Maevetheeuropan - Maeve The Europan

More Posts from Maevetheeuropan and Others
Spacewalk Friday: Installing a New "Parking Spot" on Station
This Friday, Aug. 19, two U.S. astronauts will install a new gateway for American commercial crew spacecraft at the International Space Station.

Commercial crew flights from Florida’s Space Coast to the International Space Station will restore America’s human spaceflight launch capability and increase the time U.S. crews can dedicate to scientific research.

The adapter being installed (imaged below) was launched on a SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft and arrived on orbit July 20. NASA astronauts Jeff Williams and Kate Rubins will perform the spacewalk to install the equipment this Friday, Aug. 19. This will be the fourth spacewalk in Williams’ career and the first for Rubins.

Four previous spacewalks…like the one below…helped set the stage for installation of this docking adapter. During those previous spacewalks, other crew members laid hundreds of feet of power and data cables outside the space station.

On Wednesday, the robotics team using the Canadarm2 and its attached “Dextre” manipulator, will reach into the SpaceX Dragon trunk and pull out the docking adapter and position it for Friday’s spacewalk activities.

The morning of the spacewalk, while the astronauts are getting suited up, the robotic arm will position the docking adaptor near the port so that it will be ready for installation.

The two astronauts will venture outside the space station to install the first International Docking Adapter (IDA). This new adapter port will provide a parking space for U.S. Commercial Crew vehicles.
Watch LIVE!
Coverage of the spacewalk begins at 6:30 a.m. EDT on Friday, Aug. 19; with the spacewalk scheduled to begin at 8:05 a.m. EDT. Stream live online HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Space Station Research: Cardiovascular Health
Each month, we highlight a different research topic on the International Space Station. In February, our focus is cardiovascular health, which coincides with the American Hearth Month.
Like bones and muscle, the cardiovascular system deconditions (gets weaker) in microgravity. Long-duration spaceflight may increase the risk of damage and inflammation in the cardiovascular system primarily from radiation, but also from psychological stress, reduced physical activity, diminished nutritional standards and, in the case of extravehicular activity, increased oxygen exposure.

Even brief periods of exposure to reduced-gravity environments can result in cardiovascular changes such as fluid shifts, changes in total blood volume, heartbeat and heart rhythm irregularities and diminished aerobic capacity.

The weightless environment of space also causes fluid shifts to occur in the body. This normal shift of fluids to the upper body in space causes increased inter-cranial pressure which could be reducing visual capacity in astronauts. We are currently testing how this can be counteracted by returning fluids to the lower body using a “lower body negative pressure” suit, also known as Chibis.
Spaceflight also accelerates the aging process, and it is important to understand this process to develop specific countermeasures. Developing countermeasures to keep astronauts’ hearts healthy in space is applicable to heart health on Earth, too!

On the space station, one of the tools we have to study heart health is the ultrasound device, which uses harmless sound waves to take detailed images of the inside of the body. These images are then viewed by researchers and doctors inside Mission Control. So with minimal training on ultrasound, remote guidance techniques allow astronauts to take images of their own heart while in space. These remote medicine techniques can also be beneficial on Earth.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
ooooo how awesome!

Prototype of Space Station’s Advanced Plant Habitat via NASA http://ift.tt/2fremIw

This is hands down one of the most beautiful images I’ve ever seen. This is a visible-light image of Jupiter’s clouds from a mere 5000 km away.
What’s even more amazing is that this image was taken by JunoCam, NASA’s camera essentially being controlled by regular folks, not scientists. The public takes part in selecting targets to photograph, as well as having access to the raw data that comes back and you can even take the raw images that come back and process your own picture! Learn more about it all right here.
Thank you NASA!
(Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Gerald Eichstaedt/John Rogers)
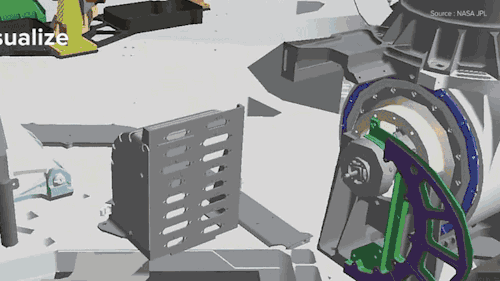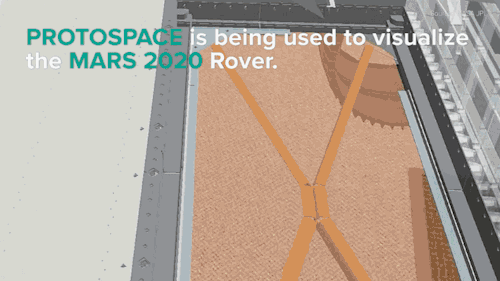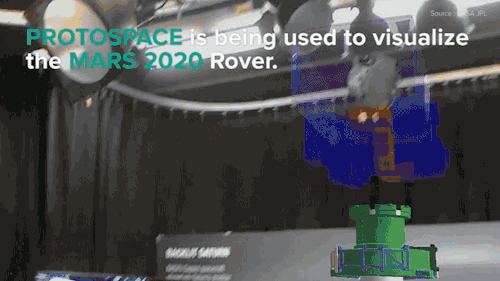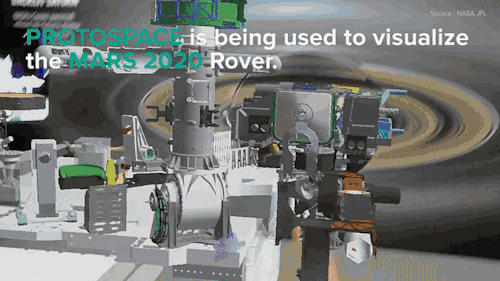
NASA is building the next Mars rover in mixed reality and It’s absolutely jaw-dropping!


Elon Musk wants to put people on Mars in less than a decade
Musk has already said he wants SpaceX to start sending unmanned missions to Mars in 2018. He has even planned out the details of the future expeditions.
Follow @the-future-now
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Learn about the science of photonics to create space communications, get updates on Juno, mining data from Voyager for new discoveries and more.

1. Carried on a Beam of Light
One of our major priorities is to make space communications more efficient. While our communications systems have matured over the decades, they still use the same radio-frequency system developed in the earliest days of the agency. After more than 50 years, we’re investing in new ways to increase data rates while also finding more efficient communications systems. Photonics–generating, detecting and manipulating particles of light–may provide the solution.
+ See how it works

2. It’s No Joke: Two New Moons for the Seventh Planet
Voyager 2 spacecraft flew by Uranus 30 years ago, but researchers are still making discoveries using the data it gathered. A new study led by University of Idaho researchers suggests there could be two tiny, previously undiscovered moonlets orbiting near two of the planet’s rings.
+ Find out how they were discovered

3. Vortex of Mystery
As southern winter solstice approaches in the Saturn system, our Cassini spacecraft has revealed dramatic seasonal changes in the atmospheric temperature and composition of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. Winter is taking a grip on Titan’s southern hemisphere, and a strong, whirling vortex has intensified in the upper atmosphere over the south pole.
+See more

4. The Spiders of Mars
Ten thousand volunteers viewing images of Martian south polar regions have helped identify targets for closer inspection, yielding new insights about seasonal slabs of frozen carbon dioxide and erosional features known as “spiders.” From the comfort of home, the volunteers have been exploring the surface of Mars by reviewing images from the Context Camera on our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and identifying certain types of seasonal terrains near Mars’ south pole.
+ Learn more and see how you can join in

7. Better Safe than Sorry
Juno entered safe mode last week and early indications are a software performance monitor induced a reboot of the spacecraft’s onboard computer. In this case, the safe mode turned off instruments and a few non-critical spacecraft components, and it confirmed the spacecraft was pointed toward the sun to ensure the solar arrays received power.The spacecraft acted as expected during the transition into safe mode, restarted successfully and is healthy. High-rate data has been restored, and the spacecraft is conducting flight software diagnostics. Meanwhile, the Juno science team continues to analyze returns from the first close Jupiter flyby on Aug. 27. Revelations so far include that Jupiter’s magnetic fields and aurora are bigger and more powerful than thought. Scientists have also had their first glimpse below the planet’s swirling cloud deck. The next close flyby is scheduled on Dec. 11, with all science instruments on.
+ Get the details
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com







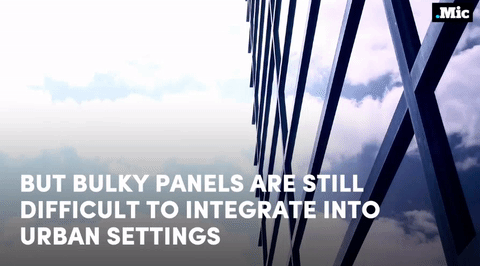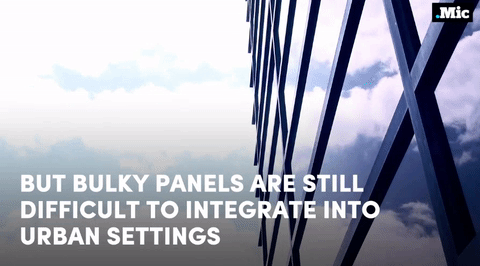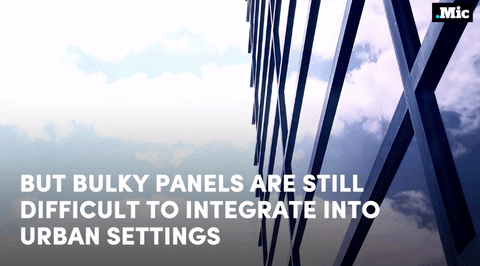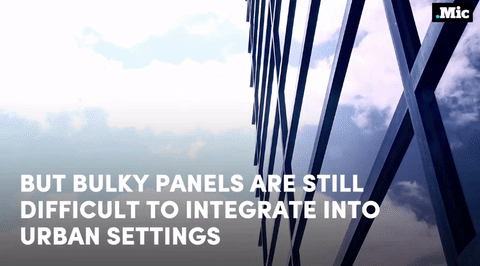


this is a massive step forward for renewable energy (x) | follow @the-future-now
-
 thekawaiibutterflygirl reblogged this · 7 years ago
thekawaiibutterflygirl reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 thekawaiibutterflygirl liked this · 7 years ago
thekawaiibutterflygirl liked this · 7 years ago -
 bi-stronomer reblogged this · 7 years ago
bi-stronomer reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 thisnewjoe liked this · 7 years ago
thisnewjoe liked this · 7 years ago -
 animate-mush reblogged this · 7 years ago
animate-mush reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 residentcrazy reblogged this · 7 years ago
residentcrazy reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 residentcrazy liked this · 7 years ago
residentcrazy liked this · 7 years ago -
 serayashadowharper liked this · 7 years ago
serayashadowharper liked this · 7 years ago -
 ununnilium reblogged this · 7 years ago
ununnilium reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 ununnilium liked this · 7 years ago
ununnilium liked this · 7 years ago -
 fredscience-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
fredscience-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 obsessively-me-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
obsessively-me-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 terminalseventeen liked this · 7 years ago
terminalseventeen liked this · 7 years ago -
 fifthconfiguration liked this · 7 years ago
fifthconfiguration liked this · 7 years ago -
 moon-pizza-action reblogged this · 7 years ago
moon-pizza-action reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 dreams-of-nostalgia reblogged this · 7 years ago
dreams-of-nostalgia reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 rhysgfrelsa-eudyptula liked this · 7 years ago
rhysgfrelsa-eudyptula liked this · 7 years ago -
 lunafiores reblogged this · 7 years ago
lunafiores reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 lunafiores liked this · 7 years ago
lunafiores liked this · 7 years ago -
 kiss-my-ascot liked this · 7 years ago
kiss-my-ascot liked this · 7 years ago -
 the-fabulous-book liked this · 7 years ago
the-fabulous-book liked this · 7 years ago -
 lavendertownsghost reblogged this · 7 years ago
lavendertownsghost reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 snakefeathers liked this · 7 years ago
snakefeathers liked this · 7 years ago -
 onceuponatmi liked this · 7 years ago
onceuponatmi liked this · 7 years ago -
 purple-bandanaman reblogged this · 7 years ago
purple-bandanaman reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 sandisupastar liked this · 7 years ago
sandisupastar liked this · 7 years ago -
 gamingmadereality reblogged this · 7 years ago
gamingmadereality reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 gamingmadereality liked this · 7 years ago
gamingmadereality liked this · 7 years ago -
 turq8 reblogged this · 7 years ago
turq8 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 corvidae-quills reblogged this · 7 years ago
corvidae-quills reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 lari2311 liked this · 7 years ago
lari2311 liked this · 7 years ago -
 of-moss liked this · 7 years ago
of-moss liked this · 7 years ago -
 bodhishadow liked this · 7 years ago
bodhishadow liked this · 7 years ago -
 cutthroatbitchcult liked this · 7 years ago
cutthroatbitchcult liked this · 7 years ago -
 frostedmeats liked this · 7 years ago
frostedmeats liked this · 7 years ago -
 jubilational liked this · 7 years ago
jubilational liked this · 7 years ago -
 nightfalltwen reblogged this · 7 years ago
nightfalltwen reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 nthd-jen liked this · 7 years ago
nthd-jen liked this · 7 years ago -
 unactivenotactiveanymorebye liked this · 7 years ago
unactivenotactiveanymorebye liked this · 7 years ago


