Over 800 Terrestrial Exoplanets Visualized And Arranged According To Their Equilibrium Temperature And

Over 800 terrestrial exoplanets visualized and arranged according to their equilibrium temperature and size.
chart by u/mVargic
More Posts from Bombil-fry and Others
" You look like melted cheese slice on a grilled burger-good." - Kashish
The Lives, Times, and Deaths of Stars
Who among us doesn’t covertly read tabloid headlines when we pass them by? But if you’re really looking for a dramatic story, you might want to redirect your attention from Hollywood’s stars to the real thing. From birth to death, these burning spheres of gas experience some of the most extreme conditions our cosmos has to offer.

All stars are born in clouds of dust and gas like the Pillars of Creation in the Eagle Nebula pictured below. In these stellar nurseries, clumps of gas form, pulling in more and more mass as time passes. As they grow, these clumps start to spin and heat up. Once they get heavy and hot enough (like, 27 million degrees Fahrenheit or 15 million degrees Celsius), nuclear fusion starts in their cores. This process occurs when protons, the nuclei of hydrogen atoms, squish together to form helium nuclei. This releases a lot of energy, which heats the star and pushes against the force of its gravity. A star is born.

Credit: NASA, ESA and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
From then on, stars’ life cycles depend on how much mass they have. Scientists typically divide them into two broad categories: low-mass and high-mass stars. (Technically, there’s an intermediate-mass category, but we’ll stick with these two to keep it straightforward!)
Low-mass stars

A low-mass star has a mass eight times the Sun’s or less and can burn steadily for billions of years. As it reaches the end of its life, its core runs out of hydrogen to convert into helium. Because the energy produced by fusion is the only force fighting gravity’s tendency to pull matter together, the core starts to collapse. But squeezing the core also increases its temperature and pressure, so much so that its helium starts to fuse into carbon, which also releases energy. The core rebounds a little, but the star’s atmosphere expands a lot, eventually turning into a red giant star and destroying any nearby planets. (Don’t worry, though, this is several billion years away for our Sun!)

Red giants become unstable and begin pulsating, periodically inflating and ejecting some of their atmospheres. Eventually, all of the star’s outer layers blow away, creating an expanding cloud of dust and gas misleadingly called a planetary nebula. (There are no planets involved.)

Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
All that’s left of the star is its core, now called a white dwarf, a roughly Earth-sized stellar cinder that gradually cools over billions of years. If you could scoop up a teaspoon of its material, it would weigh more than a pickup truck. (Scientists recently found a potential planet closely orbiting a white dwarf. It somehow managed to survive the star’s chaotic, destructive history!)

High-mass stars
A high-mass star has a mass eight times the Sun’s or more and may only live for millions of years. (Rigel, a blue supergiant in the constellation Orion, pictured below, is 18 times the Sun’s mass.)

Credit: Rogelio Bernal Andreo
A high-mass star starts out doing the same things as a low-mass star, but it doesn’t stop at fusing helium into carbon. When the core runs out of helium, it shrinks, heats up, and starts converting its carbon into neon, which releases energy. Later, the core fuses the neon it produced into oxygen. Then, as the neon runs out, the core converts oxygen into silicon. Finally, this silicon fuses into iron. These processes produce energy that keeps the core from collapsing, but each new fuel buys it less and less time. By the point silicon fuses into iron, the star runs out of fuel in a matter of days. The next step would be fusing iron into some heavier element, but doing requires energy instead of releasing it.
The star’s iron core collapses until forces between the nuclei push the brakes, and then it rebounds back to its original size. This change creates a shock wave that travels through the star’s outer layers. The result is a huge explosion called a supernova.

What’s left behind depends on the star’s initial mass. Remember, a high-mass star is anything with a mass more than eight times the Sun’s — which is a huge range! A star on the lower end of this spectrum leaves behind a city-size, superdense neutron star. (Some of these weird objects can spin faster than blender blades and have powerful magnetic fields. A teaspoon of their material would weigh as much as a mountain.)

At even higher masses, the star’s core turns into a black hole, one of the most bizarre cosmic objects out there. Black holes have such strong gravity that light can’t escape them. If you tried to get a teaspoon of material to weigh, you wouldn’t get it back once it crossed the event horizon — unless it could travel faster than the speed of light, and we don’t know of anything that can! (We’re a long way from visiting a black hole, but if you ever find yourself near one, there are some important safety considerations you should keep in mind.)

The explosion also leaves behind a cloud of debris called a supernova remnant. These and planetary nebulae from low-mass stars are the sources of many of the elements we find on Earth. Their dust and gas will one day become a part of other stars, starting the whole process over again.
That’s a very brief summary of the lives, times, and deaths of stars. (Remember, there’s that whole intermediate-mass category we glossed over!) To keep up with the most recent stellar news, follow NASA Universe on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
I feel like community is objectively the best show to ever exist
Like even if it wasn’t my favourite I still think it should be considered the best show out there like they just went the extra mile in so many things
First of all humour wise it’s a kind of funny that will always be funny like it’s not reliant on reference humour in the way so many shows nowadays are, and also it’s the little things they do that make it an overall more entertaining experience like its just laced in so effortlessly while still moving the story along because they aren’t trying to hard
Second of cinematically like directing styles and that it’s amazing I don’t know much about filming and that but I feel it’s aesthetically shot and also so clever with the high concept episodes and how they do all of that like I feel the boat scene in beginners pottery is really brilliant and often overlooked like they fitted this really cool shot into what was really an unassuming episode
Thirdly the soundtrack is unparalleled they used music in such a good and clever way like in epidemiology for comedy purposes or to explore characters like Jeff being a hardcore Dave Matthews fan and also Ludwig Göransson composed so many Greta peices that really fitted with the vibe of the show but even individually were amazing
They also had such nuanced and developed relationships that all worked and were realistic and showed the dynamics so well in such a way you understood why they were all friends in such a way that even most other character driven shows don’t do like it showed such a range of different types of relationships and you saw how they all affected each other
Fifth the actual characters were so unique like you know how people say there are like 8 types of sitcom characters well none of the community characters fit into that like really they are so original in a way that hadn’t been done and hasn’t been replicated all of them are separately funny even the background characters like Leonard and Garrett are entertaining and you somehow feel as if you know them even if they haven’t had like loads of screen time and development
The characters all have good arcs it’s unrealistic for all of the characters to not grow at all during a show and yet many tv shows don’t give their characters growth and development in the way community does the ones that most standout to me are Jeff and Troy
It done all of this amazing work on such a small budget like I watched the dvd commentary and they had basically nothing compared to most shows but they did so much with what they did it’s astounding how they managed that
Anyway this was basically just a really long rant about how much I love community but I truly do believe they are unparalleled in what they did like I don’t think it can ever be replicated because overall it is just such an astounding piece of television and I think it should be appreciated more
Love it here, I'm gonna bring my friends next time I visit :)
“But [Tumblr’s] value, of course, is more than just what it isn’t, and what it points away from. Despite all the drama and discourse lurking in its corners, it’s easy to make your own Tumblr life as simple and as happy as you want it to be. There are no algorithmic threats lurking around every corner, no onslaught of promoted posts from politicians or influencers. More than anything else, Tumblr in 2020 is a self-sustaining ecosystem. It’s a semi-sealed and increasingly fertile terrarium, a nigh-impossible perpetual-motion machine of a platform going productively psychotic in its isolation.”
— @areyougonnabe, “The Ever-Mutating Life of Tumblr Dot Com”

Amy Lowell, from lilacs in “the complete poetical works of Amy Lowell”



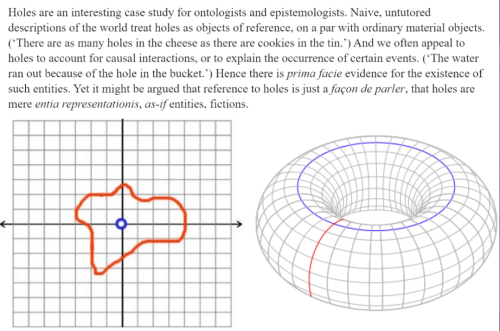








































define hole / is a hole a real thing? / Marco Poloni, Black Hole, from The Majorana Experiment, 2010 / Flatfields Fotografien / What We Talk About When We Talk About Holes / Dark (2017-2020) / post / Disco Elysium / Twin Peaks: The Return (2017) / Donnie Darko (2001) / Outer Range (2022) / Kaveh Akbar, from “The Miracle,” Pilgrim Bell / post / Weizmann Institute of Science / Mathworld / post / post / post / post / Anne Boyer, from “Woman Sitting at the Machine,” in A Handbook of Disappointed Fate / Dennis Patrick Slattery, The Wounded Body: Remembering the Markings of Flesh / The Incredulity of Saint Thomas, Caravaggio, 1601–1602 (detail) / The Incredulity of St. Thomas, Bernardo Strozzi, 1582-1644 (detail) / Don McKay, from “Twinflower,” Field Marks: The Poetry of Don McKay, intro. Méira Cook (Wilfrid Laurier University Press, 2006) / thierryetherve / Pathologic / post / Gregory Orr, from How Beautiful the Beloved / Tomas Tranströmer, tr. by Robert Bly, from a poem titled “Track” / Disco Elysium / Anne Carson, Economy of the Unlost / Pathologic 2 / Jonas Burgert, Sand brennt Blatt (2010) / Disco Elysium / Carl Phillips, from “Givingly”, Wild is the Wind / post / Pathologic / The Juniper Tree (Nietzchka Keene | 1990) / John Banville, Eclipse / Twin Peaks / Disco Elysium / VectorStock / True Detective / Night in the Woods
I also want to give credit to @arairah for being the lead holologist on this site and the intermediate source for a lot of this, thank you!
“I had learned one thing from Kizuki’s death, and I believed that I had made it a part of myself in the form of a philosophy: “Death exists, not as the opposite but as a part of life”. By living our lives, we nurture death. True as this might be, it was only one of the truths we had to learn. What I learned from Naoko’s death was this: no truth can cure the sadness we feel from losing a loved one. No truth, no sincerity, no strength, no kindness, can cure that sorrow. All we can do is see that sadness through to the end and learn something from it, but what we learn will be no help in facing the next sadness that comes to us without warning.”
— Norwegian Woods, Haruki Murakami
Muted tones

-
 cloudgathererhera liked this · 2 months ago
cloudgathererhera liked this · 2 months ago -
 sweetweetyss liked this · 2 months ago
sweetweetyss liked this · 2 months ago -
 nullsk reblogged this · 2 months ago
nullsk reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 voidgivnfocus liked this · 2 months ago
voidgivnfocus liked this · 2 months ago -
 4gottenname reblogged this · 2 months ago
4gottenname reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 4gottenname liked this · 2 months ago
4gottenname liked this · 2 months ago -
 jimbob505 reblogged this · 2 months ago
jimbob505 reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 jerek liked this · 2 months ago
jerek liked this · 2 months ago -
 simptasia reblogged this · 2 months ago
simptasia reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 pennypyro reblogged this · 2 months ago
pennypyro reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 kagedtiger liked this · 2 months ago
kagedtiger liked this · 2 months ago -
 feel-alright-for-ten-minutes liked this · 2 months ago
feel-alright-for-ten-minutes liked this · 2 months ago -
 protectorofthesmoll reblogged this · 2 months ago
protectorofthesmoll reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 protectorofthesmoll liked this · 2 months ago
protectorofthesmoll liked this · 2 months ago -
 niknakss liked this · 2 months ago
niknakss liked this · 2 months ago -
 maikelfist reblogged this · 2 months ago
maikelfist reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 chambergambit reblogged this · 2 months ago
chambergambit reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 brain-of-soup reblogged this · 2 months ago
brain-of-soup reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 hraeiou liked this · 2 months ago
hraeiou liked this · 2 months ago -
 vnsnctz reblogged this · 3 months ago
vnsnctz reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 tempestinateacup4 liked this · 3 months ago
tempestinateacup4 liked this · 3 months ago -
 somadyoucouldbite reblogged this · 3 months ago
somadyoucouldbite reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 dancingzoe liked this · 3 months ago
dancingzoe liked this · 3 months ago -
 sqydliminal liked this · 3 months ago
sqydliminal liked this · 3 months ago -
 4eversweetdreams reblogged this · 3 months ago
4eversweetdreams reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 loveisloveisfandom reblogged this · 3 months ago
loveisloveisfandom reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 insane-typewriter liked this · 4 months ago
insane-typewriter liked this · 4 months ago -
 mai-tmblracc liked this · 4 months ago
mai-tmblracc liked this · 4 months ago -
 dutchdelicacyy reblogged this · 4 months ago
dutchdelicacyy reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 survivalmotif reblogged this · 4 months ago
survivalmotif reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 wandering-cynic reblogged this · 4 months ago
wandering-cynic reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 chroniclesofreven reblogged this · 4 months ago
chroniclesofreven reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 john-erby liked this · 4 months ago
john-erby liked this · 4 months ago -
 9teen7tsix liked this · 5 months ago
9teen7tsix liked this · 5 months ago -
 moriartyeva reblogged this · 5 months ago
moriartyeva reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 lilacssmelllikeroses reblogged this · 5 months ago
lilacssmelllikeroses reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 aearon reblogged this · 5 months ago
aearon reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 possiblefish reblogged this · 5 months ago
possiblefish reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 possiblefish liked this · 5 months ago
possiblefish liked this · 5 months ago -
 aezuliamah reblogged this · 5 months ago
aezuliamah reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 cacy11 liked this · 5 months ago
cacy11 liked this · 5 months ago -
 firebirdmaximus reblogged this · 5 months ago
firebirdmaximus reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 young-elderfolk reblogged this · 5 months ago
young-elderfolk reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 calcitecrime liked this · 5 months ago
calcitecrime liked this · 5 months ago -
 penguinabluebox reblogged this · 5 months ago
penguinabluebox reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 towersofviolet reblogged this · 5 months ago
towersofviolet reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 corporateclone liked this · 5 months ago
corporateclone liked this · 5 months ago -
 typewritersnail reblogged this · 5 months ago
typewritersnail reblogged this · 5 months ago

