Maevetheeuropan - Maeve The Europan





More Posts from Maevetheeuropan and Others

bioshock infinite is about to become reality

When Japan began to rebuild after the 2011 earthquake and tsunami, artist Manabu Ikeda started a massive pen & ink piece. He worked 10 hours a day, 6 days a week, for 3.5 years before finishing ‘Rebirth’, a 13x10 foot drawing of a tree rising from chaos and ruin. Source Source 2




Creepy or adorable? Researchers at Harvard University have demonstrated the first autonomous, untethered, entirely soft robot: the octobot.
Instead of being controlled by electronics, the robot’s logic board is powered by chemical reactions and fluid passing along tiny channels. Scientist have struggled to create completely soft robots because rigid components like circuit boards, power sources and electronic controls are difficult to replace.
Learn more about the octobot and soft robotics here and see the full study published in Nature here.
Videos Credit: Harvard SEAS/Image Credit Lori Sanders







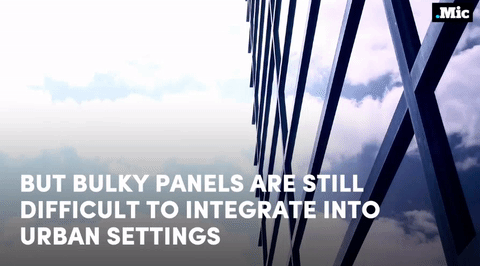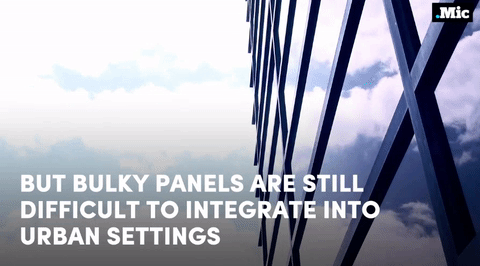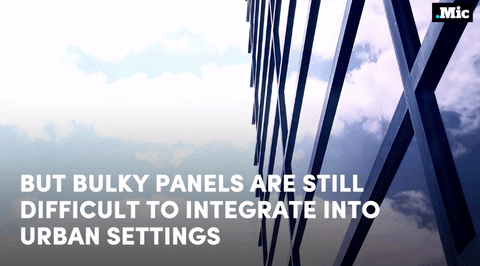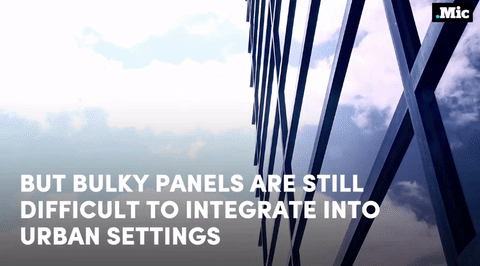


this is a massive step forward for renewable energy (x) | follow @the-future-now
Kate Rubins’ Space Station Science Scrapbook
As a child, Kate Rubins dreamed of being an astronaut and a scientist. During the past four months aboard the International Space Station, that dream came full circle. She became the first person to sequence DNA in space, among other research during her recent mission, adding to her already impressive experience. She holds a doctorate in molecular biology, and previously led a lab of 14 researchers studying viruses, including Ebola.

Here’s a look back at Rubins in her element, conducting research aboard your orbiting laboratory.
Kate inside Destiny, the U.S. Laboratory Module
The U.S. national laboratory, called Destiny, is the primary research laboratory for U.S. payloads, supporting a wide range of experiments and studies contributing to health, safety, and quality of life for people all over the world.

Destiny houses the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG), in which Kate worked on the Heart Cells experiment.
Swabbing for Surface Samples
Microbes that can cause illness could present problems for current and future long duration space missions.

Understanding what microbe communities thrive in space habitats could help researchers design antimicrobial technology. Here, Kate is sampling various surfaces of the Kibo module for the Microbe-IV investigation.
Culturing Beating Heart Cells in Space
The Heart Cells investigation uses human skin cells that are induced to become stem cells, which can then differentiate into any type of cell.

Researchers forced the stem cells to grow into human heart cells, which Rubins cultured aboard the space station for one month.

Rubins described seeing the heart cells beat for the first time as “pretty amazing. First of all, there’s a few things that have made me gasp out loud up on board the [space] station. Seeing the planet was one of them, but I gotta say, getting these cells in focus and watching heart cells actually beat has been another pretty big one.”
Innovative Applied Research Experiment from Eli Lilly
The Hard to Wet Surfaces investigation from Eli Lilly, and sponsored by the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS), looks at liquid-solid interactions and how certain pharmaceuticals dissolve, which may lead to more potent and effective medicines in space and on Earth.

Rubins set up vials into which she injected buffer solutions and then set up photography to track how tablets dissolved in the solution in microgravity.
Capturing Dragon
Rubins assisted in the capture of the SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft in July. The ninth SpaceX resupply mission delivered more than two thousand pounds of science to the space station.

Biological samples and additional research were returned on the Dragon spacecraft more than a month later.
Sliding Science Outside the Station
Science doesn’t just happen inside the space station. External Earth and space science hardware platforms are located at various places along the outside of the orbiting laboratory.

The Japanese Experiment Module airlock can be used to access the JEM Exposed Facility. Rubins installed the JEM ORU Transfer Interface (JOTI) on the JEM airlock sliding table used to install investigations on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory.
Installing Optical Diagnostic Instrument in the MSG
Rubins installed an optical diagnostic instrument in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) as part of the Selective Optical Diagnostics Instrument (SODI-DCMIX) investigation. Molecules in fluids and gases constantly move and collide.

When temperature differences cause that movement, called the Soret effect, scientists can track it by measuring changes in the temperature and movement of mass in the absence of gravity. Because the Soret effect occurs in underground oil reservoirs, the results of this investigation could help us better understand such reservoirs.
The Sequencing of DNA in Space
When Rubins’ expedition began, DNA had never been sequenced in space. Within just a few weeks, she and the Biomolecule Sequencer team had sequenced their one billionth “base” – the unit of DNA - aboard the orbiting laboratory.

The Biomolecule Sequencer investigation seeks to demonstrate that DNA sequencing in microgravity is possible, and adds to the suite of genomics capabilities aboard the space station.
Studying Fluidic Dynamics with SPHERES
The SPHERES-Slosh investigation examines the way liquids move inside containers in a microgravity environment. The phenomena and mechanics associated with such liquid movement are still not well understood and are very different than our common experiences with a cup of coffee on Earth.

Rockets deliver satellites to space using liquid fuels as a power source, and this investigation plans to improve our understanding of how propellants within rockets behave in order to increase the safety and efficiency of future vehicle designs. Rubins conducted a series of SPHERES-Slosh runs during her mission.
Retrieving Science Samples for Their Return to Earth
Precious science samples like blood, urine and saliva are collected from crew members throughout their missions aboard the orbiting laboratory.

They are stored in the Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) until they are ready to return to Earth aboard a Soyuz or SpaceX Dragon vehicle.
Measuring Gene Expression of Biological Specimens in Space
Our WetLab-2 hardware system is bringing to the space station the technology to measure gene expression of biological specimens in space, and to transmit the results to researchers on Earth at the speed of light.

Rubins ran several WetLab-2 RNA SmartCycler sessions during her mission.
Studying the First Expandable Habitat Module on the Space Station
The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) is the first expandable habitat to be installed on the space station. It was expanded on May 28, 2016.

Expandable habitats are designed to take up less room on a spacecraft, but provide greater volume for living and working in space once expanded. Rubins conducted several evaluations inside BEAM, including air and surface sampling.
Better Breathing in Space and Back on Earth
Airway Monitoring, an investigation from ESA (the European Space Agency), uses the U.S. airlock as a hypobaric facility for performing science. Utilizing the U.S. airlock allows unique opportunities for the study of gravity, ambient pressure interactions, and their effect on the human body.

This investigation studies the occurrence and indicators of airway inflammation in crew members, using ultra-sensitive gas analyzers to evaluate exhaled air. This could not only help in spaceflight diagnostics, but that also hold applications on earth within diagnostics of similar conditions, for example monitoring of asthma.
Hot Science with Cool Flames
Fire behaves differently in space, where buoyant forces are removed. Studying combustion in microgravity can increase scientists’ fundamental understanding of the process, which could lead to improvement of fire detection and suppression systems in space and on Earth.

Many combustion experiments are performed in the Combustion Integration Rack (CIR) aboard the space station. Rubins replaced two Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Igniter Tips as part of the CIR igniter replacement operations.
Though Rubins is back on Earth, science aboard the space station continues, and innovative investigations that seek to benefit humans on Earth and further our exploration of the solar system are ongoing. Follow @ISS_Research to keep up with the science happening aboard your orbiting laboratory.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
NASA Technology in Your Life
How does NASA technology benefit life on Earth? It probably has an impact in more ways than you think! Since 1976, our Spinoff program has profiled nearly 2,000 space technologies that have transformed into commercial products and services. In celebration of Spinoff’s 40th year of publication, we’ve assembled a collection of spinoffs that have had the greatest impact on Earth.
Take a look and see how many you utilize on a regular basis:
Digital Image Sensors

Whether you take pictures and videos with a DSLR camera or a cell phone, or even capture action on the go with a device like a GoPro Hero, you’re using NASA technology. The CMOS active pixel sensor in most digital image- capturing devices was invented when we needed to miniaturize cameras for interplanetary missions. This technology is also widely used in medical imaging and dental X-ray devices.
Enriched Baby Formula

While developing life support for Mars missions, NASA-funded researchers discovered a natural source for an omega-3 fatty acid previously found primarily in breast milk that plays a key role in infant development. The ingredient has since been added to more than 90% of infant formula on the market and is helping babies worldwide develop healthy brains, eyes and hearts.
NASTRAN Software

NASTRAN is a software developed by our engineers that performs structural analysis in the 1960s. Still popular today, it’s been used to help design everything from airplanes and cars to nuclear reactors and even Disney’s Space Mountain roller coaster.
Food Safety Standards

Looking to ensure the absolute safety of prepackaged foods for spaceflight, we partnered with the Pillsbury Company to create a new, systematic approach to quality control. Now known as Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), the method has become an industry standard that benefits consumers worldwide by keeping food free from a wide range of potential chemical, physical and biological hazards.
Neutral Body Posture Specifications

What form does the human body naturally assume when all physical influences, including the pull of gravity, stop affecting it? We conducted research to find out using Skylab, America’s first space station, and later published specifications for what it called neutral body posture. The study has informed seat designs in everything from airplanes and office chairs to several models of Nissan automobiles.
Advanced Water Filtration

We recently discovered unexpected sources of water on the moon and Mars, but even so, space remains a desert for human explorers, and every drop must be recycled and reused. A nano filter devised to purify water in orbit is currently at work on Earth, in devices that supply water to remote villages as well as in a water bottle that lets hikers and adventurers stay hydrated using streams and lakes.
Swimsuit Designs

Wind-tunnel testing at our Langley Research Center played a key role in the development of Speedo’s LZR Racer swimsuit, proving which materials and seams best reduced drag as a swimmer cuts through the water. The swimsuit made a splash during its Olympic debut in 2008, as nearly every medal winner and world-record breaker wore the suit.
Air Purifier

When plants grow, they release a gas called ethylene that accelerates decay, hastening the wilting of flowers and the ripening of fruits and vegetables. Air circulation on Earth keeps the fumes from building up, but in the hermetically sealed environment of a spacecraft, ethylene poses a real challenge to the would-be space farmers. We funded the development of an ethylene scrubber for the International Space Station that has subsequently proved capable of purifying air on Earth from all kinds of pathogens and particulates. Grocery stores use it to keep produce fresh longer. It’s also been marketed for home use and has even been embraced by winemakers, who employ the scrubber to keep aging wine in barrels free from mold, mildew and musty odors.
Scratch-Resistant, UV-Reflective Lenses

Some of the earliest research into effective scratch-resistant coatings for prescription and sunglass lenses drew from work done at Ames Research Center on coatings for astronaut helmet visors and plastic membranes used in water purification systems. In the 1980s, we developed sunlight-filtering lenses to provide eye protection and enhance colors, and these lenses have found their way into sunglasses, ski goggles and safety masks for welders.
Dustbuster

An Apollo-era partnership with Black & Decker to build battery-operated tools for moon exploration and sample collection led to the development of a line of consumer, medical and industrial hand-held cordless tools. This includes the popular Dustbuster cordless vacuum.
To see even more of our spinoff technologies, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/offices/oct/40-years-of-nasa-spinoff
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

@little-laced Here are some test shots I took of the moon. It’s hard to tell because I had to reduce the image size drastically but the telescope was extremely difficult to keep focused. The image quality loss I incurred uploading this only adds to the ‘out-of-focus’ness
Also shout out to the Sea of Crises visible as the circular, dark-gray splotch on the right
omg okay so this is pretty interesting but I HAVE SO MANY QUESTIONS . . . I need to think more about this but I have my . . . doubts XD
@maevemauvaise I can’t vouch for the veracity but this is pretty damn cool.
-
 maevetheeuropan reblogged this · 8 years ago
maevetheeuropan reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 chocothunderac reblogged this · 8 years ago
chocothunderac reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 shutakadai0017 reblogged this · 8 years ago
shutakadai0017 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 shutakadai0017 liked this · 8 years ago
shutakadai0017 liked this · 8 years ago -
 naritaan liked this · 8 years ago
naritaan liked this · 8 years ago -
 robotichermitblog liked this · 9 years ago
robotichermitblog liked this · 9 years ago -
 solluxisms liked this · 9 years ago
solluxisms liked this · 9 years ago -
 shimadagans reblogged this · 9 years ago
shimadagans reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 shimadagans liked this · 9 years ago
shimadagans liked this · 9 years ago -
 grimreaperchibi reblogged this · 9 years ago
grimreaperchibi reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 idkmybffflamingo liked this · 9 years ago
idkmybffflamingo liked this · 9 years ago -
 kaitoleen reblogged this · 9 years ago
kaitoleen reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 buzzlette liked this · 9 years ago
buzzlette liked this · 9 years ago -
 graydama reblogged this · 9 years ago
graydama reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 greenriderglen liked this · 9 years ago
greenriderglen liked this · 9 years ago -
 ladyauroradewinter reblogged this · 9 years ago
ladyauroradewinter reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 bonrurgandy reblogged this · 9 years ago
bonrurgandy reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 bonrurgandy liked this · 9 years ago
bonrurgandy liked this · 9 years ago -
 sillura reblogged this · 9 years ago
sillura reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 craftssakura liked this · 9 years ago
craftssakura liked this · 9 years ago -
 amyole liked this · 9 years ago
amyole liked this · 9 years ago -
 kaitoleen liked this · 9 years ago
kaitoleen liked this · 9 years ago -
 lifeaftermeteor reblogged this · 9 years ago
lifeaftermeteor reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 takinchimera liked this · 9 years ago
takinchimera liked this · 9 years ago -
 maevemauvaise reblogged this · 9 years ago
maevemauvaise reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 cylinanightshade liked this · 9 years ago
cylinanightshade liked this · 9 years ago -
 outofworkshinigami reblogged this · 9 years ago
outofworkshinigami reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 maevemauvaise liked this · 9 years ago
maevemauvaise liked this · 9 years ago -
 shinigamistorm reblogged this · 9 years ago
shinigamistorm reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 gundamdaycare-blog liked this · 10 years ago
gundamdaycare-blog liked this · 10 years ago -
 agentchangwufei reblogged this · 10 years ago
agentchangwufei reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 comicalsenses liked this · 11 years ago
comicalsenses liked this · 11 years ago -
 canine-guts liked this · 11 years ago
canine-guts liked this · 11 years ago -
 claraxbarton liked this · 11 years ago
claraxbarton liked this · 11 years ago








