over 6 Mars’ volumes.
For more fun Mars facts, visit HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Escape velocity
A snippet from a full page graphic - vintage scientific illustration c.1960





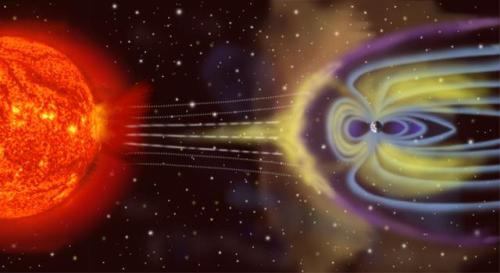
NASA’s MAVEN Discovers How Mars Lost Its Atmosphere
“The good news for us, mind you, is that the magnetic field here on Earth shows no sign of ceasing anytime soon. The dynamo in the core may do things like flip and reverse, swapping north-and-south magnetic poles, but we should continue to stay protected from the solar wind far into the foreseeable future: for billions of years (at least) to be sure. We could, conceivably, one day suffer the same fate as Mars, but our mass, our rotation and our active, dynamic core should keep the Earth’s magnetic field in business for at least as long as the Sun shines!”
If you had taken a trip to our Solar System four billion years ago, you would have found two worlds with liquid water oceans, temperate atmospheres and all the conditions we believe are needed for life. Earth would have been one of them, but Mars would have met all those criteria, too. It was long suspected that something happened to Mars around a billion years into the Solar System’s history that caused it to lose its atmosphere, something that should still be going on today. Thanks to NASA’s Maven mission, we’ve measured this atmospheric stripping by the Sun for the first time, and we’ve reached a few incredible conclusions, including that in about two billion years, Mars will be completely airless, and that if we were to terraform Mars today, it would hang onto this new atmosphere for millions of years.
Come get the full story of how Mars lost its atmosphere, and learn what NASA’s Maven mission has taught us so far!
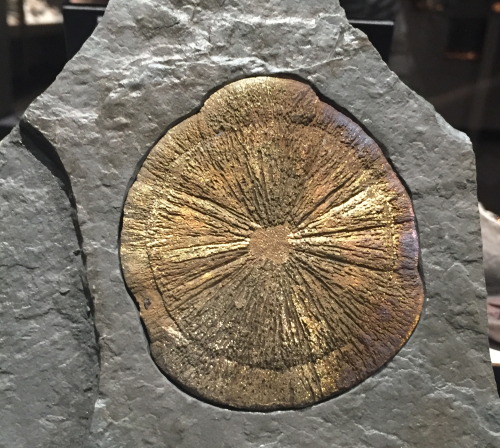


This “Pyrite Sun” may look like a sand dollar, but it is actually a concretion that was found in Illinois.


Saturn and Jupiter You can see Jupiter’s moon, Io, casting a shadow onto the gas giant. Credit and Source: nomorelickfoot
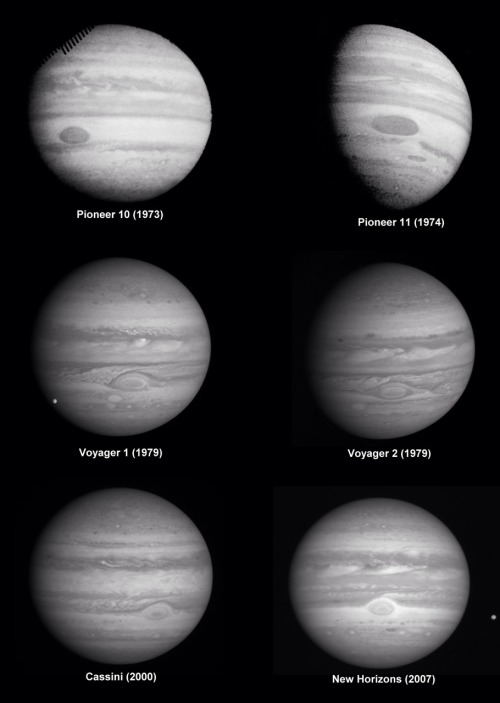

Jupiter as seen by six different spacecraft.
NASA / JPL / SSI / JHUAPL / SwRI / Björn Jónsson


Using a shortwave radio to listen to Jupiter and the Sun.
Thunder Snow!
Ground those antennas kids, winter’s got more than the white stuff today for us!
-
 marx-xiii liked this · 7 years ago
marx-xiii liked this · 7 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog liked this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 bet3hany liked this · 8 years ago
bet3hany liked this · 8 years ago -
 mishmesh reblogged this · 8 years ago
mishmesh reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 howstrangethemusicsoundstome reblogged this · 8 years ago
howstrangethemusicsoundstome reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 howstrangethemusicsoundstome liked this · 8 years ago
howstrangethemusicsoundstome liked this · 8 years ago -
 utot-atbp liked this · 8 years ago
utot-atbp liked this · 8 years ago -
 rebeccadt liked this · 8 years ago
rebeccadt liked this · 8 years ago -
 littleplasticspaceship reblogged this · 8 years ago
littleplasticspaceship reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 if-i-was-a-wyrm liked this · 8 years ago
if-i-was-a-wyrm liked this · 8 years ago -
 hipstableu reblogged this · 8 years ago
hipstableu reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 tumbleweed-chaser liked this · 8 years ago
tumbleweed-chaser liked this · 8 years ago -
 iwannabetherecusiloveu liked this · 8 years ago
iwannabetherecusiloveu liked this · 8 years ago -
 inevitablesurrender liked this · 8 years ago
inevitablesurrender liked this · 8 years ago -
 narcicious reblogged this · 8 years ago
narcicious reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 narcicious liked this · 8 years ago
narcicious liked this · 8 years ago -
 thisisacatperson reblogged this · 8 years ago
thisisacatperson reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ntrlnkd liked this · 8 years ago
ntrlnkd liked this · 8 years ago -
 chris9076 reblogged this · 8 years ago
chris9076 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 chris9076 liked this · 8 years ago
chris9076 liked this · 8 years ago -
 otterchops liked this · 8 years ago
otterchops liked this · 8 years ago -
 rabbianca liked this · 8 years ago
rabbianca liked this · 8 years ago -
 littleplasticspaceship liked this · 8 years ago
littleplasticspaceship liked this · 8 years ago -
 pequod-shipwreck reblogged this · 8 years ago
pequod-shipwreck reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 jm0ntana reblogged this · 8 years ago
jm0ntana reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 jm0ntana liked this · 8 years ago
jm0ntana liked this · 8 years ago -
 tilbnifpoe reblogged this · 8 years ago
tilbnifpoe reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 lumiharpy liked this · 8 years ago
lumiharpy liked this · 8 years ago -
 brute-force-euphoria liked this · 8 years ago
brute-force-euphoria liked this · 8 years ago -
 oneapplepiefromscratchplease reblogged this · 8 years ago
oneapplepiefromscratchplease reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 oneapplepiefromscratchplease liked this · 8 years ago
oneapplepiefromscratchplease liked this · 8 years ago -
 frenchfrymetothemoon liked this · 8 years ago
frenchfrymetothemoon liked this · 8 years ago -
 sptmcontiuum reblogged this · 8 years ago
sptmcontiuum reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 analamasblog liked this · 8 years ago
analamasblog liked this · 8 years ago -
 kammartinez reblogged this · 8 years ago
kammartinez reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 sagansense reblogged this · 8 years ago
sagansense reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 inspirement liked this · 8 years ago
inspirement liked this · 8 years ago