Meet The Real Women Behind Hidden Figures.

Meet the real women behind Hidden Figures.
In the early days of the Space Race, Dorothy Vaughan headed the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics’ (NACA) West Area Computing unit. It was an important but segregated unit of mostly female mathematicians doing aerospace calculations by hand. When NACA became NASA in 1958, the Analysis and Computation Division desegregated and Vaughan became a sought-after expert on FORTRAN – a programming language used on IBM mainframes.
Vaughan is one of the women whose work inspired the film Hidden Figures — a true story of three African American mathematicians who helped NASA launch the first Americans into space.
Feeling inspired? See how coding might figure into your life. Uncover more about Dorothy Vaughan →
More Posts from Ritasakano and Others

The polluted brain
Some of the health risks of inhaling fine and ultrafine pollutant particles are well-established, such as asthma, lung cancer, and, most recently, heart disease. But a growing body of evidence suggests that such exposure can also harm the brain, accelerating cognitive aging, and may even increase risk of Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia.
by Emily Underwood
for Science
brought to you by Graphic Services for Science and Graphic Biology

Maurice Utrillo’s Paris Street, 1914 (via here)
The Great Conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn

Credits: NASA/Bill Ingalls
Have you noticed two bright objects in the sky getting closer together with each passing night? It’s Jupiter and Saturn doing a planetary dance that will result in the Great Conjunction on Dec. 21. On that day, Jupiter and Saturn will be right next to each other in the sky – the closest they have appeared in nearly 400 years!
Skywatching Tips from NASA

Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech
For those who would like to see this phenomenon for themselves, here’s what to do:
Find a spot with an unobstructed view of the sky, such as a field or park. Jupiter and Saturn are bright, so they can be seen even from most cities.
An hour after sunset, look to the southwestern sky. Jupiter will look like a bright star and be easily visible. Saturn will be slightly fainter and will appear slightly above and to the left of Jupiter until December 21, when Jupiter will overtake it and they will reverse positions in the sky.
The planets can be seen with the unaided eye, but if you have binoculars or a small telescope, you may be able to see Jupiter’s four large moons orbiting the giant planet.
How to Photograph the Conjunction

Credits: NASA/Bill Dunford
Saturn and Jupiter are easy to see without special equipment, and can be photographed easily on DSLR cameras and many cell phone cameras. Here are a few tips and tricks:
These planets are visible in the early evening, and you’ll have about 1-2 hours from when they are visible, to when they set. A photo from the same location can look completely different just an hour later!
Using a tripod will help you hold your camera steady while taking longer exposures. If you don’t have a tripod, brace your camera against something – a tree, a fence, or a car can all serve as a tripod for a several-second exposure.
The crescent Moon will pass near Jupiter and Saturn a few days before the conjunction. Take advantage of it in your composition!
Get more tips HERE.
Still have questions about the Great Conjunction?
Our NASA expert answered questions from social media on an episode of NASA Science Live on Thursday, Dec. 17. Watch the recording HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.




The benefits of a bilingual brain
It’s obvious that knowing more than one language can make certain things easier — like traveling or watching movies without subtitles. But there are other advantages to having a bilingual brain. While bilingualism won’t necessarily make you smarter, it does make your brain more healthy, complex and actively engaged. So even if you didn’t have the good fortune of learning a second language as a child, it’s never too late to make a linguistic leap! After all, a little brain exercise can go a long way.
What does it really mean to know a language? Language ability is typically measured in two active parts (speaking and writing), and two passive parts (listening and reading). While a balanced bilingual has near equal abilities across the board in two languages, most bilinguals around the world know and use their languages in varying proportions. And depending on their situation and how they acquired each language, they can be classified into three general types.
A compound bilingual develops two linguistic codes simultaneously, with a single set of concepts. If you learned two languages from the time you were very young, chances are you are a compound bilingual. A coordinate bilingual works with two sets of concepts, for example, someone who speaks one language at home and another in school or with friends. Finally, a subordinate bilingual is someone who learns a secondary language by filtering it through their primary language.
Did you know a multilingual brain actually has more grey matter than a monolingual brain?
Source: TED-ED
Educator: Mia Nacamulli Animator: Lisa LaBracio

Olfactory perception influenced by background and semantic information
When two people smell the same thing, they can have remarkably different reactions, depending on their cultural background. Researchers at the Neuro have found that even when two cultures share the same language and many traditions, their reactions to the same smells can be different.
In a partnership with researchers from the Lyon Neuroscience Research Centre in France, clinical neuropsychologist Jelena Djordjevic and her group at the Montreal Neurological Institute tested subjects in Quebec for their subjective impressions of different scents, while their collaborators in France did the same with French subjects. They selected six scents: anise, lavender, maple, wintergreen, rose and strawberry.
Participants were asked to smell each scent first without knowing what the scent is, then again after being told its name. The subjects rated the scent on pleasantness, intensity, familiarity, and edibility. The scientists also measured the subjects’ non-verbal reactions to each scent, including sniffing, activity of facial muscles, respiration and heart rate.
The researchers found significant differences between ratings of the same odours among the French and French-Canadian subjects. For example, the French gave wintergreen much lower pleasantness ratings than French-Canadians. In France, wintergreen is used more in medicinal products than in Canada, where it is found more in candy. Canadians were more familiar with scents of maple and wintergreen than the French, while in turn people from France were more familiar with the scent of lavender. When asked to describe odours, Canadians were better at describing maple and wintergreen, while people from France were better at describing lavender. Anise was rated similarly in two cultures but was described more often as “licorice” in Quebec and as “anise” in France.
Providing the names of the odours to subjects increased their ratings of familiarity, pleasantness and edibility. Furthermore, cultural differences disappeared or decreased when the names were provided. This was true even for the non-verbal reactions to scents. The findings suggest that mental representations activated by odour names are more similar between cultures than the mental representations activated by sensory information alone. Cultural differences in perception of odours are subtle, and are easily reduced by the mere presence of odour names.
The results were published in the journal Chemical Senses.
This study reinforces the idea that our brain’s processing of odour is not simply its reaction to the chemical compounds that make up the scent. It is influenced both by our previous experience with the scent and our knowledge of what the scent is.
While previous studies have come to similar conclusions, this study is unique in that it compared two cultures which share the same language and have similar traditions. This eliminated the possibility of language being a cause of the different reactions between groups.
“In psychology, we call these effects ‘top-down influences’ and we were excited to further develop our understanding of them”, says Djordjevic. “Even basic processes, such as smelling a scent, are influenced by where we come from and what we know. The sense of smell occupies a very old part of our brain. Studying this old sensory system helps us understand how we have evolved as a species. Furthermore, olfactory loss is common in normal aging and also in many neurological conditions. Studying these disorders can provide us with clues about the disease mechanisms and possible ways to treat them.”
Interessante!!!

Everyone pitches in for protein synthesis! Here are three types of RNA helping your cells make proteins. Be sure to check out all our science GIFs here for your studyblrs, teacher websites, presentations, or general amusement! Just please keep our name on there and don’t sell them! :D
As imagens de Júpiter deixa-nos atordoado.

The cloudscape of Jupiter, observed by NASA’s Voyager 1 probe on February 3, 1979.
(Planetary Society)
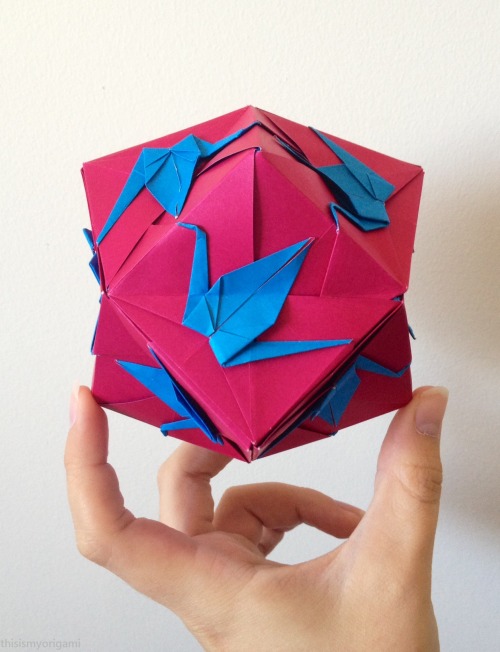
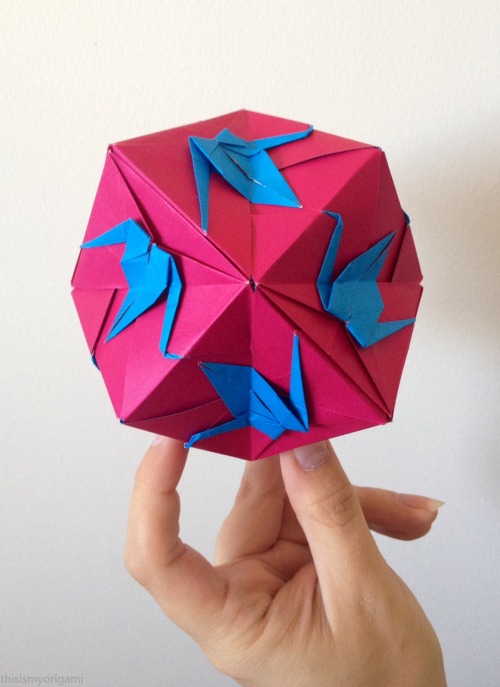
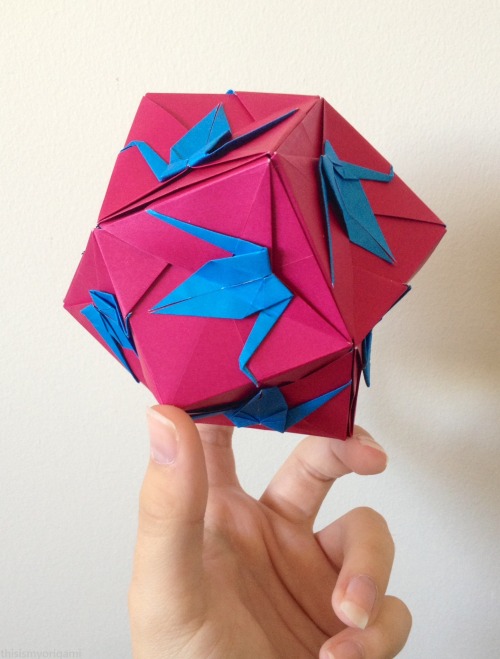
Crane Trisoctahedron designed by Fumiaki Shingu
Instructions

Al poseerse, los amantes dudan. No saben ordenar sus deseos. Se estrechan con violencia, se hacen sufrir, se muerden con los dientes los labios, se martirizan con caricias y besos. Y ello porque no es puro su placer, porque secretos aguijones los impulsan a herir al ser amado, a destruir la causa de su dolorosa pasión. Y es que el amor espera siempre que el mismo objeto que encendió la llama que lo devora, sea capaz de sofocarla. Pero no es así. No. Cuanto más poseemos, más arde nuestro pecho y más se consume. (…) No basta la visión del cuerpo deseado para satisfacerlos, ni siquiera la posesión, pues nunca logran desprender ni un ápice de esas graciosas formas sobre las que discurren, vagabundas y erráticas, sus caricias.
Al fin, cuando, los miembros pegados saborean la flor de su placer, piensan que su pasión será colmada, y estrechan codiciosamente el cuerpo de su amante, mezclando aliento y saliva, con los dientes contra su boca, con los ojos inundando sus ojos, y se abrazan una y mil veces hasta hacerse daño. Pero todo es inútil, vano esfuerzo, porque no pueden robar nada de ese cuerpo que abrazan, ni penetrarse y confundirse enteramente cuerpo con cuerpo, que es lo único que verdaderamente desean: tanta pasión inútil ponen en adherirse a los lazos de Venus, mientras sus miembros parecen confundirse, rendidos por el placer.
Y después, cuando ya el deseo, condensado en sus venas, ha desaparecido, su fuego interrumpe su llama por un instante, y luego vuelve un nuevo acceso de furor y renace la hoguera con más vigor que antes. Y es que ellos mismos saben que no saben lo que desean y, al mismo tiempo, buscan cómo saciar ese deseo que los consume, sin que puedan hallar remedio para su enfermedad mortal: hasta tal punto ignoran dónde se oculta la secreta herida que los corroe.
La herida oculta - Lucrecio En «Dē rērum natūra» (De la naturaleza de las cosas) Versión de Luis Alberto de Cuenca
-
 itzmellowmeow liked this · 5 months ago
itzmellowmeow liked this · 5 months ago -
 dawngreentv liked this · 1 year ago
dawngreentv liked this · 1 year ago -
 lovelyabstract reblogged this · 1 year ago
lovelyabstract reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 lady-gorgon liked this · 1 year ago
lady-gorgon liked this · 1 year ago -
 panda-poes reblogged this · 3 years ago
panda-poes reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 615andbeyond reblogged this · 3 years ago
615andbeyond reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 wisegladiatorkitty liked this · 4 years ago
wisegladiatorkitty liked this · 4 years ago -
 hauntedcloudtheorist liked this · 4 years ago
hauntedcloudtheorist liked this · 4 years ago -
 trans-moth-man liked this · 4 years ago
trans-moth-man liked this · 4 years ago -
 fawningparadox liked this · 4 years ago
fawningparadox liked this · 4 years ago -
 marindodouce liked this · 4 years ago
marindodouce liked this · 4 years ago -
 freakshow777 liked this · 4 years ago
freakshow777 liked this · 4 years ago -
 sleepymr reblogged this · 4 years ago
sleepymr reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 kkaebsong96 liked this · 4 years ago
kkaebsong96 liked this · 4 years ago -
 cj-riker liked this · 4 years ago
cj-riker liked this · 4 years ago -
 sakurazero10 reblogged this · 4 years ago
sakurazero10 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 sakurazero10 liked this · 4 years ago
sakurazero10 liked this · 4 years ago -
 random-fireworks liked this · 4 years ago
random-fireworks liked this · 4 years ago -
 evilqueerposts reblogged this · 4 years ago
evilqueerposts reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 perfectenthusiasttiger reblogged this · 4 years ago
perfectenthusiasttiger reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 logwire liked this · 4 years ago
logwire liked this · 4 years ago -
 introvertedmisfit liked this · 4 years ago
introvertedmisfit liked this · 4 years ago -
 earthkissedcalum liked this · 4 years ago
earthkissedcalum liked this · 4 years ago -
 iwanttodie-jpeg liked this · 4 years ago
iwanttodie-jpeg liked this · 4 years ago -
 hyperfixatingmenever reblogged this · 4 years ago
hyperfixatingmenever reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 hyperfixatingmenever liked this · 4 years ago
hyperfixatingmenever liked this · 4 years ago -
 confusedbutstillgay liked this · 4 years ago
confusedbutstillgay liked this · 4 years ago