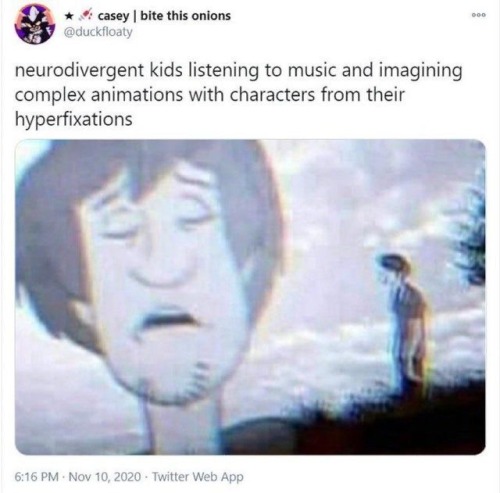
I Was About To Climb Into Bed But I Had To Turn My Computer Back On To Draw This Real Quick

I was about to climb into bed but I had to turn my computer back on to draw this real quick
More Posts from Gulliblenacho and Others
I guess why the ending of arcane still doesn’t feel real to me and why jayvik moves me so much is because it defies so much of what I was taught to expect by conventional male-dominated, heteronormative narratives. Because at the end of the story, Jayce had everything he should have wanted. Saved the world. Both Piltover and Zaun respected him. He had strength and charisma and the cool magic hammer he’d fantasized about wielding since he was a kid, and his battle scars only made him hotter somehow. And he had a goddess of a woman expressing trust and care for him, and who probably would’ve liked to get back together with him, at least in some capacity. Meanwhile, characters like Viktor are supposed to die at the end. No matter how sympathetic of a villain he is, the gay disabled guy who irreversibly gave up his humanity to be an evil robot is supposed to self-implode. That character archetype is supposed to redeem himself by taking himself out of the narrative so that the hero can get the happy ending. Someone made a great comparison to the Phantom of the Opera, but this pattern is true for pretty much every mainstream story I can think of. Hell, even Jinx sort of did that, literally ejecting herself from the narrative so that Vi can live in Piltover and get together with Cait. Viktor seemed self-aware of this trope at the end. He had closed his eyes, deciding to accept his own lonely demise if it meant Jayce would live.
But Jayce rejects all of that. The story rejects all of that. And it doesn’t even blink twice to do it. Jayce says all I want is my partner back, and he chooses to die holding hands with Viktor instead. And the story says of course Jayce will choose this, because he always loved Viktor and wanted to be with Viktor more than he wanted any of those other things men are supposed to want. More than power, or respect, or sex, or legacy. Just Viktor. Always Viktor. And in the end, Viktor finally embraces that love, accepts and reciprocates it, in allowing Jayce to be with him in his final moments.
It’s so beautiful and it’s so, so queer. Do not come at me with platonic/romantic discourse because I do not care, I genuinely do not care. The story practically sings with queer love. It’s undooming him from the ableist patriarchal narrative so you can exchange magic wedding rings and hold each others’ souls forever in the astral plane. It’s everything I was afraid to ask for from a story because I never thought I would get it. I still can’t quite believe it’s real, and canon, and carved into the very bones of the story. I love it so much.

Libraries have traditionally operated on a basic premise: Once they purchase a book, they can lend it out to patrons as much (or as little) as they like. Library copies often come from publishers, but they can also come from donations, used book sales, or other libraries. However the library obtains the book, once the library legally owns it, it is theirs to lend as they see fit. Not so for digital books. To make licensed e-books available to patrons, libraries have to pay publishers multiple times over. First, they must subscribe (for a fee) to aggregator platforms such as Overdrive. Aggregators, like streaming services such as HBO’s Max, have total control over adding or removing content from their catalogue. Content can be removed at any time, for any reason, without input from your local library. The decision happens not at the community level but at the corporate one, thousands of miles from the patrons affected. Then libraries must purchase each individual copy of each individual title that they want to offer as an e-book. These e-book copies are not only priced at a steep markup—up to 300% over consumer retail—but are also time- and loan-limited, meaning the files self-destruct after a certain number of loans. The library then needs to repurchase the same book, at a new price, in order to keep it in stock. This upending of the traditional order puts massive financial strain on libraries and the taxpayers that fund them. It also opens up a world of privacy concerns; while libraries are restricted in the reader data they can collect and share, private companies are under no such obligation. Some libraries have turned to another solution: controlled digital lending, or CDL, a process by which a library scans the physical books it already has in its collection, makes secure digital copies, and lends those out on a one-to-one “owned to loaned” ratio. The Internet Archive was an early pioneer of this technique. When the digital copy is loaned, the physical copy is sequestered from borrowing; when the physical copy is checked out, the digital copy becomes unavailable. The benefits to libraries are obvious; delicate books can be circulated without fear of damage, volumes can be moved off-site for facilities work without interrupting patron access, and older and endangered works become searchable and can get a second chance at life. Library patrons, who fund their local library’s purchases with their tax dollars, also benefit from the ability to freely access the books. Publishers are, unfortunately, not a fan of this model, and in 2020 four of them sued the Internet Archive over its CDL program. The suit ultimately focused on the Internet Archive’s lending of 127 books that were already commercially available through licensed aggregators. The publisher plaintiffs accused the Internet Archive of mass copyright infringement, while the Internet Archive argued that its digitization and lending program was a fair use. The trial court sided with the publishers, and on September 4, the Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit reaffirmed that decision with some alterations to the underlying reasoning. This decision harms libraries. It locks them into an e-book ecosystem designed to extract as much money as possible while harvesting (and reselling) reader data en masse. It leaves local communities’ reading habits at the mercy of curatorial decisions made by four dominant publishing companies thousands of miles away. It steers Americans away from one of the few remaining bastions of privacy protection and funnels them into a surveillance ecosystem that, like Big Tech, becomes more dangerous with each passing data breach. And by increasing the price for access to knowledge, it puts up even more barriers between underserved communities and the American dream.
11 September 2024

Silent Chill .2024
"In my restless dreams, I hear that sound...Silent Chill."
Instagram : Pixel Jeff





Art by Davood Moghaddami

i am so normal about her
the same 4 meals in rotation i love you. i love you the same 4 meals in rotation


-
 princess-bel liked this · 1 month ago
princess-bel liked this · 1 month ago -
 losyash reblogged this · 1 month ago
losyash reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 deeply-unserious-fellow liked this · 1 month ago
deeply-unserious-fellow liked this · 1 month ago -
 soarrenbluejay liked this · 1 month ago
soarrenbluejay liked this · 1 month ago -
 weary-liar liked this · 1 month ago
weary-liar liked this · 1 month ago -
 jayusghostyghoul liked this · 1 month ago
jayusghostyghoul liked this · 1 month ago -
 theresanaxolotlonthepinkstairs liked this · 1 month ago
theresanaxolotlonthepinkstairs liked this · 1 month ago -
 walnutbar liked this · 1 month ago
walnutbar liked this · 1 month ago -
 thenerdiestwormiest reblogged this · 1 month ago
thenerdiestwormiest reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 frillyheathen liked this · 1 month ago
frillyheathen liked this · 1 month ago -
 princes-tower liked this · 1 month ago
princes-tower liked this · 1 month ago -
 impresively-large-swan reblogged this · 1 month ago
impresively-large-swan reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 someoneverypotter liked this · 1 month ago
someoneverypotter liked this · 1 month ago -
 the-algid liked this · 1 month ago
the-algid liked this · 1 month ago -
 summercorpsebride liked this · 1 month ago
summercorpsebride liked this · 1 month ago -
 genarrogance liked this · 1 month ago
genarrogance liked this · 1 month ago -
 izzythedemigod reblogged this · 1 month ago
izzythedemigod reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 izzythedemigod liked this · 1 month ago
izzythedemigod liked this · 1 month ago -
 animalentity liked this · 1 month ago
animalentity liked this · 1 month ago -
 josharko300 liked this · 1 month ago
josharko300 liked this · 1 month ago -
 mariannehasneeds reblogged this · 1 month ago
mariannehasneeds reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 mariannehasneeds liked this · 1 month ago
mariannehasneeds liked this · 1 month ago -
 k1ju02 reblogged this · 1 month ago
k1ju02 reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 k1ju02 liked this · 1 month ago
k1ju02 liked this · 1 month ago -
 30coyotesstuckinhole liked this · 1 month ago
30coyotesstuckinhole liked this · 1 month ago -
 dragginage liked this · 1 month ago
dragginage liked this · 1 month ago -
 lumonyix liked this · 1 month ago
lumonyix liked this · 1 month ago -
 monchie11223 liked this · 1 month ago
monchie11223 liked this · 1 month ago -
 gakriele-lvs-blog liked this · 1 month ago
gakriele-lvs-blog liked this · 1 month ago -
 paintedpolarbear reblogged this · 1 month ago
paintedpolarbear reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 miggyposting reblogged this · 1 month ago
miggyposting reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 miggyposting liked this · 1 month ago
miggyposting liked this · 1 month ago -
 pecanbutterpie liked this · 1 month ago
pecanbutterpie liked this · 1 month ago -
 tessenda liked this · 1 month ago
tessenda liked this · 1 month ago -
 spade-deck reblogged this · 1 month ago
spade-deck reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 spade-deck liked this · 1 month ago
spade-deck liked this · 1 month ago -
 spaghettifromthevoid liked this · 1 month ago
spaghettifromthevoid liked this · 1 month ago -
 gay-charizard liked this · 1 month ago
gay-charizard liked this · 1 month ago -
 voidwithtoomanygooglyeyes liked this · 1 month ago
voidwithtoomanygooglyeyes liked this · 1 month ago -
 tangled-yarn-ummmm liked this · 1 month ago
tangled-yarn-ummmm liked this · 1 month ago -
 justalittleguest liked this · 1 month ago
justalittleguest liked this · 1 month ago -
 dualcock reblogged this · 1 month ago
dualcock reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 dualclock liked this · 1 month ago
dualclock liked this · 1 month ago -
 thelittlemissmisfit reblogged this · 1 month ago
thelittlemissmisfit reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 desolate-smog liked this · 1 month ago
desolate-smog liked this · 1 month ago -
 thedrunkenmanatee reblogged this · 1 month ago
thedrunkenmanatee reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 ontdekking liked this · 1 month ago
ontdekking liked this · 1 month ago -
 worm-in-a-book reblogged this · 1 month ago
worm-in-a-book reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 worm-in-a-book liked this · 1 month ago
worm-in-a-book liked this · 1 month ago