Astrotidbits-blog - Astrotidbits.info

More Posts from Astrotidbits-blog and Others
The Pillars of Creation and Spotting Comet Lovejoy
This week in space news, a new makeover for one of the Hubble Telescope’s most famous images, and tips on spotting Comet Lovejoy in the night sky.
Titan Touchdown
On Jan. 14, 2005, ESA’s Huygens probe made its descent to the surface of Saturn’s hazy moon, Titan. Carried to Saturn by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, Huygens made the most distant landing ever on another world, and the only landing on a body in the outer solar system. This video uses actual images taken by the probe during its two-and-a-half hour fall under its parachutes.

Our planet seen from Saturn, captured by the Cassini spacecraft
Image credit: NASA / Cassini
Getting ready for 8/21/17
I am making a journal as I get ready for the total eclipse of the sun on 8/21/17 and you can find it on http://www.astrotidbits.com. Irregular posts as I do something new or learn new ways of doing things.

Aerospace Engineering Magazine April 1962




Maria Mitchell - Scientist of the Day
Maria Mitchell, an American astronomer, was born Aug. 1, 1818, in Nantucket. Mitchell was the first professional woman astronomer in the United States and a role model for generations of aspiring women scientists. She was trained by her father, a school-teacher, and had the extreme good fortune to discover a comet in 1847. Not only was she the first to see the comet, she also had the mathematical skill to calculate its orbit. Her feat won her an international gold medal from the Danish government, the first such recognition for any American woman, and eventually, the professorship of astronomy at Vassar College, also the first such position for any woman. (It is probably of interest to some of this reading audience that, before she became famous, Mitchell spent 17 years as a librarian on Nantucket.) Mitchell was admitted to various male bastions, such as the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in Boston (the only woman so honored until the 20th century), but she decided early on that, instead of trying to show men that women could be good scientists, she would spend her life showing young women that they could be good scientists. She seems to have done a superb job at this task, becoming a legendary teacher at Vassar. Antonia Maury, a noted astronomer at Harvard, was one of her pupils. The lovely albumen print portrait of Maria above is at Harvard.
In 1863, Matthew Vassar, the founder of Vassar College, personally commissioned a telescope for Mitchell from Henry Fitz, a well-known New York telescope builder. With a lense 12 inches in diameter, it was second among American telescopes only to the great refractor at Harvard (see second image above). The telescope is now in the National Museum of American History in Washington. Vassar also built an observatory for Maria; a period photo can be seen above, just below the Fitz refractor.
The small telescope that Mitchell used to discover the Nantucket comet is now mounted in her childhood home on Vestal Street (see last photo above), across from the headquarters of the Maria Mitchell Association, the group her descendants founded in 1908 to continue Mitchell’s lifelong passion for the natural sciences and science education.
Dr. William B. Ashworth, Jr., Consultant for the History of Science, Linda Hall Library and Associate Professor, Department of History, University of Missouri-Kansas City

A once in a lifetime event visible every 75-76 years, Halleys comet returned in 1986. Halley is the only short-period comet that is clearly visible to the naked eye from Earth. It has been documented since 240 BC.

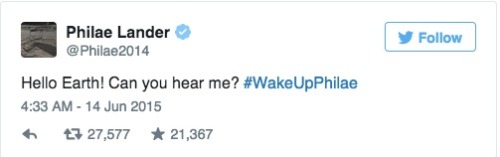
Comet lander Philae wakes up: How it happened and what’s next
By Lauren Raab
Philae, the first spacecraft to land on a comet, surprised and delighted scientists this weekend by waking up and reestablishing contact with Earth, seven months after running out of power. It “spoke” for more than a minute, according to the European Space Agency, and it’s expected to be able to continue gathering information and sending it home.
Here’s a look at what the lander has done so far and what will happen next.
Continue Reading.
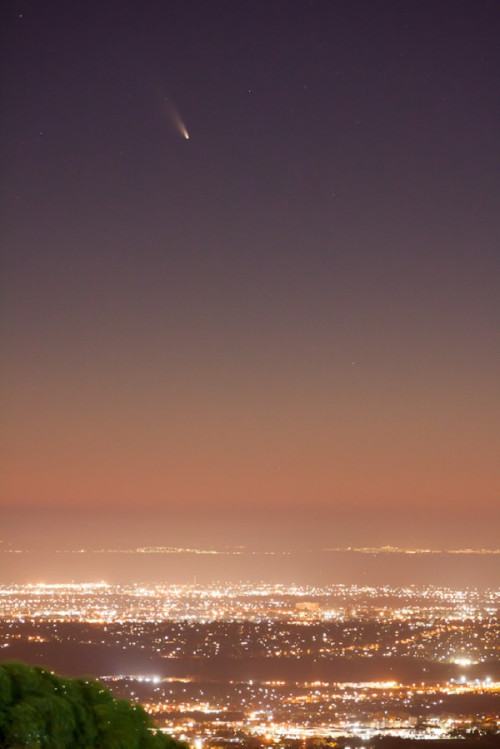

Comet PanSTARRS
Gorgeous picture of Comet PanSTARRS taken by Carl Gruber on March 2, 2013 at a mountain lookout in Melbourne.

Light at the End of the Road : The bright light at the end of this country road is actually a remarkably close conjunction of two planets. After sunset on August 27 brilliant Venus and Jupiter almost appear as a single celestial beacon in the night skyscape taken near Lake Wivenhoe, Queensland, Australia. A spectacular vertical panorama from the southern hemisphere, it shows the central Milky Way near zenith, posed on top of a pillar of Zodiacal light along the ecliptic plane. Of course Mars and Saturn are near the ecliptic too, just below the galaxy’s central bulge. Above and left of a tree on the horizon, fleeting planet Mercury also adds to the light at the end of the road. via NASA
js
-
 py2kc liked this · 6 years ago
py2kc liked this · 6 years ago -
 w4cpnhamradio reblogged this · 7 years ago
w4cpnhamradio reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 wyoty liked this · 7 years ago
wyoty liked this · 7 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog liked this · 7 years ago
astrotidbits-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 duanesouthworth liked this · 10 years ago
duanesouthworth liked this · 10 years ago -
 tacticaltom liked this · 11 years ago
tacticaltom liked this · 11 years ago -
 audiedahling liked this · 11 years ago
audiedahling liked this · 11 years ago -
 princedelesprit reblogged this · 13 years ago
princedelesprit reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 trulybadtiming liked this · 13 years ago
trulybadtiming liked this · 13 years ago -
 paranoidgemsbok liked this · 13 years ago
paranoidgemsbok liked this · 13 years ago -
 aniki-kamina reblogged this · 13 years ago
aniki-kamina reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 ignorant-to-all-the-symbols reblogged this · 13 years ago
ignorant-to-all-the-symbols reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 mojavemoproblems reblogged this · 13 years ago
mojavemoproblems reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 beautifulepoch-blog liked this · 13 years ago
beautifulepoch-blog liked this · 13 years ago -
 insanitypie reblogged this · 13 years ago
insanitypie reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 slightlyaskew-blog reblogged this · 13 years ago
slightlyaskew-blog reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 slightlyaskew-blog liked this · 13 years ago
slightlyaskew-blog liked this · 13 years ago -
 donutbutton liked this · 13 years ago
donutbutton liked this · 13 years ago -
 gabatronic0 liked this · 13 years ago
gabatronic0 liked this · 13 years ago -
 bigboss0715 reblogged this · 13 years ago
bigboss0715 reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 ignorant-to-all-the-symbols liked this · 13 years ago
ignorant-to-all-the-symbols liked this · 13 years ago -
 desuchine reblogged this · 13 years ago
desuchine reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 dear-massacre liked this · 13 years ago
dear-massacre liked this · 13 years ago -
 dijonayjones- reblogged this · 13 years ago
dijonayjones- reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 comics-and-hematolagnia liked this · 13 years ago
comics-and-hematolagnia liked this · 13 years ago -
 papillonwings reblogged this · 13 years ago
papillonwings reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 vault106acidtrip-blog reblogged this · 13 years ago
vault106acidtrip-blog reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 vault106acidtrip-blog liked this · 13 years ago
vault106acidtrip-blog liked this · 13 years ago -
 erickisacannibal reblogged this · 13 years ago
erickisacannibal reblogged this · 13 years ago -
 snnigcircles reblogged this · 13 years ago
snnigcircles reblogged this · 13 years ago