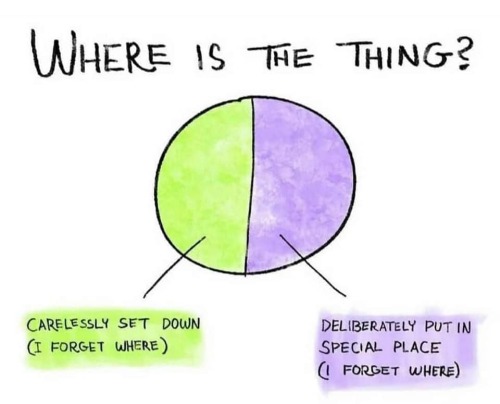
Wait A Second, Am I Tripping Balls?
Wait a second, am I tripping balls?
More Posts from Artldy and Others

2019 September 19
Along the Western Veil Image Credit & Copyright: Min Xie
Explanation: Delicate in appearance, these filaments of shocked, glowing gas, are draped across planet Earth’s sky toward the constellation of Cygnus. They form the western part of the Veil Nebula. The Veil Nebula itself is a large supernova remnant, an expanding cloud born of the death explosion of a massive star. Light from the original supernova explosion likely reached Earth over 5,000 years ago. Blasted out in the cataclysmic event, the interstellar shock wave plows through space sweeping up and exciting interstellar material. The glowing filaments are really more like long ripples in a sheet seen almost edge on, remarkably well separated into atomic hydrogen (red) and oxygen (blue-green) gas. Also known as the Cygnus Loop, the Veil Nebula now spans nearly 3 degrees or about 6 times the diameter of the full Moon. While that translates to over 70 light-years at its estimated distance of 1,500 light-years, this telescopic image of the western portion spans about half that distance. Brighter parts of the western Veil are recognized as separate nebulae, including The Witch’s Broom (NGC 6960) along the top of this view and Pickering’s Triangle (NGC 6979) below and left.
∞ Source: apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap190919.html
10 Things Einstein Got Right
One hundred years ago, on May 29, 1919, astronomers observed a total solar eclipse in an ambitious effort to test Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity by seeing it in action. Essentially, Einstein thought space and time were intertwined in an infinite “fabric,” like an outstretched blanket. A massive object such as the Sun bends the spacetime blanket with its gravity, such that light no longer travels in a straight line as it passes by the Sun.
This means the apparent positions of background stars seen close to the Sun in the sky – including during a solar eclipse – should seem slightly shifted in the absence of the Sun, because the Sun’s gravity bends light. But until the eclipse experiment, no one was able to test Einstein’s theory of general relativity, as no one could see stars near the Sun in the daytime otherwise.
The world celebrated the results of this eclipse experiment— a victory for Einstein, and the dawning of a new era of our understanding of the universe.
General relativity has many important consequences for what we see in the cosmos and how we make discoveries in deep space today. The same is true for Einstein’s slightly older theory, special relativity, with its widely celebrated equation E=mc². Here are 10 things that result from Einstein’s theories of relativity:

1. Universal Speed Limit
Einstein’s famous equation E=mc² contains “c,” the speed of light in a vacuum. Although light comes in many flavors – from the rainbow of colors humans can see to the radio waves that transmit spacecraft data – Einstein said all light must obey the speed limit of 186,000 miles (300,000 kilometers) per second. So, even if two particles of light carry very different amounts of energy, they will travel at the same speed.
This has been shown experimentally in space. In 2009, our Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope detected two photons at virtually the same moment, with one carrying a million times more energy than the other. They both came from a high-energy region near the collision of two neutron stars about 7 billion years ago. A neutron star is the highly dense remnant of a star that has exploded. While other theories posited that space-time itself has a “foamy” texture that might slow down more energetic particles, Fermi’s observations found in favor of Einstein.

2. Strong Lensing
Just like the Sun bends the light from distant stars that pass close to it, a massive object like a galaxy distorts the light from another object that is much farther away. In some cases, this phenomenon can actually help us unveil new galaxies. We say that the closer object acts like a “lens,” acting like a telescope that reveals the more distant object. Entire clusters of galaxies can be lensed and act as lenses, too.
When the lensing object appears close enough to the more distant object in the sky, we actually see multiple images of that faraway object. In 1979, scientists first observed a double image of a quasar, a very bright object at the center of a galaxy that involves a supermassive black hole feeding off a disk of inflowing gas. These apparent copies of the distant object change in brightness if the original object is changing, but not all at once, because of how space itself is bent by the foreground object’s gravity.
Sometimes, when a distant celestial object is precisely aligned with another object, we see light bent into an “Einstein ring” or arc. In this image from our Hubble Space Telescope, the sweeping arc of light represents a distant galaxy that has been lensed, forming a “smiley face” with other galaxies.

3. Weak Lensing
When a massive object acts as a lens for a farther object, but the objects are not specially aligned with respect to our view, only one image of the distant object is projected. This happens much more often. The closer object’s gravity makes the background object look larger and more stretched than it really is. This is called “weak lensing.”
Weak lensing is very important for studying some of the biggest mysteries of the universe: dark matter and dark energy. Dark matter is an invisible material that only interacts with regular matter through gravity, and holds together entire galaxies and groups of galaxies like a cosmic glue. Dark energy behaves like the opposite of gravity, making objects recede from each other. Three upcoming observatories – Our Wide Field Infrared Survey Telescope, WFIRST, mission, the European-led Euclid space mission with NASA participation, and the ground-based Large Synoptic Survey Telescope — will be key players in this effort. By surveying distortions of weakly lensed galaxies across the universe, scientists can characterize the effects of these persistently puzzling phenomena.
Gravitational lensing in general will also enable NASA’s James Webb Space telescope to look for some of the very first stars and galaxies of the universe.

4. Microlensing
So far, we’ve been talking about giant objects acting like magnifying lenses for other giant objects. But stars can also “lens” other stars, including stars that have planets around them. When light from a background star gets “lensed” by a closer star in the foreground, there is an increase in the background star’s brightness. If that foreground star also has a planet orbiting it, then telescopes can detect an extra bump in the background star’s light, caused by the orbiting planet. This technique for finding exoplanets, which are planets around stars other than our own, is called “microlensing.”
Our Spitzer Space Telescope, in collaboration with ground-based observatories, found an “iceball” planet through microlensing. While microlensing has so far found less than 100 confirmed planets, WFIRST could find more than 1,000 new exoplanets using this technique.

5. Black Holes
The very existence of black holes, extremely dense objects from which no light can escape, is a prediction of general relativity. They represent the most extreme distortions of the fabric of space-time, and are especially famous for how their immense gravity affects light in weird ways that only Einstein’s theory could explain.
In 2019 the Event Horizon Telescope international collaboration, supported by the National Science Foundation and other partners, unveiled the first image of a black hole’s event horizon, the border that defines a black hole’s “point of no return” for nearby material. NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR), Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, and Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope all looked at the same black hole in a coordinated effort, and researchers are still analyzing the results.

6. Relativistic Jets
This Spitzer image shows the galaxy Messier 87 (M87) in infrared light, which has a supermassive black hole at its center. Around the black hole is a disk of extremely hot gas, as well as two jets of material shooting out in opposite directions. One of the jets, visible on the right of the image, is pointing almost exactly toward Earth. Its enhanced brightness is due to the emission of light from particles traveling toward the observer at near the speed of light, an effect called “relativistic beaming.” By contrast, the other jet is invisible at all wavelengths because it is traveling away from the observer near the speed of light. The details of how such jets work are still mysterious, and scientists will continue studying black holes for more clues.

7. A Gravitational Vortex
Speaking of black holes, their gravity is so intense that they make infalling material “wobble” around them. Like a spoon stirring honey, where honey is the space around a black hole, the black hole’s distortion of space has a wobbling effect on material orbiting the black hole. Until recently, this was only theoretical. But in 2016, an international team of scientists using European Space Agency’s XMM-Newton and our Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NUSTAR) announced they had observed the signature of wobbling matter for the first time. Scientists will continue studying these odd effects of black holes to further probe Einstein’s ideas firsthand.
Incidentally, this wobbling of material around a black hole is similar to how Einstein explained Mercury’s odd orbit. As the closest planet to the Sun, Mercury feels the most gravitational tug from the Sun, and so its orbit’s orientation is slowly rotating around the Sun, creating a wobble.

8. Gravitational Waves
Ripples through space-time called gravitational waves were hypothesized by Einstein about 100 years ago, but not actually observed until recently. In 2016, an international collaboration of astronomers working with the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) detectors announced a landmark discovery: This enormous experiment detected the subtle signal of gravitational waves that had been traveling for 1.3 billion years after two black holes merged in a cataclysmic event. This opened a brand new door in an area of science called multi-messenger astronomy, in which both gravitational waves and light can be studied.
For example, our telescopes collaborated to measure light from two neutron stars merging after LIGO detected gravitational wave signals from the event, as announced in 2017. Given that gravitational waves from this event were detected mere 1.7 seconds before gamma rays from the merger, after both traveled 140 million light-years, scientists concluded Einstein was right about something else: gravitational waves and light waves travel at the same speed.

9. The Sun Delaying Radio Signals
Planetary exploration spacecraft have also shown Einstein to be right about general relativity. Because spacecraft communicate with Earth using light, in the form of radio waves, they present great opportunities to see whether the gravity of a massive object like the Sun changes light’s path.
In 1970, our Jet Propulsion Laboratory announced that Mariner VI and VII, which completed flybys of Mars in 1969, had conducted experiments using radio signals — and also agreed with Einstein. Using NASA’s Deep Space Network (DSN), the two Mariners took several hundred radio measurements for this purpose. Researchers measured the time it took for radio signals to travel from the DSN dish in Goldstone, California, to the spacecraft and back. As Einstein would have predicted, there was a delay in the total roundtrip time because of the Sun’s gravity. For Mariner VI, the maximum delay was 204 microseconds, which, while far less than a single second, aligned almost exactly with what Einstein’s theory would anticipate.
In 1979, the Viking landers performed an even more accurate experiment along these lines. Then, in 2003 a group of scientists used NASA’s Cassini Spacecraft to repeat these kinds of radio science experiments with 50 times greater precision than Viking. It’s clear that Einstein’s theory has held up!

10. Proof from Orbiting Earth
In 2004, we launched a spacecraft called Gravity Probe B specifically designed to watch Einstein’s theory play out in the orbit of Earth. The theory goes that Earth, a rotating body, should be pulling the fabric of space-time around it as it spins, in addition to distorting light with its gravity.
The spacecraft had four gyroscopes and pointed at the star IM Pegasi while orbiting Earth over the poles. In this experiment, if Einstein had been wrong, these gyroscopes would have always pointed in the same direction. But in 2011, scientists announced they had observed tiny changes in the gyroscopes’ directions as a consequence of Earth, because of its gravity, dragging space-time around it.

BONUS: Your GPS! Speaking of time delays, the GPS (global positioning system) on your phone or in your car relies on Einstein’s theories for accuracy. In order to know where you are, you need a receiver – like your phone, a ground station and a network of satellites orbiting Earth to send and receive signals. But according to general relativity, because of Earth’s gravity curving spacetime, satellites experience time moving slightly faster than on Earth. At the same time, special relativity would say time moves slower for objects that move much faster than others.
When scientists worked out the net effect of these forces, they found that the satellites’ clocks would always be a tiny bit ahead of clocks on Earth. While the difference per day is a matter of millionths of a second, that change really adds up. If GPS didn’t have relativity built into its technology, your phone would guide you miles out of your way!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Sweet.

Caught While Awake. Photo source.



My Frisk Cosplay for Jekyll Con 2015! Everything turned out great even though I wasn’t feeling my best.

If one remembers this particular episode from the popular sitcom ‘Friends’ where Ross is trying to carry a sofa to his apartment, it seems that moving a sofa up the stairs is ridiculously hard.
But life shouldn’t be that hard now should it?
The mathematician Leo Moser posed in 1966 the following curious mathematical problem: what is the shape of largest area in the plane that can be moved around a right-angled corner in a two-dimensional hallway of width 1? This question became known as the moving sofa problem, and is still unsolved fifty years after it was first asked.
The most common shape to move around a tight right angled corner is a square.
And another common shape that would satisfy this criterion is a semi-circle.
But what is the largest area that can be moved around?
Well, it has been conjectured that the shape with the largest area that one can move around a corner is known as “Gerver’s sofa”. And it looks like so:
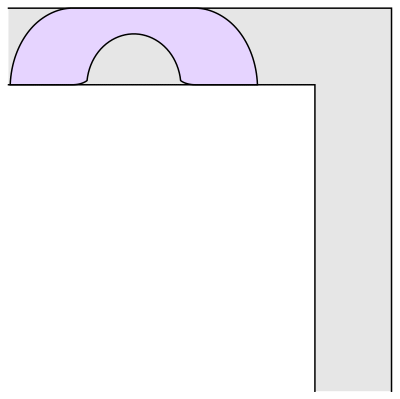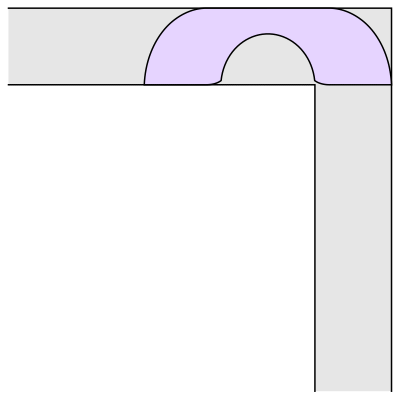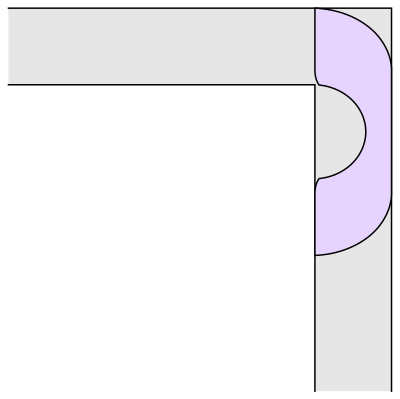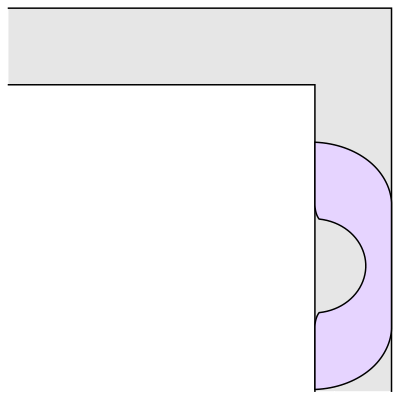
Wait.. Hang on a second
This sofa would only be effective for right handed turns. One can clearly see that if we have to turn left somewhere we would be kind of in a tough spot.
Prof.Romik from the University of California, Davis has proposed this shape popularly know as Romik’s ambidextrous sofa that solves this problem.
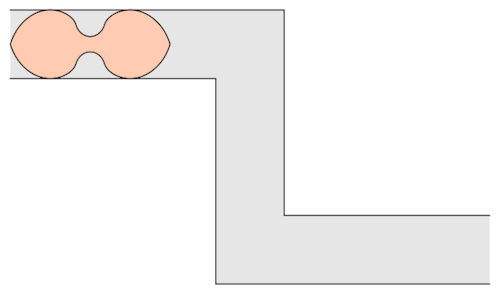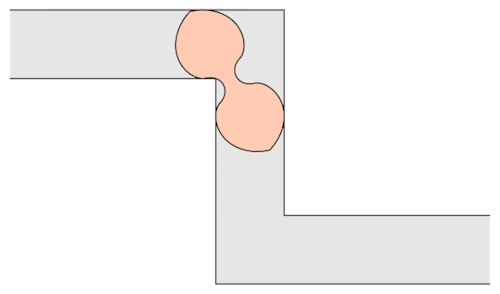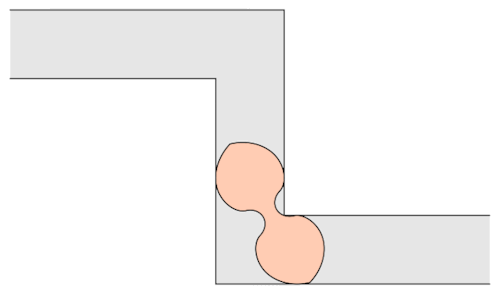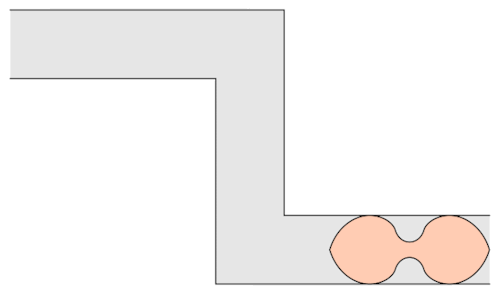
Although Prof.Romik’s sofa may/may not be the not the optimal solution, it is definitely is a breakthrough since this can pave the way for more complex ideas in mathematical analysis and more importantly sofa design.

Have a good one!



Solidarity!
I made a mini comic about a few of the similarities between ADHD and Autism, Featuring Valerie and Sophie (and Zacharie)
💖About MWDH 💖 Support on Patreon 💖 Buy me a Coffee? 💖
Still looking.






Koi Pond Coffee Tables // Epoxy Mini Store

-
 garbagehobby liked this · 2 months ago
garbagehobby liked this · 2 months ago -
 fluffyapathybunny reblogged this · 2 months ago
fluffyapathybunny reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 littledragonx777 liked this · 2 months ago
littledragonx777 liked this · 2 months ago -
 some-other-number reblogged this · 2 months ago
some-other-number reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 lizard-business liked this · 2 months ago
lizard-business liked this · 2 months ago -
 bruce-waynes-mascara reblogged this · 2 months ago
bruce-waynes-mascara reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 beesinabucket liked this · 2 months ago
beesinabucket liked this · 2 months ago -
 anomymous1 liked this · 2 months ago
anomymous1 liked this · 2 months ago -
 dabididubidi reblogged this · 2 months ago
dabididubidi reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 heartheavyy reblogged this · 2 months ago
heartheavyy reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 mother-snake reblogged this · 2 months ago
mother-snake reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 heartheavyy liked this · 2 months ago
heartheavyy liked this · 2 months ago -
 muchmoss reblogged this · 2 months ago
muchmoss reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 idrawgaystffs liked this · 2 months ago
idrawgaystffs liked this · 2 months ago -
 not2cools reblogged this · 2 months ago
not2cools reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 mmyntho reblogged this · 2 months ago
mmyntho reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 insertfandomrefhere liked this · 3 months ago
insertfandomrefhere liked this · 3 months ago -
 abiped-ungrateful reblogged this · 3 months ago
abiped-ungrateful reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 alarastirling reblogged this · 3 months ago
alarastirling reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 luka-art liked this · 3 months ago
luka-art liked this · 3 months ago -
 kylaralynn reblogged this · 3 months ago
kylaralynn reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 yourlocalpileofcrows reblogged this · 3 months ago
yourlocalpileofcrows reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 yourlocalpileofcrows liked this · 3 months ago
yourlocalpileofcrows liked this · 3 months ago -
 uchihadreams reblogged this · 3 months ago
uchihadreams reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 ninja-bunny1652 liked this · 3 months ago
ninja-bunny1652 liked this · 3 months ago -
 mushd-room reblogged this · 3 months ago
mushd-room reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 mushd-room liked this · 3 months ago
mushd-room liked this · 3 months ago -
 askkit5ever reblogged this · 3 months ago
askkit5ever reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 warriorsatthedisco reblogged this · 3 months ago
warriorsatthedisco reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 silverline7 liked this · 3 months ago
silverline7 liked this · 3 months ago -
 cannibal0vampire reblogged this · 3 months ago
cannibal0vampire reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 ajarofham reblogged this · 3 months ago
ajarofham reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 ajarofham liked this · 3 months ago
ajarofham liked this · 3 months ago -
 xxjaytehfoxxx liked this · 3 months ago
xxjaytehfoxxx liked this · 3 months ago -
 yatsurask reblogged this · 3 months ago
yatsurask reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 blitzgamev liked this · 3 months ago
blitzgamev liked this · 3 months ago -
 volumina-vetustiora liked this · 3 months ago
volumina-vetustiora liked this · 3 months ago -
 eepypigeon reblogged this · 3 months ago
eepypigeon reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 pixel-nyx reblogged this · 3 months ago
pixel-nyx reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 pixel-nyx liked this · 3 months ago
pixel-nyx liked this · 3 months ago -
 pulchrasilva reblogged this · 3 months ago
pulchrasilva reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 live-laugh-obsess reblogged this · 3 months ago
live-laugh-obsess reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 solarcicada liked this · 3 months ago
solarcicada liked this · 3 months ago -
 kelpywheat liked this · 3 months ago
kelpywheat liked this · 3 months ago -
 bell-swamp-fitzjames reblogged this · 3 months ago
bell-swamp-fitzjames reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 seismologically-silly reblogged this · 3 months ago
seismologically-silly reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 slrstrm liked this · 3 months ago
slrstrm liked this · 3 months ago -
 spiraltides liked this · 3 months ago
spiraltides liked this · 3 months ago -
 mintymaple liked this · 3 months ago
mintymaple liked this · 3 months ago