The Soul Nebula Pictured, Bright Massive Stars Near The Center Of W5, The Soul Nebula, Are Exploding

The Soul Nebula Pictured, bright massive stars near the center of W5, the Soul Nebula, are exploding and emitting ionizing light and energetic winds. The outward-moving light and gas push away and evaporate much surrounding gas and dust, but leave pillars of gas behind dense protective knots. Inside these knots, though, stars also form. The featured image highlights the inner sanctum of W5, an arena spanning about 1,000 light years that is rich in star forming pillars. The Soul Nebula, also cataloged as IC 1848, lies about 6,500 light years away toward the constellation of the Queen of Aethopia (Cassiopeia). Likely, in few hundred million years, only a cluster of the resulting stars will remain. Then, these stars will drift apart. (APOD/NASA)
Image Credit: José Jiménez Priego (Astromet)
More Posts from Maevetheeuropan and Others

Mars used to be much more Earth-like than we once thought. The Curiosity rover recently discovered high levels of manganese oxide, which can only exist in oxygen-rich environments. This means Mars used to have as much oxygen as Earth and plenty of water on its surface. Source Source 2


Shadow
The US’s GOES-16 weather satellite (still in its testing/non-operational phase) sent back this series of photos taken every 5 minutes today, showing the shadow of the moon marching across the continent. Video shared originally here:
https://twitter.com/UWSSEC/status/899707692364836866
http://www.ssec.wisc.edu
-JBB







Here’s a comic on something flaming hot!
This week’s comic: Firewall Theory
http://www.sciencealert.com/try-to-escape-a-black-hole-and-you-ll-be-burnt-to-a-crisp-new-paper-cautions
https://profmattstrassler.com/articles-and-posts/relativity-space-astronomy-and-cosmology/black-holes/black-hole-information-paradox-an-introduction/
so this happened
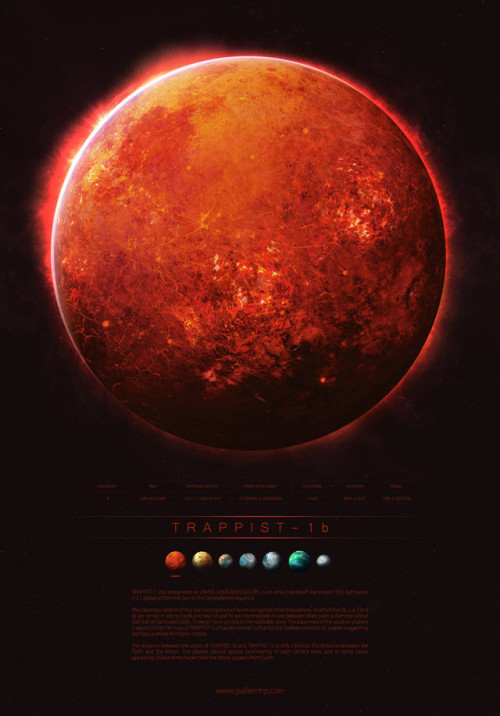
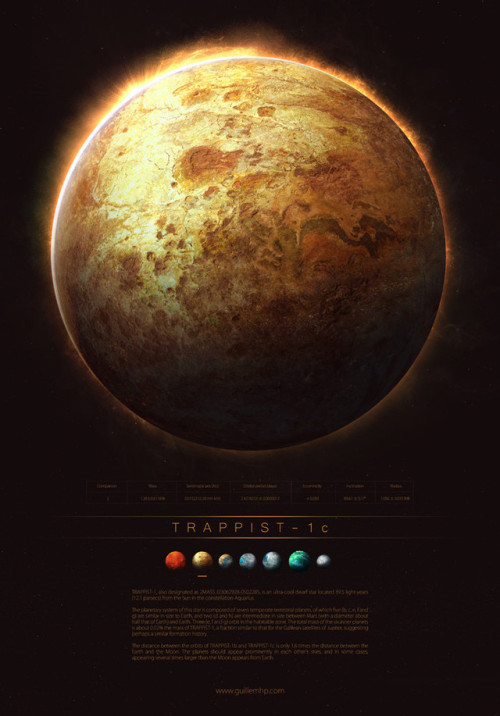








TRAPPIST - 1 by Guillem H. Pongiluppi

New Hubble Portrait of Mars (which will be at its closest to us on 30 May)
On May 12, 2016, the Hubble Space Telescope captured this vivid photo of Mars, when the planet was closer to Earth than usual and approaching the opposition (when the sun and Mars will be on exact opposite sides of Earth). Mars is especially photogenic during opposition because it can be seen fully illuminated by the sun as viewed from Earth. Mars will reach opposition on May 22.
Furthermore, the closest approach to Earth for the year will occur on 30 May, when Mars will be at a distance of 75.28 million km (46.78 million miles) from us. For comparison, the average distance between the two is 225 million km. These two events so close together make the coming week(s) the best time to observe the red planet with a telescope. You can already notice it in the night sky (check for your location) as one of the brightest dots with a red-orange glow near the Moon.
Read about the Hubble’s image here.
Image credits: NASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA), J. Bell (ASU), and M. Wolff (Space Science Institute)
-
 jumpshadow liked this · 1 year ago
jumpshadow liked this · 1 year ago -
 doomup reblogged this · 2 years ago
doomup reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 narutogudiofwo-blog liked this · 6 years ago
narutogudiofwo-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 genocider-syo-is-still-my-queen liked this · 6 years ago
genocider-syo-is-still-my-queen liked this · 6 years ago -
 ajc18615425 liked this · 6 years ago
ajc18615425 liked this · 6 years ago -
 afterthedragonflies liked this · 6 years ago
afterthedragonflies liked this · 6 years ago -
 harmonic-psyche liked this · 6 years ago
harmonic-psyche liked this · 6 years ago -
 i-s-d-m-8 liked this · 6 years ago
i-s-d-m-8 liked this · 6 years ago -
 thepizzalovingnerd liked this · 6 years ago
thepizzalovingnerd liked this · 6 years ago -
 thedoctorsawkwardhufflepuff liked this · 6 years ago
thedoctorsawkwardhufflepuff liked this · 6 years ago -
 metautske reblogged this · 6 years ago
metautske reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 metautske liked this · 6 years ago
metautske liked this · 6 years ago -
 kissmystrawberryflame liked this · 6 years ago
kissmystrawberryflame liked this · 6 years ago -
 mereoleonawifecity liked this · 6 years ago
mereoleonawifecity liked this · 6 years ago -
 youareprettierthanthestars liked this · 6 years ago
youareprettierthanthestars liked this · 6 years ago -
 theastralscribe reblogged this · 6 years ago
theastralscribe reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 edy-bastos liked this · 6 years ago
edy-bastos liked this · 6 years ago -
 sudden-sense-pdf-blog liked this · 6 years ago
sudden-sense-pdf-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 daemondamian liked this · 6 years ago
daemondamian liked this · 6 years ago -
 theroamingtaco reblogged this · 6 years ago
theroamingtaco reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 theroamingtaco liked this · 6 years ago
theroamingtaco liked this · 6 years ago -
 dirhwangdaseul-archived reblogged this · 6 years ago
dirhwangdaseul-archived reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 prettyflyforabi reblogged this · 6 years ago
prettyflyforabi reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 prettyflyforabi liked this · 6 years ago
prettyflyforabi liked this · 6 years ago -
 jeza-red reblogged this · 6 years ago
jeza-red reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 moonlitxveil liked this · 6 years ago
moonlitxveil liked this · 6 years ago -
 mysticrebel97 liked this · 6 years ago
mysticrebel97 liked this · 6 years ago -
 joyfultechnologybeautyprofe-blog liked this · 6 years ago
joyfultechnologybeautyprofe-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 arongio liked this · 6 years ago
arongio liked this · 6 years ago -
 0phiaaa-a liked this · 6 years ago
0phiaaa-a liked this · 6 years ago -
 justbottomsexaddicted liked this · 7 years ago
justbottomsexaddicted liked this · 7 years ago -
 nadolsp-blog liked this · 7 years ago
nadolsp-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 redviper12 liked this · 7 years ago
redviper12 liked this · 7 years ago -
 bandnerd15 liked this · 7 years ago
bandnerd15 liked this · 7 years ago -
 just-complete-trash liked this · 7 years ago
just-complete-trash liked this · 7 years ago -
 thorns-of-a-soul reblogged this · 7 years ago
thorns-of-a-soul reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 solvingcomics liked this · 7 years ago
solvingcomics liked this · 7 years ago -
 silver-vulpes-vulpes reblogged this · 7 years ago
silver-vulpes-vulpes reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 b3llaluna reblogged this · 7 years ago
b3llaluna reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 oetetammeurrl-blog liked this · 7 years ago
oetetammeurrl-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 kimidikimkim liked this · 7 years ago
kimidikimkim liked this · 7 years ago


