Never Thought About This, Arcane Suddenly Becomes Scarily Relatable Oh No
never thought about this, arcane suddenly becomes scarily relatable oh no

saw that post n thought of em
More Posts from Asathorin and Others
I don’t know who needs to hear this but YOUR CHARACTERS DONT NEED TO FALL IN LOVE. PLATONIC RELATIONSHIPS ARE JUST AS FULFILLING AND AMAZING AS ROMANTIC ONES. NOT EVERY STORY NEEDS A ROMANTIC SUBPLOT STOP IT
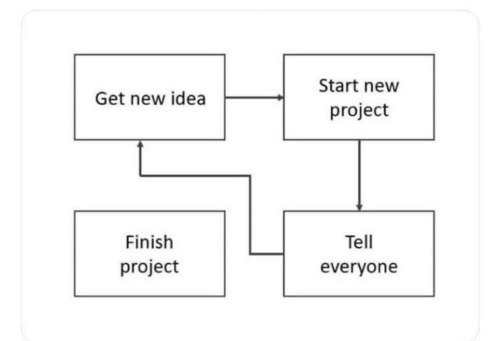
btw if you find yourself dehumanizing any person or group for any reason you've already lost
Nirvana in Fire through the socioeconomic lens

How do you depict social class disparities on a personal level, rather than masses of people with very different means and lives and the unwritten rules that divide them? How do you tell a meaningful story staked on these differences?
There are a lot of reasons why Nirvana in Fire is compelling, one of which is the assured way the narrative knows when to be subtle and when to bring the angst and drama, and its exploration of how identity is deeply entwined with social class is a great example of this.
Historical background
Though NiF is a story with a fictional historical setting/架空, it is still grounded in real history, and the choice of the Northern and Southern Dynasties as a very loose background period is no accident. During this time, the ruling class’s stranglehold on society was especially strong. In canon, you see nobles such as Xie Yu/Marquis Ning and Marquis Huaiyi own large estates and their own private militia, which was very much the situation back then. There were a large number of rebellions and unrests led by these aristocrats during this time, and being Emperor was a delicate balancing act to keep them happy but not let them gain too much power.
This kind of background is what a work of fiction generally wants to avoid directly dumping on the audience as exposition; a good period-setting story should stake its narrative conflicts on its historical basis in a logical manner and make the audience feel the conflict. As an example, the nine-rank selection system/九品中正制, the official selection process in use during the Northern and Southern Dynasties, is exactly what’s being discussed in the scene where Xiao Jingyan brings Shen Zhui and Cai Quan over to Su Manor (and in my opinion a good change from book to screen).

In particular, they’re talking about how to choose the selection officials/中正官 who grade candidates to be selected and ranked into positions of the imperial bureaucracy. Instead of the imperial examinations/科举 that many later dynasties use, this system has these selection officials recommend people to become officials and was instituted to replace the previous system (察举制) which had been fully taken over by the aristocracy. At first, the selection criteria of the nine-rank system were the candidate’s family background, virtue, and talent, but this again became corrupted over time by the ruling class to essentially only depend on background and connections with the selection officials. There was a well-known saying back then: 上品无寒门,下品无士族, which means no commoners in the top ranks, no upper class in the lower ranks.
In canon, corruption of this process is specifically linked to the ex-Crown Prince and Prince Yu’s power struggle, each packing the government full of well-to-do officials sympathetic to their own factions. Shen Zhui lists the factors in the process of choosing selection officials, from family background to houses of marriage and mentors, from which it’s clear that ruling class influence is inextricably tied to this process. They discuss whether to go for bold reforms and possible conflict and bloodshed, or something more incremental, and decide on choosing the least corrupt candidate within the pool of eligibility that would not ruffle feathers, essentially trying their best while staying within the bounds of the system.
This scene is also narratively important as the first Jingsu reunion after Mei Changsu was imprisoned in the Xuanjing Bureau and Jingyan discovered painfully that he had accused him of things he didn’t do. Through the class angle, I think Jingyan interprets Su Manor turning him away when he tried to visit earlier as the way a subject would implicitly slap the hand of their lord by reminding them of their place. If Jingyan has no official business to be at Su Manor, if he is only there to make a personal visit and apologize, then he is not there as Mei Changsu’s lord, but as his friend, which Jingyan has no right to be, any longer. Of course, that’s not the real reason (at least, not the only one), but Jingyan doesn’t know that. With these boundary-enforcing interactions, Jingyan believes Mei Changsu wants to remind him that he had erred precisely because he was too emotionally invested in his relationship with Sir Su instead of thinking logically, that the boundaries are there for a reason and he should maintain them.
So what does he do instead of trying to make more personal visits? He brings Shen Zhui and Cai Quan with him on an official visit from lord to subject, one specifically designed to pave a path forward for Su Zhe’s advancement in government, showing that he knows he was wrong and wants to make amends in a useful way without making an explicit apology, which Mei Changsu neither wants nor needs. Mei Changsu receives them warmly yet professionally in return, showing in turn that he has no qualms about continuing to serve his lord and that the past is past.
All in all, I find this scene a good example of subtle layered storytelling that occurs a lot in NiF: this conversation that is about social class on the surface has its underlying structure and place in the narrative also reflecting class differences. It shows how the feudal hierarchy leads to rampant misconduct in government while also warns of the dangers of venturing too far from the rules that are in place.
Keep reading
Me: I’m asexual
Person: But you don’t look asexual
Me: Sorry let me just-


Sketch
I just read an interpretation for “the moon that year was not as bright as tonight” / “the moon that year is just like tonight” on bilibili that blew my mind:
When Di Feisheng says “the moon that year was not as bright as tonight”, he means that he did not appreciate their relationship ten years ago like he does now. And since saying “the moon is bright” is basically a love confession according to Chinese romance novel / drama conventions, Ah Fei is saying that he wasn’t in love (or didn’t realize he was in love) with Lianhua ten years ago, but realizes he loves with him now. (This is very plausible, imo, because ten years ago, he was single-mindedly focused on Lianhua’s power and channeled his obsession with Lianhua into their rivalry)
But when Li Lianhua tells him that “the moon that year is just like tonight”, he is confessing that his love for Ah Fei had never changed: he loved Ah Fei ten years ago and loves him still to this day 🥹
I really like this headcanon / implication that Lianhua was the first to fall in love with Ah Fei ten years ago (and not the other way around). Because imagine Li Xiangyi / Lianhua at the height of his power ten years ago, realizing that he has a crush on his arch-rival who only sees him as a challenge to overcome. Nevertheless, he manages to win Ah Fei’s trust and they sign a truce, only to learn shortly after that Ah Fei “betrayed” him and killed his older brother / shixiong! Imagine his despair and heartbreak as he storms into Ah Fei’s yacht / ship to fight him!
And then, ten years later, after he lost all is power and resigned himself to waste away as a dying man, Ah Fei shows up, tells him he didn’t order his shixiong’s murder, vows he will cure him, and refuses to leave his side. They settle into their old banter. They instinctively rely on each other but cannot fully trust each other.
And this is when Ah Fei, who has only known a life of violence and has never found a moment of peace until now, begins to realize that he can love! He doesn’t have to relive his childhood over and over, killing everyone better than him until he is the last man standing! For the first time in his life, Di Feisheng feels safe with someone, he wants to protect rather than destroy. With Li Lianhua, he can finally enjoy the mundane and simple pleasures of life. Of course the moon looks brighter tonight.
Honestly, the cringe is worth it. The cringe is necessary. The UK is such a cesspit of growing transphobia and has been getting worse and worse and the biggest family show on air coming out as loud and proud and supportive of trans kids is EVERYTHING.
Just watched Mean Girls!
I wish I were both more like and less Cady. I will not elaborate.
How To Name Your Chinese Characters:
1) LAST NAMES:
I’ve pasted the Top 100 common last names in alphabetical order, and bolded the ones that appear in CQL:
B: 白 Bai C: 蔡 Cai ; 曹 Cao ; 常 Chang ; 曾 Ceng ; 陈 Chen ; 程 Cheng ; 崔 Cui ; D: 戴 Dai ; 邓 Deng ; 丁 Ding ; 董 Dong ; 杜 Du ; F: 范 Fan ; 方 Fang ; 冯 Feng ; 付 Fu ; G: 高 Gao ; 葛 Ge ; 龚 Gong ; 顾 Gu ; 郭 Guo ; H: 韩 Han ; 何 He ; 贺 He 洪 Hong ; 侯 Hou ; 黄 Hua ; 胡 Hu ; J: 贾 Jia ; 蒋 Jiang ; 姜 Jiang ; 江 Jiang ; 金 Jin ; K: 康 Kang ; L: 赖 Lai ; 李 Li ; 黎 Li ; 廖 Liao ; 梁 Liang ; 林 Lin ; 刘 Liu ; 陆 Lu ; 卢 Lu ; 路 Lu ; 吕 Lü ; 罗 Luo ; M: 马 Ma ; 麦 Mai ; 毛 Mao ; 孟 Meng ; N: 倪 Ni ; 牛 Niu ; P: 潘 Pan ; 彭 Peng ; Q: 钱 Qian ; 秦 Qin ; 邱 Qiu ; R:任 Ren ; S: 邵 Shao ; 沈 Sheng ; 史 Shi ; 石 Shi ; 施 Shi ; 宋 Song ; 苏 Su ; 孙 Sun ; T: 陶 Tao ; 谭 Tan ; 唐 Tang ; 田 Tian ; W: 万 Wan ; 王 Wang ; 汪 Wang ; 魏 Wei ; 吴 Wu ; X: 邢 Xing ; 夏 Xia ; 蕭 Xiao ; 谢 Xie ; 徐 Xu ; 许 Xu ; 薛 Xue ; Y: 阎 Yan ; 严 Yan ; 杨 Yang ; 姚 Yao ; 叶 Ye ; 余 Yu ; 于 Yu ; 袁 Yuan ; Z: 张 Zhang ; 赵 Zhao ; 郑 Zheng ; 钟 Zhong ; 周 Zhou ; 朱 Zhu ; 庄 Zhuang ; 邹 Zou ;
Above are all single character last names, but there are some double character Chinese last names, seen below (list not exhaustive):
独孤 Du’Gu ; 公孙 Gong’Sun ; 南宫 Nan’Gong 欧阳 Ou’Yang ; 司马 Si’Ma ; 上官 Shang’Guan ; 宇文 Yu’Wen ; 长孙 Zhang’Sun ; 诸葛 Zhu’GE ;
2) GIVEN NAMES/COURTESY NAMES
《Elements》:
Light*: 光 (guāng) - light, 亮 liàng - bright / shine, 明 (míng) - bright, 曦 (xī) - early dawn, 昀 (yún) - daylight, 昭 (zhāo) - light, clear,照 (zhào) - to shine upon,
Fire: 焰 (yàn) - flames, 烟 (yān) - smoke,炎 (yán) - heat/burn, 烨 (yè) - dazzling light,
Water: also see “weather” OR “bodies of water” under nature; note the words below while are related to water have meanings that mean some kind of virtue: 清 (qīng) - clarity / purity, 澄 (chéng) - clarity/quiet, 澈 (chè) - clear/penetrating, 涟 (lián) - ripple, 漪 (yī) - ripple, 泓 (hóng) - vast water, 湛 (zhàn) - clear/crystal, 露 (lù) - dew, 泠 (líng) - cool, cold, 涛 (tāo) - big wave,泽 (zé),浩 hào - grand/vast (water),涵 (han) - deep submergence / tolerance / educated
Weather: 雨 (yǔ) - rain, 霖 (lín) - downpouring rain, 冰 (bīng) - ice, 雪 (xuě) - snow, 霜 (shuāng) - frost
Wind: 风 (fēng) - wind
* some “Light” words overlap in meaning with words that mean “sun/day”
《Nature》:
Season: 春 (chūn) - spring, 夏 (xià) - summer, 秋 (qíu) - aumtum, 冬 (dōng) - winter
Time of Day: 朝 (zhāo) - early morning / toward, 晨 (chén) - morning / dawn, 晓 (xiǎo) - morning, 旭 (xù) - dawn/rising sun,昼 (zhòu) - day,皖 (wǎn) - late evening,夜 (yè) - night
Star/Sky/Space: 云 (yún) - cloud,天 (tiān) - sky/ heaven,霞 (xiá) - afterglow of a rising or setting sun,月 (yuè) - moon,日 (ri) - day / sun,阳 (yáng) - sun,宇 (yǔ) - space,星 (xīng) - star
Birds: 燕 (yàn) - sparrow, 雁 (yàn) - loon, 莺 (yīng) - oriole, 鸢 (yuān) - kite bird (family Accipitridae),羽 (yǔ) - feather
Creatures: 龙 (lóng) - dragon/imperial
Plants/Flowers:* 兰 (lán) - orchids, 竹 (zhú) - bamboo, 筠 (yún) - tough exterior of bamboos, 萱 (xuān) - day-lily, 松 (sōng) - pine, 叶 (yè) - leaf, 枫 (fēng) - maple, 柏 bó/bǎi - cedar/cypress, 梅 (méi) - plum, 丹 (dān) - peony
Mountains: 山 (shān), 峰 (fēng) - summit, 峥 (zhēng),
Bodies of water: 江 (jiāng) - large river/straits, 河 (hé) - river, 湖 (hú) - lake, 海 (hǎi) - sea, 溪 (xī) - stream, 池 (chí) - pond, 潭 (tán) - larger pond, 洋 (yáng) - ocean
* I didn’t include a lot of flower names because it’s very easy to name a character with flowers that heavily implies she’s a prostitute.
《Virtues》:
Astuteness: 睿 ruì - astute / foresight, 智 (zhi), 慧 (hui), 哲 (zhé) - wise/philosophy,
Educated: 博 (bó) - extensively educated, 墨 (mo) - ink, 诗 (shi) - poetry / literature, 文 (wén) - language / gentle / literary, 学 (xue) - study, 彦 (yàn) - accomplished / knowledgeable, 知 (zhi) - to know, 斌 (bīn) - refined, 赋 (fù) - to be endowed with knowledge
Loyalty: 忠 (zhōng) - loyal, 真 (zhēn) - true
Bravery: 勇 (yǒng) - brave, 杰 (jié) - outstanding, hero
Determination/Perseverance: 毅 (yì) - resolute / brave, 恒 (héng) - everlasting, 衡 (héng) - across, to judge/evaluate,成 (chéng) - to succeed, 志 (zhì) - aspiration / the will
Goodness/Kindness: 嘉 (jiā) - excellent / auspicious,磊 (lěi) - rock / open & honest, 正 (zhèng) - straight / upright / principle,
Elegance: 雅 (yǎ) - elegant, 庄 (zhuāng) - respectful/formal/solemn, 彬 (bīn) - refined / polite,
Handsome: 俊 jùn - handsome/talented
Peace: 宁 (níng) - quietness/to pacify, 安 (ān) - peace, safety
Grandness/Excellence:宏 (hóng) - grand,豪 (háo) - grand, heroic,昊 (hào) - limitless / the vast sky,华 (huá) - magnificent, 赫 (hè) - red/famous/great, 隆 (lóng) - magnificent, 伟 (wěi) - greatness / large,轩 (xuān) - pavilion with a view/high,卓 (zhuó) - outstanding
Female Descriptor/Virtues/Beauty: 婉 (wǎn),惠 (huì), 妮 (nī), 娇 (jiāo), 娥 (é), 婵 (chán) (I didn’t include specific translations for these because they’re all adjectives for women meaning beauty or virtue)
《Descriptors》:
Adverbs: 如 (rú) - as,若 (ruò) - as, alike,宛 (wǎn) - like / as though,
Verbs: 飞 (fēi) - to fly, 顾 (gù) - to think/consider, 怀 (huái) - to miss, to possess, 落(luò) - to fall, to leave behind,梦 (mèng) - to dream, 思 (sī) - to consider / to miss (someone),忆 (yì) - memory, 希 (xī) - yearn / admire
Colours: 红 (hóng) - red, 赤 (chì) - crimson, 黄 (huàng) - yellow, 碧 (bì) - green,青(qīng) - azure,蓝 (lán) - blue, 紫 (zǐ) - violet ,玄 (xuán) - black, 白 (baí) - white
Number:一 (yī), 二 (er) - two, 三 (san) - three, 四 (si) - four, 五 (wu) - five, 六 (liu) - six, 七(qi) - seven, 八 (ba) - eight, 九 (jiu) - nine, 十 (shi) - ten
Direction: 东 (dōng) - east, 西 (xi) - west, 南 (nan) - south, 北 (bei) - north,
Other: 子 (zǐ) - child, 然 (rán) - correct / thusly
《Jade》: *there are SO MANY words that generally mean some kind of jade, bc when ppl put jade in their children’s name they don’t literally mean the rock, it’s used to symbolize purity, goodness, kindness, beauty, virtue etc* 琛 (chen), 瑶 (yao), 玥 (yue), 琪 (qi), 琳 (lin)
《Spirituality》
凡 (fan) - mortality
色 (se) - colour, beauty. In buddhism, “se” symbolizes everything secular
了 (liao) - finished, done, letting go
尘 (chen) - dust, I’m not… versed in buddhism enough to explain “chen”, it’s similar to “se”
悟 (wu) - knowing? Cognition? To understand a higher meaning
无 (wu) - nothing, the void, also part of like “letting go”
戒 (jie) - to “quit”, but not in a bad way. In buddhism, monks are supposed to “quit” their earthly desires.
极 (ji) - greatness, also related to the state of nirvana (? I think?)
-
 evan-on-the-internet reblogged this · 5 months ago
evan-on-the-internet reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 evan-on-the-internet liked this · 5 months ago
evan-on-the-internet liked this · 5 months ago -
 amargo-lex liked this · 5 months ago
amargo-lex liked this · 5 months ago -
 turnthelightsoffplease reblogged this · 6 months ago
turnthelightsoffplease reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 georgiaspeachy liked this · 6 months ago
georgiaspeachy liked this · 6 months ago -
 hwody liked this · 6 months ago
hwody liked this · 6 months ago -
 nadiapym liked this · 7 months ago
nadiapym liked this · 7 months ago -
 keentrashcollector liked this · 10 months ago
keentrashcollector liked this · 10 months ago -
 spectrophobiia liked this · 11 months ago
spectrophobiia liked this · 11 months ago -
 mariapanpan1833 liked this · 11 months ago
mariapanpan1833 liked this · 11 months ago -
 chara-baskerville liked this · 11 months ago
chara-baskerville liked this · 11 months ago -
 strawberryicecreamin reblogged this · 11 months ago
strawberryicecreamin reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 modernmessydisaster liked this · 1 year ago
modernmessydisaster liked this · 1 year ago -
 chamjam-enthusiast liked this · 1 year ago
chamjam-enthusiast liked this · 1 year ago -
 wellhellothere21 liked this · 1 year ago
wellhellothere21 liked this · 1 year ago -
 beenatural-11-5 reblogged this · 1 year ago
beenatural-11-5 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 beenatural-11-5 liked this · 1 year ago
beenatural-11-5 liked this · 1 year ago -
 jpasserii reblogged this · 1 year ago
jpasserii reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 theblehthatbloos reblogged this · 1 year ago
theblehthatbloos reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 theblehthatbloos liked this · 1 year ago
theblehthatbloos liked this · 1 year ago -
 bruce-waynes-mascara liked this · 1 year ago
bruce-waynes-mascara liked this · 1 year ago -
 lizard-business reblogged this · 1 year ago
lizard-business reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 cottonwater liked this · 1 year ago
cottonwater liked this · 1 year ago -
 lanismusings liked this · 1 year ago
lanismusings liked this · 1 year ago -
 bunnyphobic liked this · 1 year ago
bunnyphobic liked this · 1 year ago -
 schismismism liked this · 1 year ago
schismismism liked this · 1 year ago -
 lunaferrous liked this · 1 year ago
lunaferrous liked this · 1 year ago -
 letsagomario liked this · 1 year ago
letsagomario liked this · 1 year ago -
 keatkikis liked this · 1 year ago
keatkikis liked this · 1 year ago -
 demiboy-jinx reblogged this · 1 year ago
demiboy-jinx reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 littleeggrock liked this · 1 year ago
littleeggrock liked this · 1 year ago -
 fruitypieq reblogged this · 1 year ago
fruitypieq reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 fruitypieq liked this · 1 year ago
fruitypieq liked this · 1 year ago -
 flunkett reblogged this · 1 year ago
flunkett reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 zombiefingers liked this · 1 year ago
zombiefingers liked this · 1 year ago -
 yeetyessir333222111 liked this · 1 year ago
yeetyessir333222111 liked this · 1 year ago -
 jayvikyaoi reblogged this · 1 year ago
jayvikyaoi reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 jayvikyaoi liked this · 1 year ago
jayvikyaoi liked this · 1 year ago -
 moonlett liked this · 1 year ago
moonlett liked this · 1 year ago -
 cheyenneisgay liked this · 1 year ago
cheyenneisgay liked this · 1 year ago -
 into-the-basement liked this · 1 year ago
into-the-basement liked this · 1 year ago -
 arslanjae liked this · 1 year ago
arslanjae liked this · 1 year ago -
 fish-mage liked this · 1 year ago
fish-mage liked this · 1 year ago -
 undeadhousewife reblogged this · 1 year ago
undeadhousewife reblogged this · 1 year ago
