Perfect Magnets
Perfect magnets
More Posts from Science-is-magical and Others

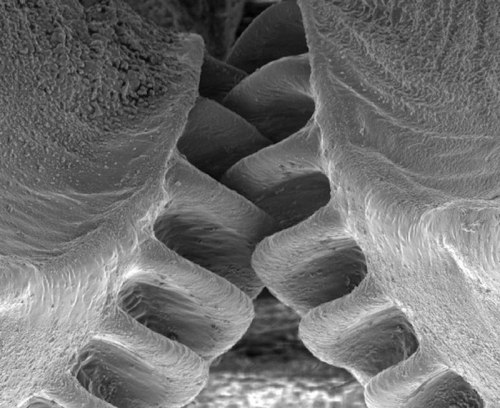
Close-Up of the First Mechanical Gear Ever Found in Nature
The biological form of a mechanical gear was observed in nature for the first time in juvenile planthoppers (Genus: Issus), a common insect that can be found in gardens across Europe.
The insect has hind-leg joints with curved cog-like strips of opposing ‘teeth’ that intermesh, rotating like mechanical gears to synchronize the animal’s legs when it launches into a jump. The finding demonstrates that gear mechanisms previously thought to be solely man-made have an evolutionary precedent.
(Continue Reading)


ALL ROLLED UP
A newly identified mineral christened merelaniite tightly rolls up like a scroll as it crystallizes, forming shiny dark gray needles up to a few millimeters in length (Minerals 2016, DOI: 10.3390/min6040115). The overall formula of the mineral is Mo₄Pb₄VSbS₁₅. It crystallizes into a sheet composed primarily of alternating ultrathin layers of MoS₂ and PbS. “It’s like a natural nanocomposite,” says research team leader John A. Jaszczak of Michigan Technological University. Strain from the interacting layers likely causes the crystalline sheets to wrap around themselves as they grow. Jaszczak and coworkers named the mineral for the Merelani mining district in Tanzania, where the merelaniite samples originated. Collaborating research institutions included the U.K. Natural History Museum, U.S. National Museum of Natural History, and University of Florence.
Credit: Minerals (both)
Related C&EN content:
Minerals in Medicine Exhibition
Worldwide Hunt For Missing Carbon Minerals Begins
Neuroscientist Discovers Potential New Source for Pain Inhibition
A UT Dallas scientist has found a new neurological mechanism that appears to contribute to a reduction in pain.
According to Dr. Ted Price, associate professor in the School of Behavioral and Brain Sciences, the discovery of neuroligin-2 as a cause exacerbating chronic pain is significant for the research community. Although the findings likely won’t immediately lead to new pain therapies, the findings offer a potential new therapeutic direction to investigate, he said.
Price’s research on the topic has recently been published online in Pain, the journal of the International Association for the Study of Pain.
The study focused on the body’s inhibitory networks — a series of biochemical reactions that decrease certain neurological activity, such as pain. Price said a great deal of previous research in this area has focused on the activity of the neurotransmitter GABA, a chemical released by nerve cells in the brain.
Normally, a GABA neurotransmitter acts to inhibit neuronal activity, such as pain. However, when pain becomes chronic there is strong evidence that a process called GABAergic plasticity can cause GABA to lose its inhibitory activity, sometimes making the pain even worse.
The source of these excitatory actions in neuronal circuits has been broadly attributed to chloride ions, but Price’s research has found another potential cause of GABAergic plasticity: synaptic adhesion molecules called neuroligin-2.
“From a basic science perspective, we’re really excited about it because it demonstrates that the types of GABAergic plasticity that can occur in the setting of chronic pain are more diverse than we’ve appreciated before,” he said.
Price, who heads the undergraduate research program in neuroscience in the school, focuses much of his research on understanding the neuroscience behind pain, particularly chronic pain. He said individuals with chronic pain typically don’t receive the pain-reduction benefits delivered by inhibitory systems. Instead, they often experience increased pain.
“When you hit your hand with a hammer, almost everybody has the same reflex reaction — that is, to rub your finger which, in turn, helps to reduce pain. The reason that works is because it increases GABAergic inhibition in the spinal cord,” Price said. “However, people who have chronic pain — if they do the same thing — find that rubbing it actually makes the pain worse. That’s because the GABAergic system loses its efficacy and, in fact, can become excitatory.”
Price said the research is another step in determining why the GABAergic system stops working correctly in some people and provides a second theory for what drives the system.
“Having two ideas and different models will allow us to determine what the therapeutic opportunities are — creating something that will change that back to normal. The lack of performance in the inhibitory system is very detrimental to those who are in chronic pain,” he said.
Price said the development of chronic pain is, in essence, one’s body “learning” something that is bad.
“It’s changing the way the body functions — it’s learning. That learning, in the case of chronic pain, is aberrant — it’s causing the situation to get worse. If we can figure out what that form of learning was, then we can potentially reverse it. Understanding that the GABAergic system changes during this form of learning potentially offers a new therapeutic avenue,” he said.
-
 radgalacticacrew liked this · 1 month ago
radgalacticacrew liked this · 1 month ago -
 storm-writer reblogged this · 1 month ago
storm-writer reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 narihira8 liked this · 2 months ago
narihira8 liked this · 2 months ago -
 hakkirimoses liked this · 2 months ago
hakkirimoses liked this · 2 months ago -
 uchimatanoinu liked this · 2 months ago
uchimatanoinu liked this · 2 months ago -
 hin2048 reblogged this · 2 months ago
hin2048 reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 gensha reblogged this · 2 months ago
gensha reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 ihavetitanium reblogged this · 2 months ago
ihavetitanium reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 ihavetitanium liked this · 2 months ago
ihavetitanium liked this · 2 months ago -
 the-lavender-flock reblogged this · 2 months ago
the-lavender-flock reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 alohaje12 liked this · 2 months ago
alohaje12 liked this · 2 months ago -
 pietasu59 liked this · 2 months ago
pietasu59 liked this · 2 months ago -
 frogwithastrawberry reblogged this · 2 months ago
frogwithastrawberry reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 frogwithastrawberry liked this · 2 months ago
frogwithastrawberry liked this · 2 months ago -
 destinywillowleaf reblogged this · 2 months ago
destinywillowleaf reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 saraneth-1 reblogged this · 2 months ago
saraneth-1 reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 saraneth-1 liked this · 2 months ago
saraneth-1 liked this · 2 months ago -
 wannabetokiorockstar liked this · 2 months ago
wannabetokiorockstar liked this · 2 months ago -
 glitchinthevisuals reblogged this · 2 months ago
glitchinthevisuals reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 glitchinthevisuals liked this · 2 months ago
glitchinthevisuals liked this · 2 months ago -
 immcfuckinglosingmyshit reblogged this · 2 months ago
immcfuckinglosingmyshit reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 queerture reblogged this · 2 months ago
queerture reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 saitamainspace reblogged this · 2 months ago
saitamainspace reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 sheiswrappedinrainbows reblogged this · 2 months ago
sheiswrappedinrainbows reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 completeellipse reblogged this · 2 months ago
completeellipse reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 honeyedbrie reblogged this · 2 months ago
honeyedbrie reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 honeyedbrie liked this · 2 months ago
honeyedbrie liked this · 2 months ago -
 sink-drainage reblogged this · 2 months ago
sink-drainage reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 chasing-phi reblogged this · 2 months ago
chasing-phi reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 porkchopsammie reblogged this · 2 months ago
porkchopsammie reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 3b0nyb0n3s liked this · 2 months ago
3b0nyb0n3s liked this · 2 months ago -
 nonchalantxfish liked this · 2 months ago
nonchalantxfish liked this · 2 months ago -
 mandolindoodler liked this · 2 months ago
mandolindoodler liked this · 2 months ago -
 tonfea reblogged this · 2 months ago
tonfea reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 stopaskingformykik reblogged this · 2 months ago
stopaskingformykik reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 void-of-nonsense reblogged this · 2 months ago
void-of-nonsense reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 sexyprise liked this · 2 months ago
sexyprise liked this · 2 months ago -
 hangeslilcumslut liked this · 2 months ago
hangeslilcumslut liked this · 2 months ago -
 malarkeyenthusiast liked this · 2 months ago
malarkeyenthusiast liked this · 2 months ago -
 girl-of-ink reblogged this · 2 months ago
girl-of-ink reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 faemorningstar liked this · 2 months ago
faemorningstar liked this · 2 months ago -
 fatmoonbear reblogged this · 2 months ago
fatmoonbear reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 crunchyduckwings liked this · 2 months ago
crunchyduckwings liked this · 2 months ago -
 anotherdragonsfan reblogged this · 2 months ago
anotherdragonsfan reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 saintsandmisfit liked this · 2 months ago
saintsandmisfit liked this · 2 months ago -
 let-me-eat-my-cookie reblogged this · 2 months ago
let-me-eat-my-cookie reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 lets-get-ready-to-ramble liked this · 2 months ago
lets-get-ready-to-ramble liked this · 2 months ago -
 let-me-eat-my-cookie liked this · 2 months ago
let-me-eat-my-cookie liked this · 2 months ago -
 guinevereslancelot reblogged this · 2 months ago
guinevereslancelot reblogged this · 2 months ago





