Packin’ Up



packin’ up
More Posts from Mousoudi20 and Others

If #NationalCheeseDay has you thinking about the Moon, you’re not alone. 🧀
In 1965, the Ranger 9 probe captured these sharp images of a cratered lunar surface just moments before its planned impact. What we learned paved the way for Apollo. #Apollo50th
The scaffolding has come off the lower cylinder of the #ITER #cryostat. Clad in thin film it is now being scanned by metrologists for reverse engineering and will then be cocooned for storage until assembly. #fusionenergy #WeAreITER https://t.co/DOag9p1rPp https://t.co/xoi5GTq0Vc

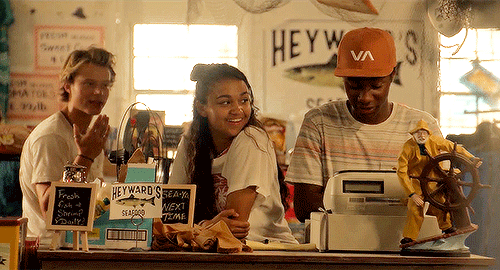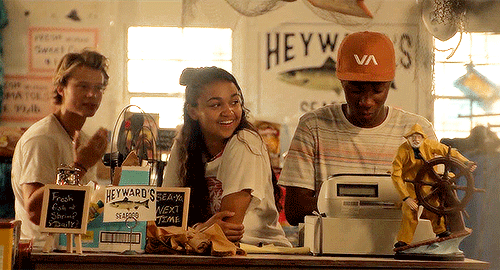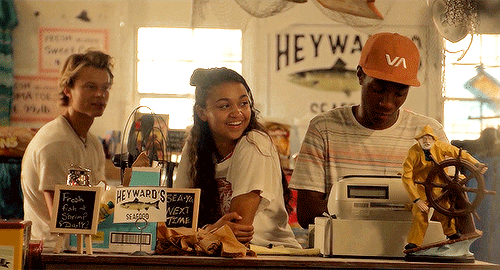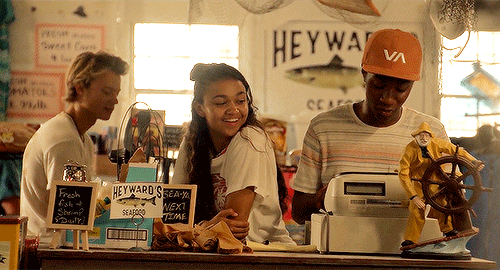

outer banks → places: heyward’s seafood

50 years ago, three Apollo astronauts rode this 363 foot tall rocket, the Saturn V, embarking on one of the greatest missions of mankind – to step foot on another world. On July 20, 1969, astronauts Buzz Aldrin, Michael Collins and Neil Armstrong made history when they arrived at the Moon. Thanks to the Saturn V rocket, we were able to complete this epic feat, returning to the lunar surface a total of six times. The six missions that landed on the Moon returned a wealth of scientific data and almost 400 kilograms of lunar samples.
In honor of this historic launch, the National Air and Space Museum is projecting the identical rocket that took our astronauts to the Moon on the Washington Monument in Washington, D.C.
This week, you can watch us salute our Apollo 50th heroes and look forward to our next giant leap for future missions to the Moon and Mars. Tune in to a special two-hour live NASA Television broadcast at 1 p.m. ET on Friday, July 19. Watch the program at www.nasa.gov/live.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
The Perseid Meteor Shower Is Here!

Image Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
The Perseids are at their peak this week!
The Perseid meteor shower, one of the biggest meteor showers of the year, will be at its brightest early in the morning on Wednesday, August 12. Read on for some tips on how to watch the night sky this week – and to find out: what exactly are the Perseids, anyway?

Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
Your best chance to spot the Perseids will be between 2 AM and dawn (local time) the morning of August 12. Find a dark spot, avoid bright lights (yes, that includes your phone) and get acclimated to the night sky.
Your eyes should be at peak viewing capacity after about 30 minutes; though the Moon may block out some of the dimmer meteors, you should still be able to see up to 15-20 an hour. If you’re not an early bird, you can try and take a look soon after sunset (around 9 PM) on the 11th, though you may not see as many Perseids then.

Credit: NASA/MEO
If it’s too cloudy, or too bright, to go skywatching where you are, you can try again Wednesday or Thursday night – or just stay indoors and watch the Perseids online!
Our Meteor Watch program will be livestreaming the Perseids from Huntsville, Alabama on Facebook (weather permitting), starting around 9 p.m. EDT on August 11 and continuing through sunrise.
So… why are they called the Perseids?
Because all of a meteor shower’s meteors have similar orbits, they appear to come from the same place in the sky – a point called the radiant.

The radiant for the Perseids, as you might guess from the name, is in the constellation Perseus, found near Aries and Taurus in the night sky.
But they’re not actually coming from Perseus, right?

Credit: NASA/Joel Kowsky
Right! The Perseids are actually fragments of the comet Swift-Tuttle, which orbits within our solar system.
If you want to learn more about the Perseids, visit our Watch the Skies blog or check out our monthly “What’s Up” video series. Happy viewing!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
#IBF2019 participants on tour at #ITER. Here in the Assembly Hall where the two giant tools stand ready to assemble the vacuum vessel sectors. #fusionenergy #WeAreITER https://t.co/MLh2Z7gbr3
Researchers at DIII-D achieve surprising results by flipping the plasma's "D" shape: higher pressure and more stable plasma. https://t.co/DqacQEjflH #fusionenergy

2019 August 14
Saturn Behind the Moon Image Credit: Peter Patonai (Astroscape Photography)
Explanation: What’s that next to the Moon? Saturn. In its monthly trip around the Earth – and hence Earth’s sky – our Moon passed nearly in front of Sun-orbiting Saturn earlier this week. Actually the Moon passed directly in front of Saturn from the viewpoints of a wide swath of Earth’s Southern Hemisphere. The featured image from Sydney, Australia captured the pair a few minutes before the eclipse. The image was a single shot lasting only 1/500th of a second, later processed to better highlight both the Moon and Saturn. Since Saturn is nearly opposite the Sun, it can be seen nearly the entire night, starting at sunset, toward the south and east. The gibbous Moon was also nearly opposite the Sun, and so also visible nearly the entire night – it will be full tomorrow night. The Moon will occult Saturn again during every lap it makes around the Earth this year.
∞ Source: apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap190814.html
.@ScottAdamsSays
#GreenNuclearDeal
"Scientists achieved high pressure plasma perhaps laying the groundwork to achieve fusion power at an old fusion reactor in San Diego by reversing the orientation of the vessel that houses the plasma."
https://t.co/gXsKDDEHY3
-
 thenewthingunderthesun liked this · 5 months ago
thenewthingunderthesun liked this · 5 months ago -
 luminousluciano reblogged this · 1 year ago
luminousluciano reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 justathing1741 liked this · 1 year ago
justathing1741 liked this · 1 year ago -
 monotonefont liked this · 1 year ago
monotonefont liked this · 1 year ago -
 emeliastewart liked this · 1 year ago
emeliastewart liked this · 1 year ago -
 loomslis liked this · 1 year ago
loomslis liked this · 1 year ago -
 iceskatingonsummer reblogged this · 1 year ago
iceskatingonsummer reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 lemming-surf liked this · 1 year ago
lemming-surf liked this · 1 year ago -
 noparuto liked this · 1 year ago
noparuto liked this · 1 year ago -
 sarahwilliamsblogsblog liked this · 1 year ago
sarahwilliamsblogsblog liked this · 1 year ago -
 tomyukooutback liked this · 1 year ago
tomyukooutback liked this · 1 year ago -
 enoe-of-noen liked this · 1 year ago
enoe-of-noen liked this · 1 year ago -
 bookwormtea liked this · 1 year ago
bookwormtea liked this · 1 year ago -
 enaislami liked this · 1 year ago
enaislami liked this · 1 year ago -
 the-omnivorous-cannibal liked this · 1 year ago
the-omnivorous-cannibal liked this · 1 year ago -
 raehilopetli liked this · 1 year ago
raehilopetli liked this · 1 year ago -
 weeeeemeee4663 liked this · 1 year ago
weeeeemeee4663 liked this · 1 year ago -
 wolfgurl821 liked this · 1 year ago
wolfgurl821 liked this · 1 year ago -
 slowdivecat liked this · 1 year ago
slowdivecat liked this · 1 year ago -
 ismobordefort liked this · 1 year ago
ismobordefort liked this · 1 year ago -
 lockverpehalean liked this · 1 year ago
lockverpehalean liked this · 1 year ago -
 merridelicious reblogged this · 1 year ago
merridelicious reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 merridelicious liked this · 1 year ago
merridelicious liked this · 1 year ago -
 briqxx liked this · 1 year ago
briqxx liked this · 1 year ago -
 dehydratedidiot22 liked this · 1 year ago
dehydratedidiot22 liked this · 1 year ago -
 boringsyndromeinfection liked this · 1 year ago
boringsyndromeinfection liked this · 1 year ago -
 alehhgirkkklll liked this · 1 year ago
alehhgirkkklll liked this · 1 year ago -
 willow-the-outcast1123 liked this · 1 year ago
willow-the-outcast1123 liked this · 1 year ago -
 adorelas liked this · 1 year ago
adorelas liked this · 1 year ago -
 hotchnerslays liked this · 1 year ago
hotchnerslays liked this · 1 year ago -
 marketingdata liked this · 1 year ago
marketingdata liked this · 1 year ago -
 theworsttimeever liked this · 1 year ago
theworsttimeever liked this · 1 year ago -
 mrmaliciousintent liked this · 1 year ago
mrmaliciousintent liked this · 1 year ago -
 theonewhostrugleswithands liked this · 1 year ago
theonewhostrugleswithands liked this · 1 year ago -
 ih8skepi liked this · 1 year ago
ih8skepi liked this · 1 year ago -
 landbread liked this · 1 year ago
landbread liked this · 1 year ago
