Computational Modeling Of Fusion Plasmas Is Very Challenging: Scales To Be Covered Range From Micrometers
Computational modeling of fusion plasmas is very challenging: scales to be covered range from micrometers to meters and picoseconds to minutes. With largest supercomputers available, our understanding was pushed forward by modelling and still is.
#FusionFriday
(GIF: Waltz/Candy) https://t.co/hKdD5VGNNf
More Posts from Mousoudi20 and Others
good smell with good day!!

Five Record-Setting Gamma-ray Bursts!
For 10 years, our Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope has scanned the sky for gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), the universe’s most luminous explosions!

Most GRBs occur when some types of massive stars run out of fuel and collapse to create new black holes. Others happen when two neutron stars, superdense remnants of stellar explosions, merge. Both kinds of cataclysmic events create jets of particles that move near the speed of light.
A new catalog of the highest-energy blasts provides scientists with fresh insights into how they work. Below are five record-setting events from the catalog that have helped scientists learn more about GRBs:
1. Super-short burst in Boötes!

The short burst 081102B, which occurred in the constellation Boötes on Nov. 2, 2008, is the briefest LAT-detected GRB, lasting just one-tenth of a second!
2. Long-lived burst!

Long-lived burst 160623A, spotted on June 23, 2016, in the constellation Cygnus, kept shining for almost 10 hours at LAT energies — the longest burst in the catalog.
For both long and short bursts, the high-energy gamma-ray emission lasts longer than the low-energy emission and happens later.
3. Highest energy gamma-rays!

The highest-energy individual gamma ray detected by Fermi’s LAT reached 94 billion electron volts (GeV) and traveled 3.8 billion light-years from the constellation Leo. It was emitted by 130427A, which also holds the record for the most gamma rays — 17 — with energies above 10 GeV.
4. In a constellation far, far away!

The farthest known GRB occurred 12.2 billion light-years away in the constellation Carina. Called 080916C, researchers calculate the explosion contained the power of 9,000 supernovae.
5. Probing the physics of our cosmos!

The known distance to 090510 helped test Einstein’s theory that the fabric of space-time is smooth and continuous. Fermi detected both a high-energy and a low-energy gamma ray at nearly the same instant. Having traveled the same distance in the same amount of time, they showed that all light, no matter its energy, moves at the same speed through the vacuum of space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
The scaffolding has come off the lower cylinder of the #ITER #cryostat. Clad in thin film it is now being scanned by metrologists for reverse engineering and will then be cocooned for storage until assembly. #fusionenergy #WeAreITER https://t.co/DOag9p1rPp https://t.co/xoi5GTq0Vc
We Like Big Rockets and We Cannot Lie: Saturn V vs. SLS
On this day 50 years ago, human beings embarked on a journey to set foot on another world for the very first time.

At 9:32 a.m. EDT, millions watched as Apollo astronauts Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins lifted off from Launch Pad 39A at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, flying high on the most powerful rocket ever built: the mighty Saturn V.

As we prepare to return humans to the lunar surface with our Artemis program, we’re planning to make history again with a similarly unprecedented rocket, the Space Launch System (SLS). The SLS will be our first exploration-class vehicle since the Saturn V took American astronauts to the Moon a decade ago. With its superior lift capability, the SLS will expand our reach into the solar system, allowing astronauts aboard our Orion spacecraft to explore multiple, deep-space destinations including near-Earth asteroids, the Moon and ultimately Mars.

So, how does the Saturn V measure up half a century later? Let’s take a look.
Mission Profiles: From Apollo to Artemis
Saturn V

Every human who has ever stepped foot on the Moon made it there on a Saturn V rocket. The Saturn rockets were the driving force behind our Apollo program that was designed to land humans on the Moon and return them safely back to Earth.

Developed at our Marshall Space Flight Center in the 1960s, the Saturn V rocket (V for the Roman numeral “5”) launched for the first time uncrewed during the Apollo 4 mission on November 9, 1967. One year later, it lifted off for its first crewed mission during Apollo 8. On this mission, astronauts orbited the Moon but did not land. Then, on July 16, 1969, the Apollo 11 mission was the first Saturn V flight to land astronauts on the Moon. In total, this powerful rocket completed 13 successful missions, landing humans on the lunar surface six times before lifting off for the last time in 1973.
Space Launch System (SLS)

Just as the Saturn V was the rocket of the Apollo generation, the Space Launch System will be the driving force behind a new era of spaceflight: the Artemis generation.

During our Artemis missions, SLS will take humanity farther than ever before. It is the vehicle that will return our astronauts to the Moon by 2024, transporting the first woman and the next man to a destination never before explored – the lunar South Pole. Over time, the rocket will evolve into increasingly more powerful configurations to provide the foundation for human exploration beyond Earth’s orbit to deep space destinations, including Mars.
SLS will take flight for the first time during Artemis 1 where it will travel 280,000 miles from Earth – farther into deep space than any spacecraft built for humans has ever ventured.
Size: From Big to BIGGER
Saturn V

The Saturn V was big.
In fact, the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center is one of the largest buildings in the world by volume and was built specifically for assembling the massive rocket. At a height of 363 feet, the Saturn V rocket was about the size of a 36-story building and 60 feet taller than the Statue of Liberty!
Space Launch System (SLS)

Measured at just 41 feet shy of the Saturn V, the initial SLS rocket will stand at a height of 322 feet. Because this rocket will evolve into heavier lift capacities to facilitate crew and cargo missions beyond Earth’s orbit, its size will evolve as well. When the SLS reaches its maximum lift capability, it will stand at a height of 384 feet, making it the tallest rocket in the world.
Power: Turning Up the Heat
Saturn V
For the 1960s, the Saturn V rocket was a beast – to say the least.
Fully fueled for liftoff, the Saturn V weighed 6.2 million pounds and generated 7.6 million pounds of thrust at launch. That is more power than 85 Hoover Dams! This thrust came from five F-1 engines that made up the rocket’s first stage. With this lift capability, the Saturn V had the ability to send 130 tons (about 10 school buses) into low-Earth orbit and about 50 tons (about 4 school buses) to the Moon.
Space Launch System (SLS)

Photo of SLS rocket booster test
Unlike the Saturn V, our SLS rocket will evolve over time into increasingly more powerful versions of itself to accommodate missions to the Moon and then beyond to Mars.
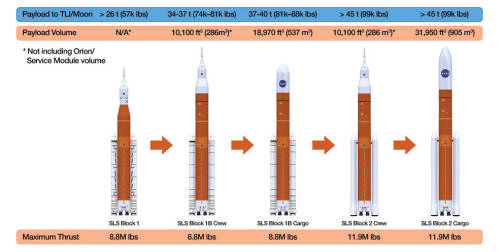
The first SLS vehicle, called Block 1, will weigh 5.75 million pounds and produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust at time of launch. That’s 15 percent more than the Saturn V produced during liftoff! It will also send more than 26 tons beyond the Moon. Powered by a pair of five-segment boosters and four RS-25 engines, the rocket will reach the period of greatest atmospheric force within 90 seconds!

Following Block 1, the SLS will evolve five more times to reach its final stage, Block 2 Cargo. At this stage, the rocket will provide 11.9 million pounds of thrust and will be the workhorse vehicle for sending cargo to the Moon, Mars and other deep space destinations. SLS Block 2 will be designed to lift more than 45 tons to deep space. With its unprecedented power and capabilities, SLS is the only rocket that can send our Orion spacecraft, astronauts and large cargo to the Moon on a single mission.
Build: How the Rockets Stack Up
Saturn V

The Saturn V was designed as a multi-stage system rocket, with three core stages. When one system ran out of fuel, it separated from the spacecraft and the next stage took over. The first stage, which was the most powerful, lifted the rocket off of Earth’s surface to an altitude of 68 kilometers (42 miles). This took only 2 minutes and 47 seconds! The first stage separated, allowing the second stage to fire and carry the rest of the stack almost into orbit. The third stage placed the Apollo spacecraft and service module into Earth orbit and pushed it toward the Moon. After the first two stages separated, they fell into the ocean for recovery. The third stage either stayed in space or crashed into the Moon.
Space Launch System (SLS)
Much like the Saturn V, our Space Launch System is also a multi-stage rocket. Its three stages (the solid rocket boosters, core stage and upper stage) will each take turns thrusting the spacecraft on its trajectory and separating after each individual stage has exhausted its fuel. In later, more powerful versions of the SLS, the third stage will carry both the Orion crew module and a deep space habitat module.
A New Era of Space Exploration
Just as the Saturn V and Apollo era signified a new age of exploration and technological advancements, the Space Launch System and Artemis missions will bring the United States into a new age of space travel and scientific discovery.
Join us in celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 Moon landing and hear about our future plans to go forward to the Moon and on to Mars by tuning in to a special two-hour live NASA Television broadcast at 1 p.m. ET on Friday, July 19. Watch the program at www.nasa.gov/live.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
.@ScottAdamsSays
#GreenNuclearDeal
"Scientists achieved high pressure plasma perhaps laying the groundwork to achieve fusion power at an old fusion reactor in San Diego by reversing the orientation of the vessel that houses the plasma."
https://t.co/gXsKDDEHY3
#ITER DG Bernard Bigot opened #IBF2019 this morning, urging ITER’s industrial partners to continue to deliver their contributions on time and at the highest level of quality. #WeAreITER https://t.co/VVAVlnkFlR

Say hello to the Butterfly Nebula 👋
It looks like our Hubble Space Telescope captured an image of a peaceful, cosmic butterfly unfurling its celestial wings, but the truth is vastly more violent. In the Butterfly Nebula, layers of gas are being ejected from a dying star. Medium-mass stars grow unstable as they run out of fuel, which leads them to blast tons of material out into space at speeds of over a million miles per hour!
Streams of intense ultraviolet radiation cause the cast-off material to glow, but eventually the nebula will fade and leave behind only a small stellar corpse called a white dwarf. Our middle-aged Sun can expect a similar fate once it runs out of fuel in about six billion years.
Planetary nebulas like this one aren’t actually related to planets; the term was coined by astronomer William Herschel, who actually discovered the Butterfly Nebula in 1826. Through his small telescope, planetary nebulas looked like glowing, planet-like orbs. While stars that generate planetary nebulas may have once had planets orbiting them, scientists expect that the fiery death throes these stars undergo will ultimately leave any planets in their vicinity completely uninhabitable.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
