Mercury In Enhanced Color, Imaged By MESSENGER
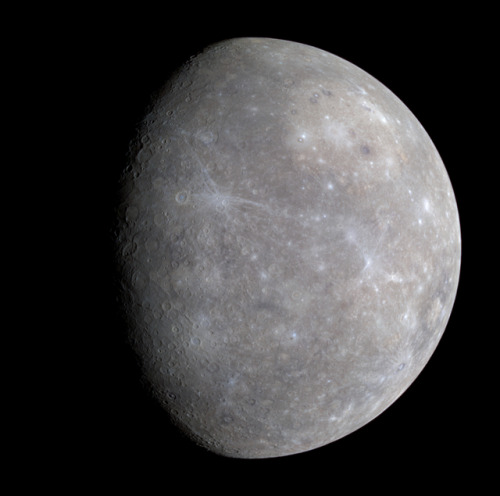

Mercury in enhanced color, imaged by MESSENGER
Credit: NASA / JPL
More Posts from Astrotidbits-blog and Others
Experiment resolves mystery about wind flows on Jupiter
Using a spinning table and a massive garbage can, geophysicist leads team in simulating the planet’s atmosphere
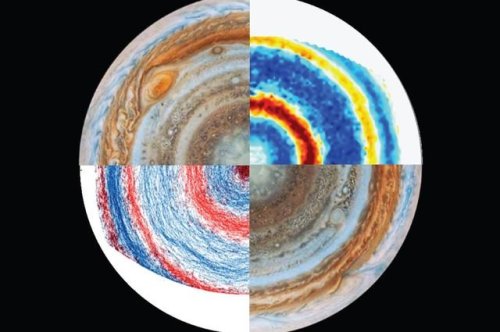
One mystery has been whether the jets exist only in the planet’s upper atmosphere – much like Earth’s own jet streams – or whether they plunge into Jupiter’s gaseous interior. If the latter is true, it could reveal clues about the planet’s interior structure and internal dynamics.
Now, UCLA geophysicist Jonathan Aurnou and collaborators in Marseille, France, have simulated Jupiter’s jets in the laboratory for the first time. Their work demonstrates that the winds likely extend thousands of miles below Jupiter’s visible atmosphere.
This research is published online in Nature Physics.
Keep reading

How I Discovered Halley’s Comet, by Edmond Halley
On Monday, June 10, in the Evening, the Sky being very serene and calm, I was desirous to take a view of the disk of Mars (then very near the Earth, and appearing very glorious) to see if I could distinguish in my 24 Foot Telescope, the Spots said to be seen on him. Directing my Tube for the purpose, I accidentally fell upon a small whitish Appearance near the Planet, resembling in all respects such a Nebula … The Reverend Mr. Miles Williams, Mr. Alban Thomas, and myself contemplated this Appearance for above an Hour … and we could not be deceiv’d as to its Reality; but the slowness of its Motion made us at that time conclude that it had none, and that it was rather a Nebula than a Comet.
Read more. [Image: Wikimedia Commons]
4 hour star trails timelapse at Point Reyes
Hydra 3K Medium Mech da Marco Marozzi


China’s giant alien-hunting telescope is ready
Our alien-hunting game just got a lot stronger with the completion of a huge radio telescope in the Guizhou province of China. It’s called the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST), and it’s designed to listen for signs of alien life out in the cosmos. The telescope is finished, but the construction was not without human rights controversy.
Follow @the-future-now
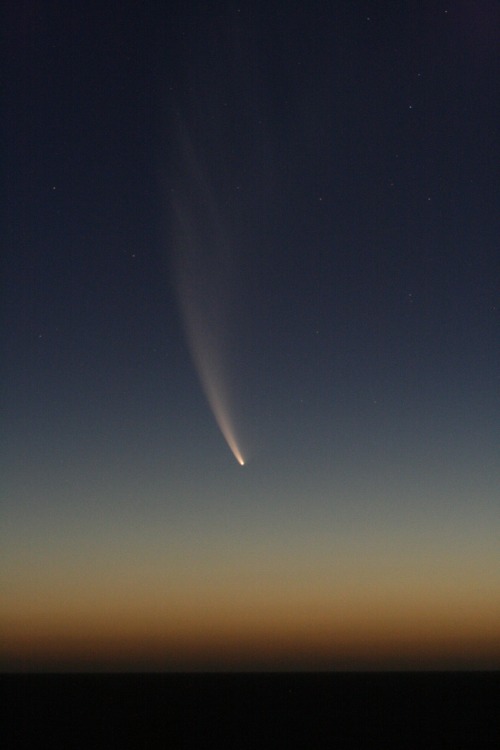

Comet McNaught.

Observing the Skies Above by Kirby Wright on Flickr.
Scientists slow the speed of light
By Kenneth Macdonald
A team of Scottish scientists has made light travel slower than the speed of light.
They sent photons - individual particles of light - through a special mask. It changed the photons’ shape - and slowed them to less than light speed.
The photons remained travelling at the lower speed even when they returned to free space.
The experiment is likely to alter how science looks at light.
Continue Reading

Image of Saturn taken by Cassini spacecraft in October 28, 2016.
Credit: NASA / JPL / Cassini

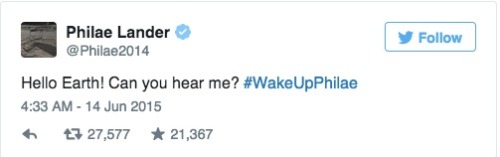
Comet lander Philae wakes up: How it happened and what’s next
By Lauren Raab
Philae, the first spacecraft to land on a comet, surprised and delighted scientists this weekend by waking up and reestablishing contact with Earth, seven months after running out of power. It “spoke” for more than a minute, according to the European Space Agency, and it’s expected to be able to continue gathering information and sending it home.
Here’s a look at what the lander has done so far and what will happen next.
Continue Reading.
-
 wisent15 liked this · 2 years ago
wisent15 liked this · 2 years ago -
 wisent15 reblogged this · 2 years ago
wisent15 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 sssccrr liked this · 2 years ago
sssccrr liked this · 2 years ago -
 bitterblue reblogged this · 3 years ago
bitterblue reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 lashtal939393 liked this · 3 years ago
lashtal939393 liked this · 3 years ago -
 gigi-orosco reblogged this · 3 years ago
gigi-orosco reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 tiefeblicke reblogged this · 3 years ago
tiefeblicke reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 doofnoof liked this · 4 years ago
doofnoof liked this · 4 years ago -
 ohdasit liked this · 4 years ago
ohdasit liked this · 4 years ago -
 osiflandia reblogged this · 4 years ago
osiflandia reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 the-path-inside reblogged this · 5 years ago
the-path-inside reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 wolfsong-the-bloody-beast reblogged this · 5 years ago
wolfsong-the-bloody-beast reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 n1ppleless-cag3 reblogged this · 5 years ago
n1ppleless-cag3 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 n1ppleless-cag3 liked this · 5 years ago
n1ppleless-cag3 liked this · 5 years ago -
 wtfismylife2319 liked this · 5 years ago
wtfismylife2319 liked this · 5 years ago -
 mellowmelancholia reblogged this · 5 years ago
mellowmelancholia reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 mellowbearr liked this · 5 years ago
mellowbearr liked this · 5 years ago -
 healing-stars reblogged this · 5 years ago
healing-stars reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 anderwhohn-moved reblogged this · 5 years ago
anderwhohn-moved reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 iiemergingii liked this · 5 years ago
iiemergingii liked this · 5 years ago -
 blackcoffeedreams reblogged this · 5 years ago
blackcoffeedreams reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 cluelesslyfalling4u liked this · 5 years ago
cluelesslyfalling4u liked this · 5 years ago -
 esamnoor liked this · 5 years ago
esamnoor liked this · 5 years ago -
 spatzsworld liked this · 5 years ago
spatzsworld liked this · 5 years ago -
 middlechildspice reblogged this · 5 years ago
middlechildspice reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 cunty-mystic reblogged this · 5 years ago
cunty-mystic reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 vytashuth liked this · 5 years ago
vytashuth liked this · 5 years ago -
 drabglam liked this · 5 years ago
drabglam liked this · 5 years ago -
 neutrogentle reblogged this · 5 years ago
neutrogentle reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 pizzamunchies reblogged this · 5 years ago
pizzamunchies reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 pixshi reblogged this · 5 years ago
pixshi reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ragazzeadolescenza liked this · 5 years ago
ragazzeadolescenza liked this · 5 years ago -
 rh35211 reblogged this · 5 years ago
rh35211 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 jmsconn liked this · 5 years ago
jmsconn liked this · 5 years ago -
 writing-history reblogged this · 5 years ago
writing-history reblogged this · 5 years ago