Infrared Horsehead Nebula By Hubble Heritage

Infrared Horsehead Nebula by Hubble Heritage
More Posts from Starry-shores and Others

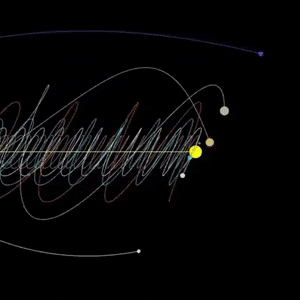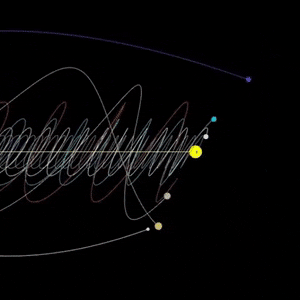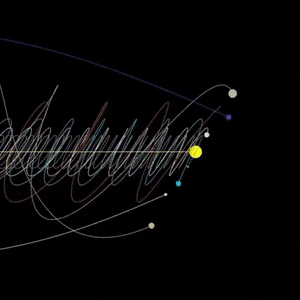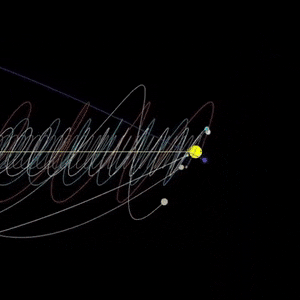
Jupiter seen by NASA’s Voyager spacecraft
Animation taken from video: Jeff Quitney
Helicoprion: What if, like, teeth,
Mesosaurus: Yeah?
Helicoprion: but WHEEL
Mesosaurus: No don't -
Helicoprion:

(Image by ДиБгд)
QUETZALCOATLUS

Quetzalcoatlus goes down in history as the largest flying organism of all time, with a wingspan of 12 metres, which is larger than some planes. Quetzalcoatlus was the undisputed king of the Late cretaceous skies, so it seems fitting that its name is derived from an Aztec god, Quetzalcoatl. Although its wingspan is impressive, Quetzalcoatlus also had a huge 2.5 metre long skull, that is the average height of an Asian elephant! To get such a huge animal in the air, a complex system of air sacs was needed inside the bones, this meant that Quetzalcoatlus probably weighed no more than 250kg. Quetzalcoatlus, along with many pterosaurs, was originally thought to spend most of its time gliding over the oceans, skimming fish out from the surface of the water with their elongated beaks. However, due to the skull and beak morphology and the presence of fossils far inland it has become more widely accepted that Quetzalcoatlus stalked prey far below on the land. The fore and hind limb morphology of Quetzalcoatlus also suggests that they were competent walkers on the land, they would have stood up to 3 metres tall.

The feeding habits of Quetzalcoatlus still remain something of a mystery. It was originally thought to be more of a scavenger, but the blunt beak was unsuited to stripping and picking flesh of a bony creature. It is more likely that Quetzalcoatlus hunted like modern-day storks, stalking the land from the skies above for smaller animals and then swooping down to eat them whole.

Hubble’s Messier Catalog by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center
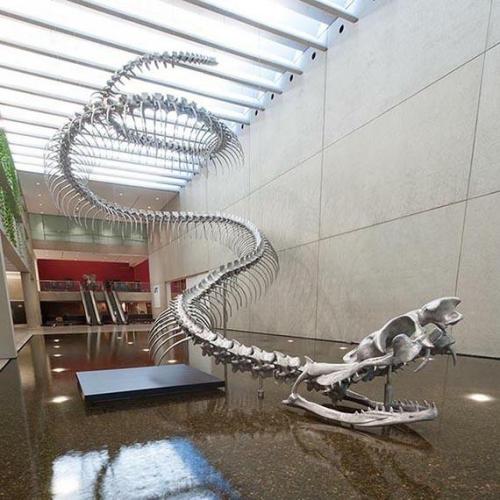



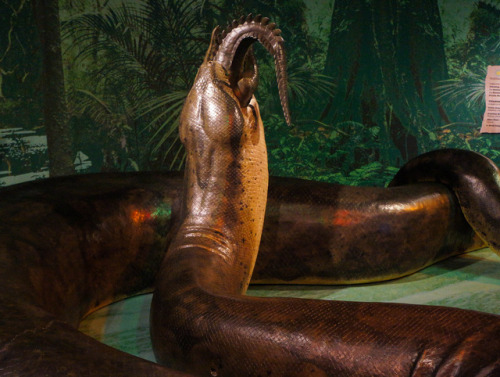



Titanoboa
Titanoboa is an extinct genus of snakes that is known to have lived in present-day La Guajira in northern Colombia. The giant snake lived during the Middle to Late Paleocene epoch, a 10-million-year period immediately following the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event.
The only known species is Titanoboa cerrejonensis, the largest snake ever discovered. By comparing the sizes and shapes of its fossilized vertebrae to those of extant snakes, researchers estimated that the largest individuals of T. cerrejonensis found had a total length around 42 feet and weighed about 2,500 pounds.
While initially thought to have been an apex predator of the Paleocene ecosystem in which it lived, evidence has pointed to the genus being predominantly piscivorous. Titanoboa’s massive size would have made it difficult to move on land, so the giant snake would probably have spent most of its life in the water, hunting for fish and other aquatic prey.
-
 lonelydollworld liked this · 1 year ago
lonelydollworld liked this · 1 year ago -
 man-of-the-world-returns reblogged this · 2 years ago
man-of-the-world-returns reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 hannaparrisa reblogged this · 2 years ago
hannaparrisa reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 love-mesome-me liked this · 2 years ago
love-mesome-me liked this · 2 years ago -
 alwaysamaritimer reblogged this · 2 years ago
alwaysamaritimer reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 alwaysamaritimer liked this · 2 years ago
alwaysamaritimer liked this · 2 years ago -
 specsnsarcasm reblogged this · 2 years ago
specsnsarcasm reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 drcouts liked this · 2 years ago
drcouts liked this · 2 years ago -
 endlesslydev0ted reblogged this · 2 years ago
endlesslydev0ted reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 endlesslydev0ted liked this · 2 years ago
endlesslydev0ted liked this · 2 years ago -
 saucerkommand liked this · 2 years ago
saucerkommand liked this · 2 years ago -
 airesbrown reblogged this · 2 years ago
airesbrown reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 snarktacular-grumpbeast liked this · 2 years ago
snarktacular-grumpbeast liked this · 2 years ago -
 beginningofourend reblogged this · 2 years ago
beginningofourend reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 beginningofourend liked this · 2 years ago
beginningofourend liked this · 2 years ago -
 von-hauerland liked this · 2 years ago
von-hauerland liked this · 2 years ago -
 cosmicretreat reblogged this · 2 years ago
cosmicretreat reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 cosmicretreat liked this · 2 years ago
cosmicretreat liked this · 2 years ago -
 theeaesthete liked this · 2 years ago
theeaesthete liked this · 2 years ago -
 teagirl-loves liked this · 2 years ago
teagirl-loves liked this · 2 years ago -
 tobeeclectic liked this · 2 years ago
tobeeclectic liked this · 2 years ago -
 vivalate liked this · 2 years ago
vivalate liked this · 2 years ago -
 celestialily liked this · 2 years ago
celestialily liked this · 2 years ago -
 saucerkommand reblogged this · 2 years ago
saucerkommand reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 esdras64 liked this · 2 years ago
esdras64 liked this · 2 years ago -
 singedfingers reblogged this · 2 years ago
singedfingers reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 phylogeny reblogged this · 2 years ago
phylogeny reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 the-summer-sun-au liked this · 3 years ago
the-summer-sun-au liked this · 3 years ago -
 sheengg liked this · 3 years ago
sheengg liked this · 3 years ago -
 elpadrin0 liked this · 3 years ago
elpadrin0 liked this · 3 years ago -
 jmiy reblogged this · 3 years ago
jmiy reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 bryllando reblogged this · 3 years ago
bryllando reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 shyyyguy reblogged this · 3 years ago
shyyyguy reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 tazminj reblogged this · 3 years ago
tazminj reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 inebriated-knowledge liked this · 3 years ago
inebriated-knowledge liked this · 3 years ago -
 haitianloveee liked this · 3 years ago
haitianloveee liked this · 3 years ago -
 senpaapi reblogged this · 3 years ago
senpaapi reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 whyseegreen reblogged this · 3 years ago
whyseegreen reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 thisladyisawesome liked this · 3 years ago
thisladyisawesome liked this · 3 years ago -
 sexynakedblackguy reblogged this · 3 years ago
sexynakedblackguy reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 grapefruith reblogged this · 3 years ago
grapefruith reblogged this · 3 years ago

Amateur astronomer, owns a telescope. This is a side blog to satiate my science-y cravings! I haven't yet mustered the courage to put up my personal astro-stuff here. Main blog : @an-abyss-called-life
212 posts