SpaceX Announced They Are Planning To Send Their Red Dragon Capsule To Mars As Soon As 2018

SpaceX announced they are planning to send their Red Dragon capsule to Mars as soon as 2018
To send Red Dragon spacecraft to Mars, SpaceX is building a mega-rocket called Falcon Heavy. Based on the company’s successful Falcon 9, Falcon Heavy consists of three core rocket stages, each of which is equipped with landing legs for reusability. They would use the capsule’s thrusters to make a landing.

This artist’s illustration shows how the capsule could enter Mars’ atmosphere. SpaceX has successfully returned their capsules to Earth during space station resupply missions for NASA.
The Dragon can carry seven astronauts to and from destinations like the International Space Station (not yet a manned mission to Mars I’d guess 😄). Here’s an illustration of the Dragon Version 1 (the new version has some differences), to get the idea:
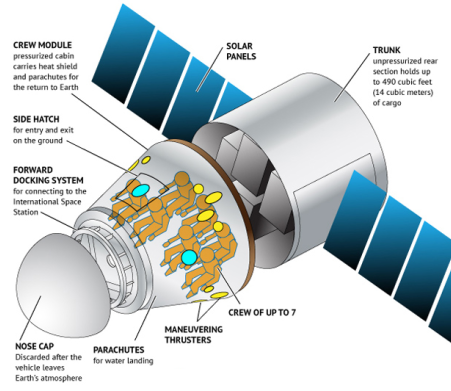
credit: SpaceX, Karl Tate/Space.com
More Posts from Astrotidbits-blog and Others

GoPro Hero 5










Cassini prepares for final orbital “Grand Finale” at Saturn.
Erik Wernquist, the same filmmaker who created 2014’s “Wanderers” and a stunning New Horizons promotional film in 2015, has created a new video highlighting NASA’s Cassini mission’s final days at Saturn. The Cassini spacecraft will begin its final series of orbits to cap a 13-year groundbreaking science mission known as the Grand Finale. For the first time ever in Cassini’s time at Saturn, the spacecraft will fly in between the planet’s rings and atmosphere. No spacecraft has ever before flown in this region of any of the solar system’s ringed planets. After 23 orbits, Cassini will dive into Saturn’s upper atmosphere September 15 where it will be destroyed. In 2008, mission managers explored a range of End of Mission scenarios that would protect Saturn’s moon’s from Earthly contaminants before ultimately deciding on atmospheric reentry. Cassini began her End of Mission manoeuvres on November 26, 2016, when it began the first of 20 ring-grazing orbits. A close flyby of Titan April 22 will alter the spacecraft’s trajectory to begin the first of 23 orbits in the Grand Finale, which will begin April 26.

Cassini launched from Earth on October 15, 1997, and entered Saturn orbit June 30, 2004. Six months later, on January 14, 2005, the European-built Huygens probe attached to the spacecraft landed on Titan, becoming the first probe to land in the outer solar system.
Originally scheduled for a four-year mission ending in 2008, Cassini received two mission extensions in 2008 and 2010, with the latter ending in 2017. With the spacecraft’s fuel reserves low, the Cassini team decided to end the mission. P/C: JPL/Erik Wernquist





Maria Mitchell - Scientist of the Day
Maria Mitchell, an American astronomer, was born Aug. 1, 1818, in Nantucket. Mitchell was the first professional woman astronomer in the United States and a role model for generations of aspiring women scientists. She was trained by her father, a school-teacher, and had the extreme good fortune to discover a comet in 1847. Not only was she the first to see the comet, she also had the mathematical skill to calculate its orbit. Her feat won her an international gold medal from the Danish government, the first such recognition for any American woman, and eventually, the professorship of astronomy at Vassar College, also the first such position for any woman. (It is probably of interest to some of this reading audience that, before she became famous, Mitchell spent 17 years as a librarian on Nantucket.) Mitchell was admitted to various male bastions, such as the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in Boston (the only woman so honored until the 20th century), but she decided early on that, instead of trying to show men that women could be good scientists, she would spend her life showing young women that they could be good scientists. She seems to have done a superb job at this task, becoming a legendary teacher at Vassar. Antonia Maury, a noted astronomer at Harvard, was one of her pupils. The lovely albumen print portrait of Maria above is at Harvard.
In 1863, Matthew Vassar, the founder of Vassar College, personally commissioned a telescope for Mitchell from Henry Fitz, a well-known New York telescope builder. With a lense 12 inches in diameter, it was second among American telescopes only to the great refractor at Harvard (see second image above). The telescope is now in the National Museum of American History in Washington. Vassar also built an observatory for Maria; a period photo can be seen above, just below the Fitz refractor.
The small telescope that Mitchell used to discover the Nantucket comet is now mounted in her childhood home on Vestal Street (see last photo above), across from the headquarters of the Maria Mitchell Association, the group her descendants founded in 1908 to continue Mitchell’s lifelong passion for the natural sciences and science education.
Dr. William B. Ashworth, Jr., Consultant for the History of Science, Linda Hall Library and Associate Professor, Department of History, University of Missouri-Kansas City
Jupiter and beyond the Infinite…
How do we know light is a wave?
Before I answer this question, I’ll need to briefly go over a wave property called superposition. Basically, superposition is the idea that two waves can be in the same position at the same time, and interfere with each other:
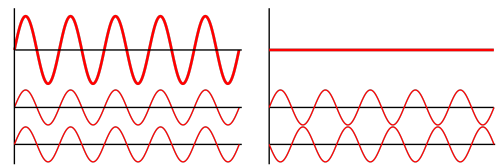
When the two waves add to each other and make a larger wave, we call this constructive interference. When the waves cancel each other out, we call this destructive interference.
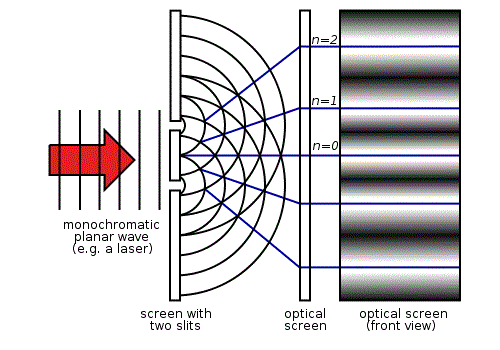
Now we’re going to move on to the Double Slit Experiment. Basically, you shine a beam of light at a piece of metal, cardboard, etc with two slits in it, with a surface behind it where you can see the light hit it.
If light is a wave, what we’d expect to see would be an interference pattern created by the light from the first slit interfering with light from the second slit, which is exactly what we see. It’s a pattern of constructive interference (brighter regions) and destructive interference (darker regions), looking like this:
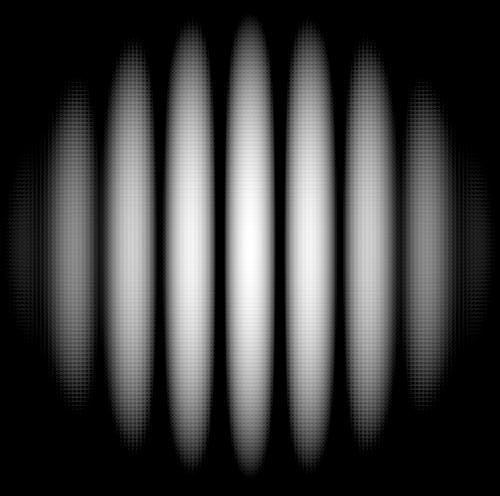

These images are helpful:
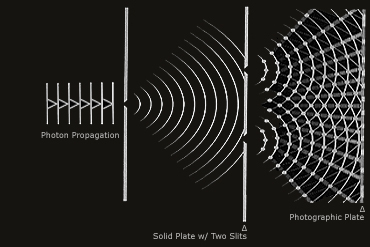
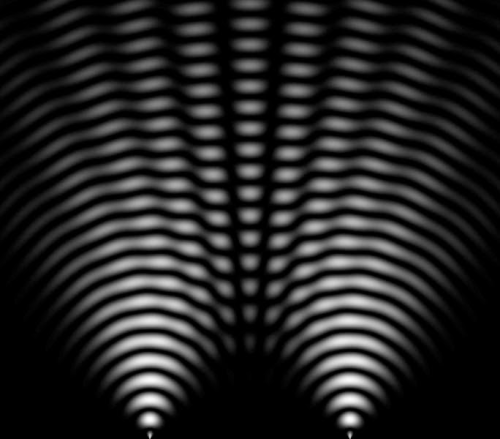
that is how we know light acts as a wave!!

I have waited a long goddamn time for this.
Thunder Snow!
Ground those antennas kids, winter’s got more than the white stuff today for us!


Saturn and Jupiter You can see Jupiter’s moon, Io, casting a shadow onto the gas giant. Credit and Source: nomorelickfoot

-
 blueartofnature-blog liked this · 2 years ago
blueartofnature-blog liked this · 2 years ago -
 annabethjacksonchasepercabeth liked this · 7 years ago
annabethjacksonchasepercabeth liked this · 7 years ago -
 zadakspiefels-blog liked this · 8 years ago
zadakspiefels-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 lutefisk-kingdom liked this · 8 years ago
lutefisk-kingdom liked this · 8 years ago -
 crashskull liked this · 8 years ago
crashskull liked this · 8 years ago -
 faith-the-demon-blog liked this · 8 years ago
faith-the-demon-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 manaisstoredintheballs liked this · 8 years ago
manaisstoredintheballs liked this · 8 years ago -
 atheist743 reblogged this · 8 years ago
atheist743 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 jzacblr reblogged this · 9 years ago
jzacblr reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 buddawesomest reblogged this · 9 years ago
buddawesomest reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 ironically-gold-old-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
ironically-gold-old-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 ironically-gold-old-blog liked this · 9 years ago
ironically-gold-old-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 whathamdidyouslap20universe reblogged this · 9 years ago
whathamdidyouslap20universe reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 noxxx5 liked this · 9 years ago
noxxx5 liked this · 9 years ago -
 tchjetil liked this · 9 years ago
tchjetil liked this · 9 years ago -
 iamdetour303 liked this · 9 years ago
iamdetour303 liked this · 9 years ago -
 mywonderworld2 reblogged this · 9 years ago
mywonderworld2 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 auiva reblogged this · 9 years ago
auiva reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 me1234000 liked this · 9 years ago
me1234000 liked this · 9 years ago -
 alifromfl reblogged this · 9 years ago
alifromfl reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 danbarrett88 liked this · 9 years ago
danbarrett88 liked this · 9 years ago -
 captainzo liked this · 9 years ago
captainzo liked this · 9 years ago -
 cheetahwithwings liked this · 9 years ago
cheetahwithwings liked this · 9 years ago -
 iridium2013 liked this · 9 years ago
iridium2013 liked this · 9 years ago -
 h-falcon reblogged this · 9 years ago
h-falcon reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 notlooking23 liked this · 9 years ago
notlooking23 liked this · 9 years ago -
 geomsf liked this · 9 years ago
geomsf liked this · 9 years ago -
 thedarkjoker88 liked this · 9 years ago
thedarkjoker88 liked this · 9 years ago -
 alwaysxcreeping liked this · 9 years ago
alwaysxcreeping liked this · 9 years ago -
 wordhord liked this · 9 years ago
wordhord liked this · 9 years ago -
 obeeragain liked this · 9 years ago
obeeragain liked this · 9 years ago -
 andywinds liked this · 9 years ago
andywinds liked this · 9 years ago -
 space-bit reblogged this · 9 years ago
space-bit reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 space-bit liked this · 9 years ago
space-bit liked this · 9 years ago -
 mysteriousninja reblogged this · 9 years ago
mysteriousninja reblogged this · 9 years ago